Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite
- 1. PROTOCOLS AND THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE Made by Atharva Deshmukh
- 2. CONTENT 1. History 2. TCP/IP Suite Layer a} Network Interface b} Internet Layer c} Transport Layer d} Application Layer 3.Comparison of OSI and IP
- 3. The Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol suite of protocol form the basis of the internet. It is TCP/IP that creates a virtual network when multiple computer networks are connected together. The TCP/IP networks was earlier known as ARPANET, but is now known as internet. History Of TCP/IP Suite
- 4. What is IP, Protocol? Protocol: - In information technology, a protocol is the special set of rules that end points in a telecommunication connection use when they communicate. Protocols specify interactions between the communicating entities. IP: - An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
- 6. TCP/IP Suite layer TCP/IP Suite consists of Four layer Network Interface: - It include the function of physical layer and data link layer. TCP/IP protocol suite includes Host-to-network layer protocols such as Serial Line internet protocol and point to point protocol Internet Layer: - The internet layer is exactly same to the network layer of OSI model. IP is the primary protocol operating at this layer and it provides data encapsulation routing, addressing and fragmentation services to the protocols at the transport layer above it.
- 7. TCP/IP Suite layer Transport Layer: - TCP/IP Suite includes two protocol at this layer, the transmission control protocol and the user datagram protocol These protocol provides connection or connectionless data transfer services. Application layer: - The TCP/IP protocol at the application layer can take different forms of Protocols, such as the File Transfer Protocol, Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
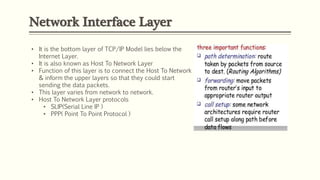
- 8. Network Interface Layer • It is the bottom layer of TCP/IP Model lies below the Internet Layer. • It is also known as Host To Network Layer • Function of this layer is to connect the Host To Network & inform the upper layers so that they could start sending the data packets. • This layer varies from network to network. • Host To Network Layer protocols • SLIP(Serial Line IP ) • PPP( Point To Point Protocol )
- 9. Serial Line Internet Protocol Serial line Internet protocol is very simple and used to connect the workstation to internet over dial-up line using a modem. SLIP(Serial line Internet protocol ) is not a standard protocol for carrying IP Packets over the a serial line between a home user and The ISP server. But , it has become popular because of its simplicity . The role of SLIP begins only when there is a proper connection between the two modem.
- 10. Problem with SLIP Protocol • It is not an approved internet standard. • It does not provide any authentication. • SLIP provides no way for the two devices to communicate control information between them to manage the link. • SLIP doesn't provide any way of detecting or correcting errors in transmissions.
- 11. Point to Point Protocol ( PPP ) Point to Point Protocol is a data link layer Protocol. PPP is another examples of the evolving the nature of internet. It has become standard internet protocol for remote access, using dial-up connection. The basic Functionality of PPP is similar to the SLIP. It passes the and other packets in the form of frames between a client and ISP Server. PPP is more complex than SLIP.
- 12. PPP Set of Protocol Are as given below: • Line control Protocol(LCP): - The Line control protocol is responsible for establishing , maintaining the connection between the Two end ( Home User and the ISP ) • Password Authentication Protocol( PAP ) : - password authentication protocol is used. • Here the user must establish a proof of identity , so that he can connect to ISP. • Network Control protocol ( NCP ): - Once the Authentication is done, PPP on the client side sends out a NCP packet. This packet tells the ISP server what kind of traffic is to be passed over this PPP link. • IP Control Protocol ( IPCP ) : - the IP Control Protocol takes over. Here , actual IP packet are now exchanged. IPCP establishes the connection between the Host user and ISP.
- 13. Comparison between The SLIP And PPP
- 14. Internet Layer The fives network layer protocol are as follows:- 1. ARP 2. RARP 3. IP 4. ICMP 5. IGMP IP is an Important protocol in this layer. ARP ( Address resolution protocol ) Every machine on internet has one address, these address cannot actually be used for sending packets data because data link layer does not understand the internet address. ARP Provides an essential services when TCP/IP is running in LAN. IP Address ARP Physical Address
- 15. RARP ( Reverse Address Resolution Protocol ) IP Address RARP Physical Address The Reverse Address Resolution Protocol is used to obtain the IP address of a Host based on Its physical address. That is , it preform a job that is exactly opposite to that of ARP. RARP works in a very similar way to ARP. but in the exactly opposite direction , as shown in the side figure. Note: - IP Address is a universally unique address and inter-networked address. MAC Address is local address. It is unique locally but not universally.
- 16. Internet Protocol ( IP ) • Internet Protocol is very important protocol present in this network layer. • IP is the protocol responsible for carrying data, generated by nearly all the other TCP/IP protocol, from the source system to its destination . IP Features : - i. Unreliable IP is unreliable , it means that it does not provide a guarantee that a datagram send from a source computer definitely will arrive at the destination. i. Connectionless IP services is similar to the postal service. It is possible that the order in which the message are sent and the order in which they are received is different.
- 17. Difference Between IPv4 And IPv6 IPv4 IPv6
- 18. Transport Layer ( TCP and UDP ) The transport layer runs on the top of internet layer and is mainly concerned with transport of packets from the source to the destination. The main function of transport layer is to deliver packets between the end points. In TCP/IP, the transport layer include to protocols : TCP and UDP. Transport Layer Protocols User datagram protocols ( USP ) Transmission control Protocol( TCP )
- 19. Comparison between TCP And UDP Parameter UDP TCP Data Transfer Data is sent in discrete packages by the application. Data is sent by the application with no particular structure. Transmission speed Very High High but not as high s UDP Protocol connection setup Connectionless Connection oriented Used UDP is useful when speed of delivery is critical TCP is useful for transmission of data without error.
- 20. Application Layer The TCP/IP Model Does Not have Session or presentation layer on the top of the transport layer. It is just has the application layer. It contains all higher level protocols. Higher Level Protocols Used in application layer are as Follows:
- 21. Types Of Protocol In application Layer TELNET: - the virtual terminal protocol allows a user on one machine to log onto a distant machine and work there. FTP: - File Transfer protocol provides a way to move data efficiently from one machine to another. SMTP: - Simple mail transfer protocol developed for email transfer. DNS: -Domain Name System Protocol is used for mapping the host names onto their network address. HTTP: -hyper Text transfer Protocol is used for fetching pages on the world wide web (WWW) and many others.
- 23. Comparison Of OSI and TCP/IP OSI TCP/IP Its has seven Layer Its has four layer It Supports both connection oriented and connectionless communication. Its support only connectionless communication. Transport layer provides connection oriented communication. Transport layer provides connection oriented communication and connectionless. Transport layer guarantees delivery of packets Transport layer does not guarantees delivery of packets Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data link Physical Application Transport Internet Network Interface
- 24. END OF CHAPTER