Python language data types
- 1. Introduction to the Python Language Part 1. Python data types
- 2. Install Python • Find the most recent distribution for your computer at: http://www.python.org/download/releases/ • Download and execute Python MSI installer for your platform – For version 2.7 or higher – Note: You may need to be logged in as administrator to your computer to run the installation!
- 3. Modes of Interaction with Python • You can interact with the Python interpreter through two built-in modes: – Basic (command line) – not recommended! – IDLE (Integrated development environment) - recommended for this class • Command line mode: – You can find and double click the Python.exe executable (e.g., python27) in the downloaded folder. – Make sure to right click it, and then create a shortcut to it, and pin it to the taskbar for convenience! – Click the icon on your taskbar to start the command line You will get the >>> Python prompt Type ‘exit’ at the command prompt to get out of the console! >>> exit # or ctrl z – Note: you can use the Home, Pg up, Pg dn, and End keys, to scroll through previous entries, and repeat them by pressing the Enter key!
- 5. IDLE • This is the integrated development environment for Python • Involves interactive interpreter with editing and debugging capabilities (it prompts you for the names of functions, etc., and color codes code)! • You can find and double click the Pythonw.exe executable (e.g., python27) in the downloaded folder • Pin it to the taskbar.
- 6. Python IDLE Shell Window • The IDLE (Python shell window) is more convenient than the basic python command line • Provides automatic indentation and highlights the code • You can use the Home, Pg up, Pg dn, and End keys to search the buffer in your session!
- 7. Learn Basic parts of Python • Like other languages, Python has many data types – These can be manipulated with operators, functions, and methods • You can also make your own types (classes) and instantiate and manipulate them with operators, functions, and your own methods • Python also has conditional and iterative control, e.g.: – if-elif-else – while loop – for loop
- 8. Python’s suggested naming style • Function name is lower case >>> def add (): # a function to add numbers; returns the result; # note that function calls end with the : character • Variable names are written in lower case, and are case sensitive! inputFieldName >>> fc # a variable to hold a feature class as in: fc=“Roads.shp” Note: the two variables Road and road are different variables! • Class name is UpperCamelCase Class StrikeSlipFault, or class Lake • Constants are written in all caps, e.g. PI, SPREADING_RATE • Indentation: 4 spaces per level, do not use tabs! – IDLE does it for you! So don’t worry about it.
- 9. Data types 10/3 = 3, but 10/3.0 = 3.33333 The // operator is for integer division (quotient without remainder). 10//3 = 3 and 4//1.5 = 2, and 13//4 = 3
- 10. Python has several data types: • Numbers, lists, strings, tuples, tuples, dictionaries, etc. • Numbers: – Integers • 5, -8, 43, -234, 99933 – Floats • 6.8, 24e12, -4e-2 #2e3 = 2000, scientific notation – Complex numbers: • 4+3j, 8.0+4.6j – Booleans • True, False
- 11. Manipulation of numbers Addition (+) >>> x=8+2 >>> print x # prints 10 Subtraction (-) >>> x = 2 >>> x = x-2 >>> print x # prints 0 >>> (2+3j) – (5-4j) # prints (-3+7j) Multiplication (*) >>> 8*2 # prints 16 >>> 8*2.0 # prints 16.0
- 12. Division (/) # normal division >>> 7/2 3 >>> 7/2.0 3.5 >>> 7//2 3 # integer results with truncation Multiplication (*) >>> 2*3.0 6.0 Exponentiation (**) >>> 2**3.0 8.0 Modulus (%) # prints the remainder of the division >>> 5%2 1 >>> 5.0%2 1.0 >>> 5.0%2.5 0.0 >>> 5%5 0
- 13. Precedence >>> 5-2*3/4 4 # same as 5-((2*3)/4) >>> 50/2+2**3-8/2 29 # (50/2)+(2**3)-(8/2) # For equal precedence go from left to right! # first power, then left division, then add them, # then right division, then subtraction >>> 24-(12-4)/2*2+3 19 # first do the parenthesis, then divide by 2, # then multiply the result by 2, then # subtract from 24, then add to 3
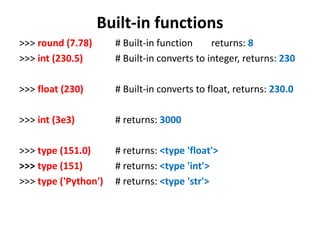
- 14. Built-in functions >>> round (7.78) # Built-in function returns: 8 >>> int (230.5) # Built-in converts to integer, returns: 230 >>> float (230) # Built-in converts to float, returns: 230.0 >>> int (3e3) # returns: 3000 >>> type (151.0) # returns: <type 'float'> >>> type (151) # returns: <type 'int'> >>> type ('Python') # returns: <type 'str'>
- 15. Calling Python’s library functions in modules >>> x = math.floor (-13.4) # leads to the following error: Traceback (most recent call last): File "<interactive input>", line 1, in <module>NameError: name 'math' is not defined >>> import math # imports the math module # now we can use math’s functions >>> x = math.floor (-13.4) # call math’s floor () function >>> print x -14.0 >>>
- 16. Python library module functions • Trigonometric, factorial, pi, sqrt, ceil, degrees, exp, floor, etc., are in the math module library >>> Import math >>> math.pi 3.14 # call a math library constant >>> math.ceil (3.14) 4 # call a module function () >>> math.sqrt (64) 8 >>> math.log10 (1000000) 6.0 >>> math.e 2.718281828459045 >>> import random # import the random module >>> x = random.uniform (1, 5) # returns a float between 1 and 5 >>> x 2.8153025790665516 >>> x = random.randint (1, 5) # returns an integer between 1 and 5 >>> x 1
- 17. Python’s built-in numeric functions abs (), float (), hex (), oct (), long (), max (), min (), pow (), round () • There are many more functions for trigonometry, etc. • ‘none’ is a special data type for empty value – e.g., when a function does not return a value – It is used as a placeholder. Similar to null.
- 18. Built-in numeric functions - examples >>> range (6, 18, 3) # returns: [6, 9, 12, 15] >>> range (10) # returns: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> abs (-17) # returns: 17 >>> max (12, 89) # returns: 89 >>> round (12.7) # returns: 13.0 >>> hex (10) # returns: '0xa‘ >>> oct (10) # returns: '012'
- 19. Use Built in functions
- 20. Getting input from user >>> age = int (input("What is your age? ")) # displays a dialog for user to enter data # user enters a number (e.g., 45) >>> print age # prints the entered age (45) 45
- 21. Assignment to a variable • To assign a value to a variable, you put the variable on the left side of an equal sign (=) and put (or retrieve) the value to the right, for example: >>> result = pow (4, 2) >>> print result # prints 16 • Let’s assign the number of zip codes in a GIS layer by calling the GetCount tool’s management () function in arcpy and passing it the name of the “zipcodes” layer as argument. >>> count =arcpy.GetCount_management (“zipcodes’) # This will return a number and assigns it to the count variable, # which can then be used in another call , for example: >>> print count
- 22. arcpy package for ArcGIS • Geoprocessing in ArcGIS is done through the arcpy package >>> import arcpy >>> arcpy.env.workspace = “C:/Data” # sets the current workspace # env is a class in arcpy, and workspace is a property. >>> from arcpy import env # this does not import the entire arcpy >>> env.workspace = “C:/Data”
- 23. Strings • Strings are immutable sequence of characters (text) • These are inserted either in “ ” or ‘ ’. • A double quote (“ ”) can contain single quote (‘ ’), e.g., “ ’dog’, ‘cat’ ” in a string • and vice versa, e.g., ‘ ”dog”, “cat” ’ in a string • They can also be in triple single or double quotes: ‘’’ ‘‘‘ or “”” “””. – This is used for multi-line commenting
- 24. Escape characters ’ Single quote ” Double quote Backslash bBackspace n newline r Carriage return t tab We have to escape special characters such as or “ >>> x = "Location of the file is: C:GeologyGeoinformatics“ >>> print x Location of the file is: C:GeologyGeoinformatics >>> print ("tabc") # t is tab abc >>> x="tHello Python World!“ >>> print x Hello Python World! >>> tictactoe = ("XtOtXnXtXtXnOtOtO") >>> print tictactoe X O X X X X O O O
- 25. Strings # The split () function breaks a string into pieces completely or at a specific character. >>> x = "Chattahoochie“ >>> x.split ("oo") ['Chattah', 'chie']
- 26. Strings …
- 27. Strings … The find() function returns the index of the first occurrence of a character. The replace (a, b) function takes two arguments . Replaces a with b.
- 28. Formatting strings with the string modulus operator %
- 29. String operators + and * >>> x = "Mississippi“ >>> y = "River“ >>> z = x + ' ' + y # concatenates the two strings, puts space in between >>> print z Mississippi River >>> T = 32 # note: 32 is a number (not a string). >>> print ("Today is freezing! The temperature is: " + str (T) + ' ' + "degrees Fahrenheit") # we cast the number into string by str (T) Today is freezing! The temperature is: 32 degrees Fahrenheit >>> 3*'A‘ # * repeats the character ‘AAA‘
- 30. String’s join () methods • The join () method puts spaces or other characters between strings >>> "-".join (['to', 'be', 'or', 'not', 'to', 'be']) 'to-be-or-not-to-be‘ # put hyphen between words >>> "-".join ("To be or not to be") ‘T-o- -b-e- -o-r- -n-o-t- -t-o- -b-e‘ >>> "-".join ("Tobeornottobe") ‘T-o-b-e-o-r-n-o-t-t-o-b-e' >>> " ".join(['to', 'be', 'or', 'not', 'to', 'be']) 'to be or not to be‘ # puts a blank between them
- 31. >>> x = "Diamond is the hardest mineral" >>> print x Diamond is the hardest mineral >>> X[0] ’D’ # prints the first character of the string >>> x.split() ['Diamond', 'is', 'the', 'hardest', 'mineral'] # The following is a multi-line comment in triple quote: >>> """ Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solid ... substances with crystalline structure and composition """ >>> min = 'Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solidn substances with crystalline structure and composition‘ >>> print min Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solid substances with crystalline structure and composition >>> pi = 3.14 >>> print "The value for pi is:", pi The value for pi is: 3.14 # or >>> print "The value for pi is: ", math.pi # assume math is imported The value for pi is: 3.14159265359
- 32. >>> x = " Map is NOT territory ! “ >>> x.strip() 'Map is NOT territory!‘ # strips white space >>> x.lstrip () 'Map is NOT territory ! ‘ # strips white space from left >>> x.rstrip () ' Map is NOT territory !‘ # strips white space from right >>> email = 'www.gsu.edu/~geohab‘ >>> email.strip (“~geohab”) # strips the passed string ‘www.gsu.edu/' The strip () method
- 33. String searching >>> word = "Uniformitarianism“ >>> word.find ('i') #find the index of the first occurrence of ‘I’ 2 >>> word.find ('i', 6) #find ‘i’ after index 6 7 >>> word.rfind('m') # find index for ‘m’. moves from the right end 16 >>> word.count('i') # find how many times ‘i’ is there in the word 4 >>> word.startswith ('U') True >>> word.endswith('P') False
- 34. Strings are immutable • Cannot change a string, but can modify and return a new string! >>> x = "Mississippi“ >>> x.replace('ss', 'pp') 'Mippippippi‘ # this is a new string >>> x.upper() # original value of x is still unchanged MISSISSIPPI >>> x.lower() mississippi # original is still unchanged >>> bookTitle = "knowledge engineering for beginners" >>> bookTitle.title () 'Knowledge Engineering For Beginners‘ >>> file = 'Rivers.shp‘ >>> file.replace ('.shp', "") 'Rivers‘ >>> len ('Diamond') 7
- 35. Casting strings to numbers >>> float ("12345.34") # it works; numeric string is ok 12345.34 >>> int ('23456') # it work! 23456 >>> int ('123.45') # error: decimal does not work >>> float ("xyz") # error: letter character to number
- 36. Methods >>> course = "Geoinformatics: Geol 4123“ >>> print course.lower () geoinformatics: geol 4123 >>> print course.upper () GEOINFORMATICS: GEOL 4123 >>> 'GEO' in course False >>> 'Geo' in course True >>> course = "Geoinformatics Geol 4123“ >>> course.find ('Geo') # returns the index 0 # index of the first item >>> course.find('GEO') -1 # not found
- 37. Booleans
- 38. Lists • List is an ordered collection of objects • List is modifiable (mutable). • They can have elements of different types • Elements are comma separated in a [] >>> rivers = [Missouri, Fox, Mississippi] # assigns to the rivers list >>> x = ['apple', 3, [4.0, 5.0]] # multi-type list >>> fileExtension = ["jpg", "txt", "doc", "bmp”, "tif"] >>> print fileExtension ['jpg', 'txt', 'doc', 'bmp', 'tif']
- 39. List >>> x [:-2] -> [‘hydroxide’, ‘phosphate’, ‘carbonate’] # up to, but not including index -2, i.e., gets rid of the last two >>> x [2:] -> [‘carbonate’, ‘oxide’, ‘silicate’] # values from position 2 to the end (inclusive)
- 40. List indices • Lists start counting from 0 on the left side (using + numbers) and - 1 from the right side >>> x = ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock', 'Water', 'Air'] >>> X[2] ‘Rock’ >>> X[-5] ‘River’ >>> x[:3] ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock'] >>> X[0:3] ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock'] # includes 0 but excludes 3 >>> x[3:10] ['Water', 'Air'] # ignores if the items don’t exist >>> x[3:] ['Water', 'Air'] # index 3 and higher X = [ ‘River ‘Lake’ ‘Rock’ ‘Water’ ‘Air’ ] + index 0 1 2 3 4 - Index -5 -4 -3 -2 -1
- 41. >>> lang = ['P', ‘Y', 'T', 'H', 'O', 'N'] >>> lang[3] 'H‘ >>> lang[-1] 'N‘ >>> lang[-6] 'P‘ >>> lang[-8] Traceback (most recent call last): File "<interactive input>", line 1, in <module>IndexError: list index out of range >>> lang[:3] ['P', ‘Y', 'T'] >>> lang [-3:]['H', 'O', 'N'] >>> P Y T H O N 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1
- 42. Lists have mixed types The len () functions returns the number of elements in a list >>> x = [1, 2, 3, [3, 4]] >>> len (x) 4
- 44. More functions for lists >>> x = ['apple', 3, [4.0, 5.0]] >>> len(x) 3 # returns the number of elements >>> cities = ["Atlanta", "Athens", "Macon", "Marietta"] >>> cities.sort (reverse = True) >>> print cities ['Marietta', 'Macon', 'Atlanta', 'Athens'] >>> cities.sort () >>> print cities ['Athens', 'Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta'] >>> del cities [0] >>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta'] >>> 'Smyrna' in cities False >>> cities.append ('Smyrna') >>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna']
- 45. >>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta‘, ‘Smyrna’] >>> cities.insert (1, 'Dalton') >>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Dalton', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna'] >>> cities.remove('Atlanta') >>> print cities ['Dalton', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna'] >>> cities.pop(2) # removes item at index 2, returns the item 'Marietta‘ >>> print cities ['Dalton', 'Macon', 'Smyrna']
- 46. Lists can change >>> x = ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock'] >>> x[1] = 'Horse‘ >>> x[0:] ['River', 'Horse', 'Rock'] >>> y = x[:] # copies all x’s elements and assigns to y >>> y[0] = 'Timber‘ # substitute >>> y[2] = 'Lumber‘ # substitute >>> y[0:] #show y from the beginning ['Timber', 'Horse', 'Lumber']
- 47. Modifying lists … >>> x=[1,2,3] # let’s append a new list to the end of this list >>> x[len(x):] = [4, 5, 6, 7] # find the length; append after last index >>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] >>> x[ :0] = [-2, -1, 0] # append this list to the front of the original list >>> print x [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] >>> x[1:-1] = [] # removes elements between the 2nd and one before the last index >>> print x [-2, 7] >>> x.append("new element") # adds a new element to the list >>> print x [-2, 7, 'new element']
- 48. Modifying lists… >>> x=[1,2,3,4] >>> y=[5,6] >>> x.append(y) # adds y as an element (in this case a list) to the end of x >>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]] >>> x=[1,2,3,4] >>> y = [5,6] >>> x.extend(y) # adds the items to the end of an existing list >>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] >>> x.insert(2, 'Hello') # inserts an element after a given index; always needs two arguments >>> print x [1, 2, 'Hello', 3, 4, 5, 6] >>> x.insert(0, 'new') # insert at the beginning (at index 0) an new item >>> print x ['new', 1, 2, 'Hello', 3, 4, 5, 6]
- 49. The + and * operators and lists >>> X = [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]] >>> y = x + [7,8] #concatenation with the + charecter >>> print y [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6], 7, 8] >>> x = ['Wow'] >>> x = x + ['!'] >>> print x ['Wow', '!'] >>> x.append(‘!') >>> print x ['Wow', '!', ‘!'] >>> x = ['Wow'] >>> x.extend('!') >>> print x ['Wow', '!']
- 50. … >>> X = ['Mercury','Venus','Earth','Mars','Jupiter','Saturn','Uranus','Neptune', 'Pluto'] >>> del x[8] # removes Pluto from the Solar System list! >>> print x ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'] >>> X = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'] >>> x.append('Pluto') # add Pluto to the end >>> print x ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune', 'Pluto'] >>> x.remove('Pluto') # removes ‘Pluto’ at its first occurrence >>> print x ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune']
- 51. Sorting lists >>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'] >>> x.sort() >>> print x ['Earth', 'Jupiter', 'Mars', 'Mercury', 'Neptune', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Venus'] >>> x=[2, 0, 1,'Sun', "Moon"] >>> x.sort() >>> print x [0, 1, 2, 'Moon', 'Sun']
- 52. The in operator >>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'] >>> 'Pluto' in x False >>> 'Earth' in x True
- 53. The min, max, index, and count functions >>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'] >>> min (x) ‘Earth‘ >>> max (x) ‘Venus‘ >>> x = [8, 0, -3, -1, 45] >>> min (x) -3 >>> max (x) 45 >>> x = [8, 0, -3, -1, 45] >>> x.index(-3) 2 #returns the index for ‘-3’ >>> x.index(45) 4 #returns the index for ‘45’ >>> x = [2, 5, 3, 3, 4, 3, 6] >>> x.count(3) 3
- 54. List in ArcGIS >>> import arcpy >>> from arcpy import env >>> env.workspace = “C:/Data/study.gdb” >>> fcs = arcpy.ListFeatureClasses () >>> fcs = sort () >>> print fcs >>> fcs.sort (reverse = True) >>> print fcs
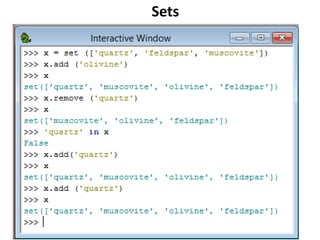
- 55. Sets: unordered collection of objects Sets are unordered collection of objects and can be changed Duplicates are removed, even when you add them The ‘in’ keyword checks for membership in the set
- 56. Sets
- 57. Tuples – () • Are similar to lists but are immutable (like strings) – can only be created but not changed! – Used as keys for dictionaries – Instead of x=[] for lists, we use x=() to create tuples • Many of the functions and operators that work with lists also work for tuples, e.g.: len(), min(), max(), and the +, and * operands.
- 58. Tuples … >>> x = () # create an empty tuple >>> print x # prints () >>> (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) = (1, 2, 3, 4) >>> Earth 3 >>> list ((Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars)) # cast by the list () function # the casting function list () converts a tuple to a list [1, 2, 3, 4] >>>
- 59. Dictionaries – {} • Called dictionary because they allow mapping from arbitrary objects (e.g., words in a dictionary) to other sets of arbitrary objects. • Values in a dictionary are accessed via keys that are not just numbers. They can be strings and other Python objects. Keys point to values. – Compare this to indices in lists • Both lists and dictionaries store elements of different types • Values in a list are implicitly ordered by their indices. • Those in dictionaries are unordered. >>> x = {} # create an empty dictionary >>> x[0] = 'Mercury‘ # assigns a value to a dictionary variable as if it is a list # this cannot be done to a list if x is not defined! Y[0] = ‘1’ does not work
- 60. >>> x = {} # declare x as a dictionary >>> x["Venus"] = 2 # indexing with non numbers (in this case string) >>> y = {} >>> y['Earth'] = 3 >>> x['Venus'] * y ['Earth'] # this cannot be done with lists (need int indices) 6 >>> phone = {} # declare phone as a dictionary # dictionaries are great for indexing lists by names (lists cannot do it) >>> phone ['Babaie'] = 1234567899 >>> print phone['Babaie'] 1234567899
- 61. >>> Eng_to_Fr ['river'] = 'fleuve‘ >>> print 'River in French is', Eng_to_Fr ['river'] River in French is fleuve >>> Eng_to_Fr = {'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'} >>> print Eng_to_Fr {'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'} >>> 'blue' in Eng_to_Fr True >>> print Eng_to_Fr.get ('green') vert # uses the get () >>> Eng_to_Fr.copy () # copy () copies the dictionary {'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'}
- 62. >>> x = {1: 'solid', 2: 'liquid', 3: 'gas'} >>> y = {4: 'plasma'} >>> y.update(x) # update y with x >>> y {1: 'solid', 2: 'liquid', 3: 'gas', 4: 'plasma'} >>> x {1: 'solid', 2: 'liquid', 3: 'gas'} # unchanged >>> x.update(y) # update x with y >>> x {1: 'solid', 2: 'liquid', 3: 'gas', 4: 'plasma'}
- 63. >>> statelookup = {"Houston": "Texas", "Atlanta": "Georgia", "Denver": "Colorado"} >>> statelookup["Atlanta"] 'Georgia‘ >>> zoning = {} # new dictionary >>> zoning["COM"] = "Commercial“ # uses list format >>> zoning ["IND"] = "Industry“ >>> zoning ["RES"] = "Residential“ >>> print zoning {'IND': 'Industry', 'RES': 'Residential', 'COM': 'Commercial'} >>> del zoning ["COM"] >>> print zoning {'IND': 'Industry', 'RES': 'Residential'} >>> zoning.keys() ['IND', 'RES']
- 64. • In Python (an OOP language) everything is an object. • All objects have id, name, and type >>> River = "Chattahoochie“ >>> type (River) <type 'str‘> # this is printed by Python >>> id (River) 46695832 # this is its address in memory >>> Python objects
- 65. Objects have methods • Objects can do things through methods • Methods are coupled to specific objects of a class • object.method (arguments) >>> course = "Geoinformatics“ >>> course.count ('i') 2 • Most of the functions which we have seen so far are method.
















![Built-in numeric functions - examples
>>> range (6, 18, 3) # returns: [6, 9, 12, 15]
>>> range (10) # returns: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> abs (-17) # returns: 17
>>> max (12, 89) # returns: 89
>>> round (12.7) # returns: 13.0
>>> hex (10) # returns: '0xa‘
>>> oct (10) # returns: '012'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-18-320.jpg)






![Strings
# The split () function breaks a string into pieces completely or at a specific character.
>>> x = "Chattahoochie“
>>> x.split ("oo")
['Chattah', 'chie']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-25-320.jpg)




![String’s join () methods
• The join () method puts spaces or other characters between
strings
>>> "-".join (['to', 'be', 'or', 'not', 'to', 'be'])
'to-be-or-not-to-be‘ # put hyphen between words
>>> "-".join ("To be or not to be")
‘T-o- -b-e- -o-r- -n-o-t- -t-o- -b-e‘
>>> "-".join ("Tobeornottobe")
‘T-o-b-e-o-r-n-o-t-t-o-b-e'
>>> " ".join(['to', 'be', 'or', 'not', 'to', 'be'])
'to be or not to be‘ # puts a blank between them](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-30-320.jpg)
![>>> x = "Diamond is the hardest mineral"
>>> print x Diamond is the hardest mineral
>>> X[0] ’D’ # prints the first character of the string
>>> x.split() ['Diamond', 'is', 'the', 'hardest', 'mineral']
# The following is a multi-line comment in triple quote:
>>> """ Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solid
... substances with crystalline structure and composition """
>>> min = 'Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solidn substances
with crystalline structure and composition‘
>>> print min
Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solid
substances with crystalline structure and composition
>>> pi = 3.14
>>> print "The value for pi is:", pi The value for pi is: 3.14 # or
>>> print "The value for pi is: ", math.pi # assume math is imported
The value for pi is: 3.14159265359](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-31-320.jpg)





![Lists
• List is an ordered collection of objects
• List is modifiable (mutable).
• They can have elements of different types
• Elements are comma separated in a []
>>> rivers = [Missouri, Fox, Mississippi] # assigns to the rivers list
>>> x = ['apple', 3, [4.0, 5.0]] # multi-type list
>>> fileExtension = ["jpg", "txt", "doc", "bmp”, "tif"]
>>> print fileExtension
['jpg', 'txt', 'doc', 'bmp', 'tif']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-38-320.jpg)
![List
>>> x [:-2] -> [‘hydroxide’, ‘phosphate’, ‘carbonate’]
# up to, but not including index -2, i.e., gets rid of the last two
>>> x [2:] -> [‘carbonate’, ‘oxide’, ‘silicate’] # values from position 2 to the end (inclusive)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-39-320.jpg)
![List indices
• Lists start counting from 0 on the left side (using + numbers) and -
1 from the right side
>>> x = ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock', 'Water', 'Air']
>>> X[2] ‘Rock’
>>> X[-5] ‘River’
>>> x[:3] ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock']
>>> X[0:3] ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock'] # includes 0 but excludes 3
>>> x[3:10] ['Water', 'Air'] # ignores if the items don’t exist
>>> x[3:] ['Water', 'Air'] # index 3 and higher
X = [ ‘River ‘Lake’ ‘Rock’ ‘Water’ ‘Air’ ]
+ index 0 1 2 3 4
- Index -5 -4 -3 -2 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-40-320.jpg)
![>>> lang = ['P', ‘Y', 'T', 'H', 'O', 'N']
>>> lang[3] 'H‘
>>> lang[-1] 'N‘
>>> lang[-6] 'P‘
>>> lang[-8]
Traceback (most recent call last): File "<interactive input>",
line 1, in <module>IndexError: list index out of range
>>> lang[:3] ['P', ‘Y', 'T']
>>> lang [-3:]['H', 'O', 'N']
>>>
P Y T H O N
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-41-320.jpg)
![Lists have mixed types
The len () functions returns the number of
elements in a list
>>> x = [1, 2, 3, [3, 4]]
>>> len (x)
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-42-320.jpg)

![More functions for lists
>>> x = ['apple', 3, [4.0, 5.0]]
>>> len(x) 3 # returns the number of elements
>>> cities = ["Atlanta", "Athens", "Macon", "Marietta"]
>>> cities.sort (reverse = True)
>>> print cities ['Marietta', 'Macon', 'Atlanta', 'Athens']
>>> cities.sort ()
>>> print cities ['Athens', 'Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta']
>>> del cities [0]
>>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta']
>>> 'Smyrna' in cities False
>>> cities.append ('Smyrna')
>>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-44-320.jpg)
![>>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Macon', 'Marietta‘, ‘Smyrna’]
>>> cities.insert (1, 'Dalton')
>>> print cities ['Atlanta', 'Dalton', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna']
>>> cities.remove('Atlanta')
>>> print cities ['Dalton', 'Macon', 'Marietta', 'Smyrna']
>>> cities.pop(2) # removes item at index 2, returns the item
'Marietta‘
>>> print cities ['Dalton', 'Macon', 'Smyrna']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-45-320.jpg)
![Lists can change
>>> x = ['River', 'Lake', 'Rock']
>>> x[1] = 'Horse‘
>>> x[0:]
['River', 'Horse', 'Rock']
>>> y = x[:] # copies all x’s elements and assigns to y
>>> y[0] = 'Timber‘ # substitute
>>> y[2] = 'Lumber‘ # substitute
>>> y[0:] #show y from the beginning
['Timber', 'Horse', 'Lumber']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-46-320.jpg)
![Modifying lists …
>>> x=[1,2,3] # let’s append a new list to the end of this list
>>> x[len(x):] = [4, 5, 6, 7] # find the length; append after last index
>>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
>>> x[ :0] = [-2, -1, 0] # append this list to the front of the original list
>>> print x [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
>>> x[1:-1] = []
# removes elements between the 2nd and one before the last index
>>> print x [-2, 7]
>>> x.append("new element") # adds a new element to the list
>>> print x [-2, 7, 'new element']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-47-320.jpg)
![Modifying lists…
>>> x=[1,2,3,4]
>>> y=[5,6]
>>> x.append(y) # adds y as an element (in this case a list) to the end of x
>>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]
>>> x=[1,2,3,4]
>>> y = [5,6]
>>> x.extend(y) # adds the items to the end of an existing list
>>> print x [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> x.insert(2, 'Hello')
# inserts an element after a given index; always needs two arguments
>>> print x [1, 2, 'Hello', 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> x.insert(0, 'new') # insert at the beginning (at index 0) an new item
>>> print x ['new', 1, 2, 'Hello', 3, 4, 5, 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-48-320.jpg)
![The + and * operators and lists
>>> X = [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]
>>> y = x + [7,8] #concatenation with the + charecter
>>> print y [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6], 7, 8]
>>> x = ['Wow']
>>> x = x + ['!']
>>> print x ['Wow', '!']
>>> x.append(‘!')
>>> print x ['Wow', '!', ‘!']
>>> x = ['Wow']
>>> x.extend('!')
>>> print x ['Wow', '!']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-49-320.jpg)
![…
>>> X = ['Mercury','Venus','Earth','Mars','Jupiter','Saturn','Uranus','Neptune',
'Pluto']
>>> del x[8] # removes Pluto from the Solar System list!
>>> print x
['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune']
>>> X = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus',
'Neptune']
>>> x.append('Pluto') # add Pluto to the end
>>> print x
['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune',
'Pluto']
>>> x.remove('Pluto') # removes ‘Pluto’ at its first occurrence
>>> print x
['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-50-320.jpg)
![Sorting lists
>>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn',
'Uranus', 'Neptune']
>>> x.sort()
>>> print x
['Earth', 'Jupiter', 'Mars', 'Mercury', 'Neptune', 'Saturn', 'Uranus',
'Venus']
>>> x=[2, 0, 1,'Sun', "Moon"]
>>> x.sort()
>>> print x
[0, 1, 2, 'Moon', 'Sun']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-51-320.jpg)
![The in operator
>>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus',
'Neptune']
>>> 'Pluto' in x
False
>>> 'Earth' in x
True](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-52-320.jpg)
![The min, max, index, and count functions
>>> x = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus',
'Neptune']
>>> min (x) ‘Earth‘
>>> max (x) ‘Venus‘
>>> x = [8, 0, -3, -1, 45]
>>> min (x) -3
>>> max (x) 45
>>> x = [8, 0, -3, -1, 45]
>>> x.index(-3) 2 #returns the index for ‘-3’
>>> x.index(45) 4 #returns the index for ‘45’
>>> x = [2, 5, 3, 3, 4, 3, 6]
>>> x.count(3) 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-53-320.jpg)


![Tuples – ()
• Are similar to lists but are immutable (like strings)
– can only be created but not changed!
– Used as keys for dictionaries
– Instead of x=[] for lists, we use x=() to create tuples
• Many of the functions and operators that work with lists
also work for tuples, e.g.:
len(), min(), max(), and the +, and * operands.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-57-320.jpg)
![Tuples …
>>> x = () # create an empty tuple
>>> print x # prints ()
>>> (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) = (1, 2, 3, 4)
>>> Earth
3
>>> list ((Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars))
# cast by the list () function
# the casting function list () converts a tuple to a list
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-58-320.jpg)
![Dictionaries – {}
• Called dictionary because they allow mapping from arbitrary objects (e.g.,
words in a dictionary) to other sets of arbitrary objects.
• Values in a dictionary are accessed via keys that are not just numbers.
They can be strings and other Python objects. Keys point to values.
– Compare this to indices in lists
• Both lists and dictionaries store elements of different types
• Values in a list are implicitly ordered by their indices.
• Those in dictionaries are unordered.
>>> x = {} # create an empty dictionary
>>> x[0] = 'Mercury‘ # assigns a value to a dictionary variable as if it is a list
# this cannot be done to a list if x is not defined! Y[0] = ‘1’ does not work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-59-320.jpg)
![>>> x = {} # declare x as a dictionary
>>> x["Venus"] = 2 # indexing with non numbers (in this case string)
>>> y = {}
>>> y['Earth'] = 3
>>> x['Venus'] * y ['Earth'] # this cannot be done with lists (need int indices)
6
>>> phone = {} # declare phone as a dictionary
# dictionaries are great for indexing lists by names (lists cannot do it)
>>> phone ['Babaie'] = 1234567899
>>> print phone['Babaie']
1234567899](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-60-320.jpg)
![>>> Eng_to_Fr ['river'] = 'fleuve‘
>>> print 'River in French is', Eng_to_Fr ['river']
River in French is fleuve
>>> Eng_to_Fr = {'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'}
>>> print Eng_to_Fr {'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'}
>>> 'blue' in Eng_to_Fr True
>>> print Eng_to_Fr.get ('green') vert # uses the get ()
>>> Eng_to_Fr.copy () # copy () copies the dictionary
{'blue': 'bleu', 'green': 'vert'}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-61-320.jpg)

![>>> statelookup = {"Houston": "Texas", "Atlanta": "Georgia",
"Denver": "Colorado"}
>>> statelookup["Atlanta"] 'Georgia‘
>>> zoning = {} # new dictionary
>>> zoning["COM"] = "Commercial“ # uses list format
>>> zoning ["IND"] = "Industry“
>>> zoning ["RES"] = "Residential“
>>> print zoning
{'IND': 'Industry', 'RES': 'Residential', 'COM': 'Commercial'}
>>> del zoning ["COM"]
>>> print zoning {'IND': 'Industry', 'RES': 'Residential'}
>>> zoning.keys() ['IND', 'RES']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c8zlpvasm6ad3jv5j8cq-signature-0762a8c9312704fceea2364892c07409daf56c3672d9678e5c1f617b777fd1dc-poli-160505164100/85/Python-language-data-types-63-320.jpg)

