Python 3000
- 1. Python 3000 (PyCon, 24-Feb-02007) Guido van Rossum [email_address] [email_address]
- 2. What Is Python 3000? The next major Python release To be released as Python 3.0 The first one in a long time to be incompatible But not completely different or unusual Concept first formed around 2000 Py3k nickname was a play on Windows 2000 Goal: to correct my early design mistakes Those that would require incompatibility to fix Reduce cognitive load for first-time learners Work and thinking started for real last year
- 3. Activity Since Last Year Lots of design discussions (too many, if you ask me :-) Some PEPs were written (but not enough…) Lots of code was written (just the right amount!) (but we're not done yet!!)
- 4. Python 3.0 Timeline PEPs to be completed: April 2007 3.0a1: June 2007 3.0 final: June 2008 For comparison, the 2.6 timeline: 2.6a1: December 2007 2.6 final: April 2008 There will also be a 2.7 timeline
- 5. Rest of the Talk Highlight some of the most visible changes print function, dict views, comparisons, unicode, … How to convert 2.x to 3.0 code Notational convention: * = incompletely implemented ** = not yet implemented
- 6. No More Classic Classes In 2.2 … 2.9: class C: # classic class (0.1 … 2.1) class C(object): # new-style class (old now :-) In 3.0: both are new-style classes (just say "classes") Differences are subtle, few of you will notice
- 7. Print is a Function print x, y -> print(x, y) print x, -> print(x, end=" ") print >>f, x -> print(x, file=f) Automatic translation is 98% correct Fails for cases involving softspace cleverness: print "x\n", "y" doesn 't insert a space before y print("x\n", "y") does ditto for print "x\t", "y"
- 8. Dictionary Views Inspired by Java Collections Framework Remove .iterkeys(), .iteritems(), .itervalues() Change .keys(), .items(), .values() These return a dict view Not an iterator A lightweight object that can be iterated repeatedly .keys(), .items() have set semantics .values() has "collection" semantics supports iteration and not much else
- 9. Default Comparison Changed Default ==, != compare object identity (this is unchanged) Default <, <=, >, >= raise TypeError Example: [1, 2, ""].sort() raises TypeError Rationale: 2.x default ordering is bogus depends on type names depends on addresses
- 10. **Unicode Strings Java-like model: strings (the str type) are always Unicode separate bytes type must explicitly specify encoding to go between these Open issues: implementation fixed-width characters for O(1) indexing maybe 3 internal widths: 1, 2, 4 byte characters C API issues (many C APIs use C char* pointers) optimize slicing and concatenation??? lots of issues, supporters, detractors
- 11. The Bytes Type A mutable sequence of small ints (0…255) b[0] is an int; b[:1] is a new bytes object Implemented efficiently as unsigned char[] Has some list-like methods, e.g. .extend() Has some string-like methods, e.g. .find() But none that depend on locale bytes literals: b"ascii or \xDD or \012" bytes has .decode() method returning a string str has a .encode() method returning bytes
- 12. **New I/O Library Stackable components (inspired by Java, Perl) Lowest level: unbuffered byte I/O platform-specific; don't use C stdio Add buffering Add unicode encoding/decoding encoding explicitly specified or somehow guessed Add CRLF/LF mapping Compatible API open(filename) returns a buffered text file read() and readline() return strings open(filename, "b") returns a buffered binary file read() returns bytes; can't use readline()
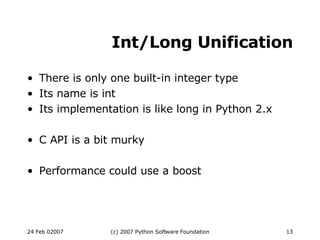
- 13. Int/Long Unification There is only one built-in integer type Its name is int Its implementation is like long in Python 2.x C API is a bit murky Performance could use a boost
- 14. Int Division Returns a Float Always! Same effect in 2.x with from __future__ import division Use // for int division Use -Q option to Python 2.x to find old usage
- 15. **Raise and Except Changes All exceptions must derive from BaseException Exceptions have __traceback__ attribute Must use raise E(arg) instead of raise E, arg Can still use raise E and raise without args Use raise E(arg).with_traceback(tb) instead of raise E, arg, tb Use "except E as v:" instead of "except E, v:" Variable v is deleted at end of except block!!!
- 16. Signature Annotations NOT type declarations! Example: def foo(x: "whatever", y: list(range(3))) -> 42*2: … Argument syntax is (roughly): NAME [':' expr] ['=' expr] Both expressions are evaluated at 'def' time foo.func_annotations is: {'a': "whatever", 'b': [0, 1, 2], "return": 84} NO other use is made of these annotations
- 17. Keyword-Only Parameters Example def: def foo(a, b=1, *, c=42, d): … Example call: foo(1, 2, d=3) Cannot use: foo(1, 2, 3) # raises TypeError
- 18. Set Literals {1, 2, 3} is the same as set([1, 2, 3]) No empty set literal; use set() No frozenset literal; use frozenset({…}) **Set comprehensions: { f ( x ) for x in S if P ( x )} same as set( f ( x ) for x in S if P ( x ))
- 19. Absolute Import Same effect in 2.5 with from __future__ import absolute_import Within a package "import foo" does NOT search the package path, only sys.path Use "from . import foo" for relative import Or use from <full-package-name> import foo
- 20. **String Formatting Examples (see PEP 3101 for more): "See {0}, {1} and {foo}".format("A", "B", foo="C") "See A, B and C" "my name is {0} :-{{}}".format("Fred") "my name is Fred :-{}" "File name {0.foo}".format(open("foo.txt")) File name foo.txt "Name is {0[name]}".format({"name": "Fred"}) "Name is Fred" Shoe size {0:8}".format(42) "Shoe size 42"
- 21. **Nonlocal Statement def outer(): x = 42 def inner(): nonlocal x # <---- new print(x) x += 1 return inner Doesn't work today; x becomes a local in inner Different keywords proposed: nonlocal, global, outer, … (see PEP 3104)
- 22. **Abstract Base Classes? Still highly speculative (no PEP yet) wiki.python.org/moin/AbstractBaseClasses Introduce a standard abstract class hierarchy for type categories like file, container, sequence, iterable etc. Standard types to use these as base classes User-defined types may use these When used, can help distinguishing e.g. sequence from mapping, or file-like behavior, or "stringiness", or "numericity", etc.
- 23. **Switch/Case Statement??? Highly speculative; see PEP 3103 switch EXPR: case EXPR: SUITE case EXPR: # or case in EXPRLIST: SUITE … [else: SUITE] Problem: when to compile EXPR? Would prefer precompilation for faster execution But this would introduce unusual semantics
- 24. Miscellaneous Changes exec becomes a function again range() becomes xrange() input() becomes raw_input() zip() returns an iterator Moved intern() into sys module Renamed __nonzero__ to __bool__ 'as' and 'with' are keywords And more, planned and implemented
- 25. Miscellaneous Removals classic classes: new-style classes default backticks: use repr() Removed <>: use != apply(): use func(*args) coerce(), __coerce__: not needed dict.has_key(): use key in dict 'softspace' attribute on file objects
- 26. **Library Reform Not my priority Others are interested, but effort seems stalled Need help! May happen after 3.0a1 is released
- 27. *C API Changes Too early to tell what will happen 3rd party extension authors want to know For now, these simple rules: Adding APIs is okay (of course) Deleting APIs is okay Changing APIs incompatibly is NOT OKAY
- 28. Converting 2.x Code to 3.0 Generic conversion tool exists sandbox/2to3 accurate source-to-source transformation parse tree decorated with whitespace & comments New conversions are easily added create a class from boilerplate add a class variable PATTERN to match nodes add a method transform() to transform one node Separately, Python 2.6 will help can warn about out-of-date usages can provide forward-compatible alternatives
- 29. Examples of What It Can Do apply(fun, args, kwds) -> fun(*args, **kwds) d.iterkeys() -> d.keys() exec a in b, c -> exec(a, b, c) print >>sys.stderr, x, -> print(x, end=" ", file=sys.stderr) except E, v: -> except E as v: d.has_key(k) -> k in d intern(s) -> sys.intern(s) a <> b -> a != b; `x` -> repr(x); int -> long automatically adds parentheses where needed
- 30. Examples of What It Can't Do detect whether d is a dict (in d.iterkeys()) detect whether you use d.keys() as a list later turn int()/int() into int()//int() fix code that depends on int() < str() remove redundant code fix custom classes emulating dictionaries fix string exceptions, non-Exception exceptions in general: limited to syntactic conversions can't follow control flow, doesn't do type inference
- 31. What You Can Do Today Don't worry about stuff that can be automated Don't try to write source-level compatible code Use Python 2.6 when it comes out Write unit tests with maximal coverage Use keys = sorted(d.iterkeys()) Use list(d.iterkeys()) when you really need a list Derive all exceptions from Exception Derive all classes from object Don't rely on subtle print/softspace semantics use print line.rstrip("\n") instead of print line, Use // for int division
- 32. Questions

![Python 3000 (PyCon, 24-Feb-02007) Guido van Rossum [email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-1-320.jpg)







![Default Comparison Changed Default ==, != compare object identity (this is unchanged) Default <, <=, >, >= raise TypeError Example: [1, 2, ""].sort() raises TypeError Rationale: 2.x default ordering is bogus depends on type names depends on addresses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-9-320.jpg)

![The Bytes Type A mutable sequence of small ints (0…255) b[0] is an int; b[:1] is a new bytes object Implemented efficiently as unsigned char[] Has some list-like methods, e.g. .extend() Has some string-like methods, e.g. .find() But none that depend on locale bytes literals: b"ascii or \xDD or \012" bytes has .decode() method returning a string str has a .encode() method returning bytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-11-320.jpg)



![Signature Annotations NOT type declarations! Example: def foo(x: "whatever", y: list(range(3))) -> 42*2: … Argument syntax is (roughly): NAME [':' expr] ['=' expr] Both expressions are evaluated at 'def' time foo.func_annotations is: {'a': "whatever", 'b': [0, 1, 2], "return": 84} NO other use is made of these annotations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-16-320.jpg)

![Set Literals {1, 2, 3} is the same as set([1, 2, 3]) No empty set literal; use set() No frozenset literal; use frozenset({…}) **Set comprehensions: { f ( x ) for x in S if P ( x )} same as set( f ( x ) for x in S if P ( x ))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-18-320.jpg)

![**String Formatting Examples (see PEP 3101 for more): "See {0}, {1} and {foo}".format("A", "B", foo="C") "See A, B and C" "my name is {0} :-{{}}".format("Fred") "my name is Fred :-{}" "File name {0.foo}".format(open("foo.txt")) File name foo.txt "Name is {0[name]}".format({"name": "Fred"}) "Name is Fred" Shoe size {0:8}".format(42) "Shoe size 42"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-20-320.jpg)


![**Switch/Case Statement??? Highly speculative; see PEP 3103 switch EXPR: case EXPR: SUITE case EXPR: # or case in EXPRLIST: SUITE … [else: SUITE] Problem: when to compile EXPR? Would prefer precompilation for faster execution But this would introduce unusual semantics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-3000-25699/85/Python-3000-23-320.jpg)








