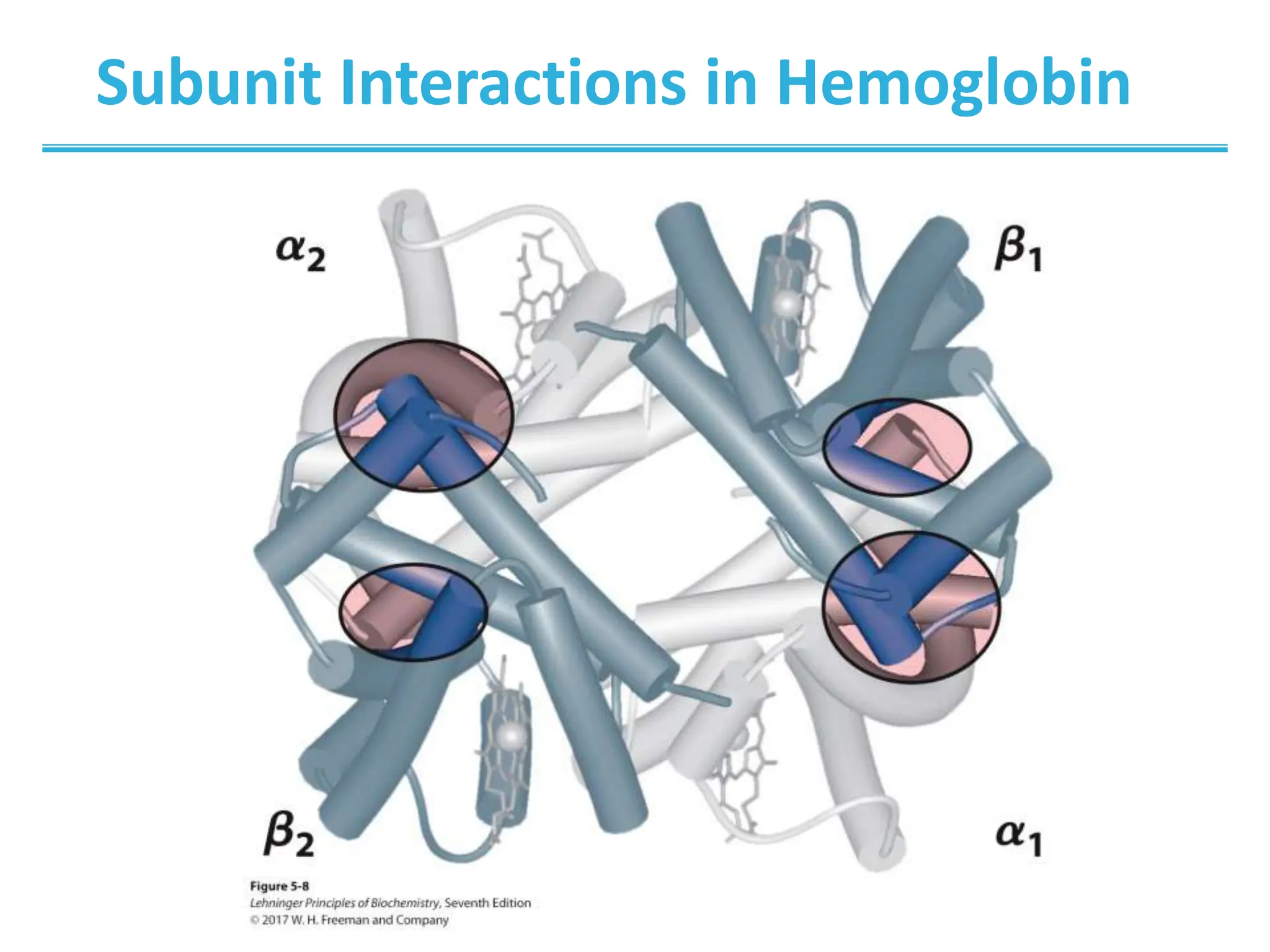
Globular proteins function through reversible ligand binding. This chapter examines oxygen transport by hemoglobin and myoglobin, antibody-antigen interactions, and muscle contraction. Key concepts include cooperative binding in hemoglobin, which increases oxygen affinity in the lungs and decreases it in tissues, and the induced fit model where ligand binding causes conformational changes for functions like oxygen transport and muscle movement.





![Example: Oxygen Binding to Myoglobin
[L]
[L]
d
K
2
50
2
O
O
p
p
p
When a ligand is a gas, binding is
expressed in terms of partial pressures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-proteinfunction-240304064356-92d71e7c/75/Protein-Function-General-Biology-2-Lesson-6-2048.jpg)