ElasticSearch - index server used as a document database
- 1. Elasticsearch - index server used as a document database ! (with examples) ! Robert Lujo, 2014
- 2. about me software professionally 17 y. freelancer more info -> linkedin
- 3. Elasticsearch search server based on Apache Lucene distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine RESTful web interface schema-free JSON documents NoSQL capabilities https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elasticsearch
- 4. Elasticsearch first release in February 2010 until now raised total funding > $100M latest release 1.3 & 1.4 beta + Logstash+ Kibana => ELK stack Apache 2 Open Source License
- 5. Very popular and used by ! ! ! ! ! … Wikimedia, Mozilla, Stack Exchange, Quora, CERN …! !
- 6. Professional services also available
- 8. Features Sys: ! real time data, distributed, multi-tenancy, real time analytics, high availability Dev:! restful api, document oriented, schema free, full text search, per-operation persistence, conflict management http://www.elasticsearch.org/overview/elasticsearch/
- 9. Install, run … prerequisite: JDK - Java (Lucene remember?) wget https://download.elasticsearch.org/.../ elasticsearch-1.3.4.zip unzip elasticsearch-1.3.4.zip elasticsearch-1.3.4/bin/elasticsearch
- 10. & use! # curl localhost:9200 { "status" : 200, "name" : "The Night Man", "version" : { "number" : "1.3.4", "build_hash" : “…”, "build_timestamp" : “…”, "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "4.9" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" }
- 11. create index & put some data # curl -XPUT localhost:9200/mainindex/company/1 -d '{ "name" : "CoolComp Ltd.", "employees" : 10, "founded" : "2014-10-05", "services" : ["software", "consulting"], "management": [ {"role" : "CEO", "name" : "Petar Petrovich"}, {"name" : "Ivan Ivić"} ], "updated" : "2014-10-05T22:31:55" }’ => {"_index":"mainindex","_type":"company","_id":"1","_ver sion":4,"created":false}
- 12. fetch document by id (key/value database) # curl -XGET localhost:9200/mainindex/company/1 ! => ! {“_index":"mainindex", “_type":"company", “_id”:"1","_version" : 4, ”found”:true, "_source":{ "name" : "CoolComp Ltd.", "employees" : 10, … }}
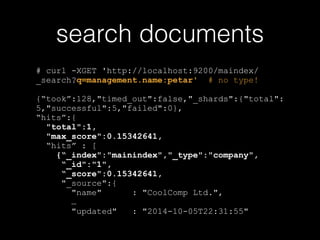
- 13. search documents # curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/maindex/ _search?q=management.name:petar' # no type! {“took”:128,"timed_out":false,"_shards":{"total": 5,"successful":5,"failed":0}, “hits”:{ "total":1, "max_score":0.15342641, “hits” : [ {“_index":"mainindex","_type":"company", “_id":"1", “_score":0.15342641, "_source":{ "name" : "CoolComp Ltd.", … "updated" : "2014-10-05T22:31:55"
- 14. Database is … an organized (or structured) collection of data ! Database management system (DBMS) is …! software system provides interface between users and database(s) 4 common groups of interactions: 1. Data definition 2. Update - CrUD 3. Retrieval - cRud 4. Administration
- 15. Elasticsearch is a database? 1. Data definition 2. Update - CrUD 3. Retrieval - cRud 4. Administration
- 16. Data representation - document-oriented-database Document-oriented-database - “NoSql branch”? Not really but … Document is … blah blah blah … something like this: ! { “_id” : 1, “_type” : “company”, "name" : "CoolComp Ltd.", "employees" : 10, "founded" : "2014-10-05", "services" : ["software", "consulting"], "management": [ {"role" : "CEO", "name" : "Petar Petrovich"}, {"name" : "Ivan Ivić"} ], "updated" : "2014-10-05T22:31:55" }
- 17. Data representation - relational databases company: id name employees founded -- --------------- --------- ------------ 1 'CoolComp Ltd.' 10 '2014-10-05' ! services: id value --- ---------------- 1 'software' 2 'consulting' ! company_services: id id_comp id_serv --- ------- -------- 1 1 1 2 1 2 ! person: id name -- ----------------- 1 'Petar Petrovich' 2 'Ivan Ivić' comp_management: id id_comp id_pers role --- ------- ------- ----- 1 1 1 CEO 2 1 2 MEM
- 18. Data definition Elasticsearch is “schemaless” But it provides defining schema - mappings Very important when setting up for search: • data types - string, integer, float, date/tst, boolean, binary, array, object, nested, geo, attachment • search analysers, boosting, etc.
- 19. Data definition - compared to RDBMS But we loose some things what RDBMS offers: • data validation / integrity • removing data redundancy - normalization • “fine grained” structure definition • standard and common usage (SQL)
- 20. Retrieval We had this example before:! ! # curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/maindex/ _search?q=management.name:petar' # no type! ! equivalent SQL query:! ! select * from company where exists( select 1 from comp_management cm inner join peron p on p.id=cm.id_pers where lower(p.name) like '%peter%');
- 21. Retrieval - ES-QDSL based on my experience, I would rather use ES: • for searches: full text, fuzzy, multi field, multi document types, multi indexes/databases • in programming - better to convert/deal with JSON than with ORM/raw SQL results • single web page applications
- 22. Retrieval - SQL on the other hand, I would rather use SQL and RDBMS: • when composing complex query - easier to do with SQL • for data exploring/researching ! SQL is much more expressive DSL
- 23. Joining & denormalization object hierarchy … must be denormalized. increases retrieval performance (since no query joining is necessary), uses more space makes keeping things consistent and up-to-date more difficult They’re excellent for write-once-read-many-workloads https://www.found.no/foundation/elasticsearch-as-nosql/
- 24. Joining options ES has several ways to “join” objects/documents/types: 1. embedding objects 2. “nested” objects 3. parent / child relation between types 4. compose manual query When fetching by id - very handy (1 & 2). When quering - not so handy.
- 25. Updating - CrUD ! Elasticsearch I would rather use Elasticsearch: • when creating, updating and deleting single nested document
- 26. Updating - CrUD! RDBMS on the other hand, RDBS I found handy: • for flat entities/documents • for mass objects manipulation • transactions & integrity (ACID)
- 27. Administration install, configure, maintenance, monitoring, scaling … quite satisfing! ! OS specific install - apt-get, yum, zypper, brew, … ! plugins installation ./bin/plugin -i Elasticsearch/marvel/latest
- 29. Elasticsearch as Database ! ! ! ! ! to avoid maintenance and development time overhead
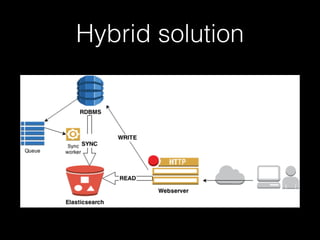
- 30. Hybrid solution Elasticsearch + …
- 31. ES + … - hybrid solution So why can you use ElasticSearch as a single point of truth (SPOT)? Elasticsearch … used in addition to another database. A database system for constraints, correctness and robustness, transactionally updatable, master record which is then asynchronously pushed/pulled to Elasticsearch
- 32. Hybrid solution
- 33. Elasticsearch rivers besides classic indexing - rivers provide alternative way for inserting data into ES service that fetches the data from an external source (one shot or periodically) and puts the data into the cluster Besides listed on official site: • RDBMS/JDBC • MongoDB • Redis • Couchbase • …
- 34. Use-case - RDBMS & Elasticsearch • Indexing & reindexing subdocuments is major job • upsert mode • issues - not indexing, memory hungry, full reindex when new field/subdoc • building AST when building a query - quite demanding • satisfied with the final result!
- 36. Riak & Solr September 16, 2014 - With 2.0, we have added distributed Solr to Riak Search. For every instance of Riak, there is an instance of Solr. While this drastically improves full-text search, it also improves Riak’s overall functionality. Riak Search now allows for Riak to act as a document store (instead of key/value) if needed. Despite being a part of Riak, Riak Search is a separate Erlang application. It monitors for changes to data in Riak and propagates those changes to indexes managed by Solr.
- 37. Couchbase and Elasticsearch integrates Couchbase Server and Elasticsearch, by streaming data in real-time from Couchbase to Elasticsearch. combined solution … with full-text search, indexing and querying and real-time analytics … content store or aggregation of data from different data sources. Couchbase Server provides easy scalability, low-latency document access, indexing and querying of JSON documents and real-time analytics with incremental map reduce.
- 38. MongoDB and Elasticsearch “addition of Elasticsearch represents only a first step in its mission to enable developers to choose the database that's right for their needs” “big weakness of MongoDB is the free text search, which MongoDB tried to address in version 2.4 in some aspects.”
- 39. Not to forget good old school …
- 40. RDBMS with FTS
- 41. Elasticsearch use when … you need very good, reliable, handy, web oriented search index engine you have intensive read and document oriented application “write” balance - depending on how much - ES as a NoSQL only or as a hybrid solution
- 42. Summary no silver bullet, “the right tool for the job” learn & get familiar with different solutions and choose optimal one be objective & productive General trend are heterogenous => lot of integration tasks lately learn new things & have fun!
- 43. Thank you for your patience! Questions? ! [email protected] @trebor74hr









![create index
& put some data
# curl -XPUT localhost:9200/mainindex/company/1
-d '{
"name" : "CoolComp Ltd.",
"employees" : 10,
"founded" : "2014-10-05",
"services" : ["software", "consulting"],
"management": [
{"role" : "CEO",
"name" : "Petar Petrovich"},
{"name" : "Ivan Ivić"}
],
"updated" : "2014-10-05T22:31:55"
}’
=>
{"_index":"mainindex","_type":"company","_id":"1","_ver
sion":4,"created":false}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robert-lujo-elasticsearch-as-document-database-141005143532-conversion-gate02/85/ElasticSearch-index-server-used-as-a-document-database-11-320.jpg)



![Data representation
- document-oriented-database
Document-oriented-database - “NoSql branch”? Not really but …
Document is … blah blah blah … something like this:
!
{
“_id” : 1,
“_type” : “company”,
"name" : "CoolComp Ltd.",
"employees" : 10,
"founded" : "2014-10-05",
"services" : ["software", "consulting"],
"management": [
{"role" : "CEO",
"name" : "Petar Petrovich"},
{"name" : "Ivan Ivić"}
],
"updated" : "2014-10-05T22:31:55"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robert-lujo-elasticsearch-as-document-database-141005143532-conversion-gate02/85/ElasticSearch-index-server-used-as-a-document-database-16-320.jpg)