Python operators
- 3. Operators An operator, in computer programming, is a symbol that usually represents an action or process. It is a symbol that perform operation on one or more operands. Operators required operands to perform their job. 3 4+ Operands Operators
- 4. List Of Operators i. Arithmetic Operator ii. Relational Operator iii. Logical Operator iv. Bitwise Operator v. Assignment Operator vi. Identity Operator vii. Membership Operator
- 5. 1. Arithmetic Operator Arithmetic operators take numerical values as their operands and return a single numerical value. Operator Example Result + Addition 4+3 7 - Subtraction 4-3 1 * Multiplication 6*6 36 / Division 3/2 1.5 % Modulus 7%3 1 ** Exponent 3**2 9 // 3//2 1
- 6. Arithmetic Operator Example 10**-2 0.01 >>> -2**3 -8 >>> -2**2 -4 >>> 10//3 3 >>> 10.0//3.0 3.0 >>> -4%3 2 >>> -4%-3 -1 >>> x='abc' >>> y='def' >>> x+y 'abcdef’ >>> True+1 2 >>> 'ab'*3 'ababab'
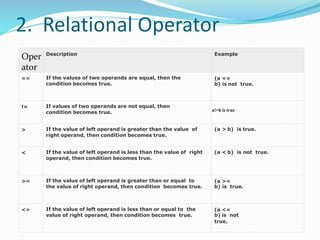
- 7. 2. Relational Operator Oper ator Description Example == If the values of two operands are equal, then the condition becomes true. (a == b) is not true. != If values of two operands are not equal, then condition becomes true. a!=b is true > If the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand, then condition becomes true. (a > b) is true. < If the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand, then condition becomes true. (a < b) is not true. >= If the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand, then condition becomes true. (a >= b) is true. <= If the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand, then condition becomes true. (a <= b) is not true.
- 8. Relational Operators Examples Relational operators always yield true or false as a result. >>>5>4 True >>>int(5>4) 1 It is also used to compare string. >>>’ac’==‘ac’ True >>>ac==ac error
- 9. 5>4<2 if any result value is false all result value is false. >>>5>4>2 True If we use equality(==) operator with any type of operand they never give error. >>>5==‘5’ False >>>’a’==97 False >>>5=5.0 True >>>’AB’==‘CD’ False
- 10. 3. Logical Operator Operator Expression Example and a>b and a>c When both operands are True ,result will be True or a>b or a>c When both operands are False result will be False not not a>b Invert the result Expression 1 Expression 2 and or not(Exp 1) T T T T F T F F T F F T F T T F F F F T
- 11. These operators return boolean value by validating more than one expression. If the operands of logical operator are boolean value then result is boolean otherwise if the operands of logical operators are integer then result is integer. >>>4>3 or 3<2 True >>> 0 or False False Logical operator must be written in lowercase only. >>>5 and 4 4 Empty string is always False non-empty string is True. >>>3 and ‘ab’ #‘ab’ is string so ab=1(True) ‘ab’
- 12. Logical Operator Examples >>>not ‘null’ #String is treated as True False >>>not ‘’ True >>>’ram’ and ‘shyam’ ‘ram’ >>>3 and x=4 #Assignment operator does not work their error >>>3 or 5/0 3 >>>3 and 5/0 #Evaluation is infinite error
- 13. 4. Bitwise Operator Bitwise operators work upon bits Ex:- 0 and 1 Operators Expression Example & 5 & 6 4 | 5 | 6 7 ~ ~5 -6 ^ 5^6 3 >> 99>>2 24 << 5<<3 40
- 14. I. &(AND):- 5 & 6 Convert 5 and 6 into binary 5 - 101 1 & 1 = 1 & 1 & 0 = 0 6 - 110 0 & 1 = 0 4 - 100 0 & 0 = 0 5 - 101 1 | 1 = 1 | 1 | 0 = 0 6 - 110 0 | 1 = 0 7 - 111 0 | 0 = 0 II. |(OR):- 5 | 6
- 15. III. ~(Complement):- >>>~12 -13 ~x = -x -1 ~12 = -12-1 = -13 Note: Our system does not store the negative numbers , first we convert the number into 2’s complement and then store. 12 = 00001100 1’s complement = 11110011 13 = 00001101 1’s complement = 11110010 2’s complement = 11110011
- 16. IV. ^(XOR):- 5^6 5 - 0101 1 ^ 1 = 0 ^ 1 ^ 0 = 1 6 - 0110 0 ^ 1 = 1 3 - 0011 0 ^ 0 = 0 V. >>(right shift) :- 99>>2 VI. <<(left shift) :- 5<<3 99=1100011 5 = 101 1st time = 0110001 1st time = 1010 2nd time = 0011000 =24 2nd time = 10100 3rd time = 101000=40
- 17. 5. Assignment Operator Operator expression = X=5 +=,-=,*=,/=,%= X+=5 //=,**= X**=2 &=,/=,^= X&=3 >>=,<<= X>>=2
- 18. (i) x=5 x*=6 x=x*6 =5*6 =30 (ii) x=5 x+=6 x=x+6 =5+6 =11 (iii) x=5 x/=6 x=x/6 =5/6 =0.833 (iv) x=5 x%=6 x=x%6 =5%6 =5 (v) x=5 x//=2 x=5//2 x=2 (vi) x=5 x**=2 x=5**2 x=25
- 19. 6. Identity Operator Operator Explanation is Return True if both variables are same object. is not Return False if both variables are same object. -> Every variable in python is an object. ->Objects are dynamically created. -> Objects do not have name but references.
- 20. x=5 x y=5 y 5 1000 >>>X=5 >>>Y=5 >>>X==Y True >>>X is Y True >>>X=5 >>>Y=5.0 >>>X==Y True >>>X is Y False >>>X is not Y True
- 21. 6. Membership Operator Operator Explanation in Return True if a sequence with the specified value is present in the object. not in Return False if a sequence with the specified value is present in the object. >>>x=“abc” >>>‘a’ in x True >>>x=“abc” >>>’A’ not in x True >>>x=256 >>>’5’ in x error >>>’5 ‘ in x False >>> x=1,2,3,4 >>> 4 in x True
- 22. Practice Session >>>x=25*3/2-1 36.5 >>>x=5>4>3>2 True >>>x=3 >>>x * = 3 + 4 21 >>>x = 3 and 4 4 >>>x = 2 or ‘Hello’ 2 >>>x = ‘Hello’ + 3 error >>>x = ‘ab’ * 4 abababab >>>x = 3 == ‘Three’ False