RomaFramework Tutorial Basics
- 1. Let's think to the application domain , then model it in simple Java Classes, write the business logic and Roma will make all the rest “ ” www.RomaFramework.org Luca Garulli Roma Meta Framework Project Leader CTO AssetData [email_address]
- 2. Problem: what should I use? J2EE Microsoft .NET 2.0 Ruby On Rails Struts WebWorks Spring MVC Apache Cocoon Apache Velocity Apache Tapestry RIFE Trails JSF NextApp Echo2 Swing Yet another… SWT JDO JDBC Hibernate iBatis Castor OS Workflow Enhydra Shark BPEL engine Apache OJB EJB3/JPA
- 3. It’s not easy to choose the right framework, since there are a lot of them Each framework is proprietary , so migration is too much difficult, or impossible Often the learning curve to know a new framework it’s quite steep and require a lot of time to learn it before to understand if it's the right one for you It may happens to notice that during the development the framework chosen doesn’t support some features we need or that the best choice was another one …Changing it’s too costly Java tools & frameworks scenario
- 4. Using a meta framework means to use a set of behaviour interfaces instead of framework APIs directly. The aim is to cover the 80-90% of most common functionalities (the most used). The other 10-20% uncovered can be used using the framework implementation directly. Just remember this will be not portable at zero cost All application code can migrate to another supported framework without change the code All application model, domain and business logic are POJOs The meta framework knows: Domain , the business model and logic Aspects (or Concerns) , as behavior interfaces Modules , Plug-ins, often as Aspect implementation Maybe you need a <Meta> Framework
- 5. Architecture atom I: behaviour aspects Domain, Model and Business Logic Persistence (repository) Session Monitoring Workflow Authentication I18N (Internationalization) View Reporting Aspects describe a behaviour and they are implemented as Java interfaces Scheduler Scheduler
- 6. Architecture atom II: modules Domain, Model and Business Logic Persistence (repository) Session Monitoring Workflow Authentication I18N View ??? Others Java Resource Bundle Echo2 JMX Tevere JSP JDO 2.0 JPOX 1.2 Roma architecture is totally modular. Modules can implement Behavior Aspects Users Module, Custom Mock Echo2 Scheduler Open Symphony Quartz Reporting Jasper Reports
- 7. Roma: let's create a new web project >roma create web tutorial-basic org.romaframework.tutorial.basic C:\work\dev\os\romaframework >roma add view-echo2 >roma add persistence-jpox >roma add web-jetty tutorial-basic/ .settings // Eclipse directory settings database // HSQLDB embedded database for develop. lib // Compile-time libs log // Log directory script // Script directory src/ // Sources directory WebContent/ dynamic // Dynamic contents static // Static contents WEB-INF/ classes/ // Java compiled classes lib/ // Run-time libs applicationContext.xml // Main Spring IoC config file .classpath // Eclipse classpath file .project // Eclipse project file build.xml // Ant build file roma-project.xml // Roma project information Generate empty project scaffolding
- 8. Roma: look to the source directory tutorial-basic/src/ commons-logging.properties // Apache Commons logging cfg (use Log4J) jetty.xml // Jetty Web Server cfg jpox-log4j.properties // JPOX's log cfg log4j.xml // Log4J logging configuration org/romaframework/tutorial/basic domain // Where to place all domain entities i18n // I18N aspect: language mapping repository // DDD Repository pattern view // View Aspect domain // Where to place all presentation related domain classes screen // Where to place screen cfgs [CRUD] // Any CRUD is generated as package here containing all CRUD classes for the entity image // All images used by Echo2 style // Echo2 stylesheets (as XML files) CustomApplicationConfiguration.java // Handle user session
- 9. Roma: start to write you Domain @Persistence(mode=”tx”) public void save (){ ObjectContext.getInstance() .getContexComponent(PersistenceAspect.class) .updateObject( this ); } public class Employee { private String name ; private String surname ; private Date birth ; // GETTER + SETTERS } Write the model behavior + business logic Run! Start to write domain classes under the package: org/romaframework/tutorial/basic/domain Roma will be able to discover them
- 10. View: Mapping type = render < bean id = " RenderingResolver " singleton = "true" class = "org.romaframework.aspect.view.echo2...ConfigurableRenderingResolver" > < property name = "configuration" > < map > < entry key = "action" value = "link" /> < entry key = "object" value = "object" /> < entry key = "java.lang.String" value = " text " /> < entry key = "java.lang.Integer" value = " text " /> < entry key = "java.lang.Float" value = " text " /> < entry key = "java.lang.Double" value = " text " /> < entry key = "java.lang.Boolean" value = " check " /> < entry key = "java.util.Date" value = " date " /> < entry key = "java.util.Collection" value = " list " /> < entry key = "java.util.Set" value = " list " /> < entry key = "java.util.Map" value = " table " /> </ map > </ property > </ bean > Inside you WebContent/WEB-INF directory you can find the applicationContext-view-echo2.xml file containing the behavior of rendering. The RenderingResolver component contains the mapping between types and rendering mode .
- 11. View: Render and Layout modes Rendering mode is the way a field or an action is rendered. By default the View Aspect delegates to the RenderingResolver component to resolve it. You can override the default behavior by assigning the rendering you want by using the annotation (Java/Xml). The supported rendering types are: default , accordion, button, check, colset, date, datetime, html, image, imagebutton, label, link, list, menu, objectlink, objectembedded, password, popup, progress, radio, richtext, rowset, select, tab, table, tableedit, text, textarea, time, tree, upload Layout mode is the way a component will be placed in to the form. By default every single field is placed inside its own area if defined (just create one and assign the same name of the field), otherwise will go in the “ fields ” area. Every single action will follow the same behavior but if not found the own area, Roma will place it in the “actions ” area. You can override this by using annotation and specifying a type between these: default , accordion, block, form, screen, expand, menu, popup Example using Java5 annotations: public class Task{ @ViewField(render=” richtext ”, layout=” form://bottom ”) private String description; }
- 12. View: Draw your form using areas I To have a form layout really portable across technologies and frameworks we can't use HTML to define the layout neither the Swing or the SWT way. We need a new generic way to tell to Roma the aspect our form should be have. Areas aim to divide your form in multiple parts. Each one must describe the way it place the component: the “ area rendering mode ”. By default is the placeholder , namely an area type that replace itself with the component rendered (and only one). You can use all the modes between the supported ones: placeholder , cell, column, grid, row, popup, tab Areas only describe the layout form. To handle the presentation aspect much deeper you need to work with the View Aspect implementation in the behind. If you're using Echo2 module you had to work with the Xml stylesheet files contained under the package <your-app-package>.view.style . Roma team choosen to not generalize features like component width, heights, colors, etc. since they are so many and so much technology-related that it's much simpler to work directly with the View Aspect implementation way it offers. Note: Remember that your application will be portable across technologies and frameworks. It can run as Web Application or as Swing Desktop application. But GUI details will be lost and need to be translated in the technology you want to use!
- 13. View: Draw your form using areas II To define the form layout write the areas in a file called <Class>.xml where Class is the class name you want change the default layout. When Roma try to discover the layout to use, it follows the class inheritance. So you can create form layouts in super-classes and all extensions will use it. Under the package domain of your application you can find the Object.xml file. Since Object is the base class of all classes in Java, it will be used if sub-classes doesn't declare a layout form. By default Object.xml contains: <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < class > < aspects > < view > < form > < area name = "main" type = "column" > < area name = "fields" type = "grid" size = "2" /> < area name = "actions" type = "row" /> </ area > </ form > </ view > </ aspects > </ class > This is the explanation: main: sub-areas will be placed in vertical (“ column ” mode) fields: 2 columns : label + field actions: will be placed in horizontal (“ row ” mode)
- 14. < area name = "main" type = "column" > < area name = "fields" type = "grid" size = "4" /> < area name = "note" /> < area name = "actions" type = "row" /> View: automatic rendering III Ok Cancel Print default area uses a GRID to place the POJO fields. You can choice how much columns to use. Order is given by Annotation or XML Annotation actions is the default area for actions. It's defined as a row You can specify custom areas where to place fields and actions. There is no limit to the number of areas you can create Name City Zion's citizen Notes Web Surname Luca Garulli Luca zioncity </ area >
- 15. @ViewClass(orderFields="name surname city web", orderActions="ok cancel print") public class Customer{ private String name; private String surname; private String city; private String web; private String notes; public void ok(){} public void cancel(){} public void print(){} } View: POJO mapping I Roma controller binds the POJO directly to the form generated. The relationship is 1-1 : if you change the content of a field in the browser, it will be updated in you Java object and viceversa. When you push any button, the action associated will be executed. Fast to write, easy to debug, simple to handle!
- 16. public class Employee{ private String name; private Company company; private List<Contact> contacts; } public class Company{ private String name; } public class Contact{ private ContactType type; private String type; } public class ContactType{ private String name; } View: POJO mapping II Roma render all complex types as link to another form containing the complex instance associated to the field. You can also display the joined object as embedded instead of link. Collections are rendered as List by default, but you can render its as select, radio buttons, table, rowset, colset, etc. Download, import and run the project Tutorial Basic from your Eclipse (romaframework\trunk\dev\tutorials\tutorial-basic)
- 17. ContactInstance.java: public class ContactInstance{ @ViewField(render = ViewConstants.RENDER_SELECT, selectionField = "entity.type") private List<ContactType> types; } ContactInstance.xml: <?xml version="1.0"?> <class> <fields> <field name="types"> <aspects> <view render="select" selectionField=”entity.type”/> </aspects> </field> </fields> </class> Detail your Domain meta-model You can use Java5+ annotations or Xml Annotations to detail your meta-data model. Remember that on conflict Xml Annotations win. Java Annotations pro: All in one file, faster to write Xml Annotations pro: Use of separate files so the Java sources remain clean
- 18. Change the meta-model at run-time You can change the meta-model at run-time in the following ways: If you're in debug mode change the Java source and save it. Roma will catch the changes and will reload it. By changing the Xml Annotation and save the file. Roma will catch the changes and will reload it. Via APIs . Example: ObjectContext.getInstance(). setClassFeature ( this, ViewAspect.class, ViewClassFeatures.LABEL, “My playlist” ); ObjectContext.getInstance(). setFieldFeature ( this, ViewAspect.class, “account”, ViewActionFeatures.VISIBLE, false ); ObjectContext.getInstance(). setActionFeature ( this, ViewAspect.class, “save”, ViewActionFeatures.ENABLED, false );
- 19. Behavior aspect orchestration Persistence (repository) I18N (Internationalization) View DB Login Authentication Session Login Flow login() display Start user session display
- 20. MVC Controller Roma controller acts between Forms and POJOs. Every time the user change some field values Roma binds changes to the POJO. This usually happens before an actions is called. You can avoid to make automatic binding by setting the “ bind ” annotation to false (use Java/Xml annotation): @ViewAction( bind =AnnotationConstants.FALSE) public void reload(){ ... } If you change some field values of your POJO you had to tell it to Roma in order to refresh the updated values on the form when the Controller receives the control again. Use this: public void reload(){ name = “”; ObjectContext.getInstance(). fieldChanged (this, ”name”); }
- 21. Validation using annotations Roma supports two kind of data validation: using supported annotations and declaring custom validation. Supported annotations are: required = <true|false> min =<int> and max =<int>. For string types tells the length, for numbers is the value to check match =<regexp>. Use the regexp syntax To execute the validation before an action is called use the annotation “ validation ” on the action. Example: public class EmployeeInstance{ @ViewField( required =AnnotationConstants.TRUE, min =3, max =32) private String name; @ViewAction( validation =AnnotationConstants.TRUE) public void save(){ ... } }
- 22. Validation: write your own When you need more power and control to validate your POJO you can use the custom validation . Just implement the CustomValidation interface. Example: public class EmployeeInstance implements CustomValidation{ @ViewField(required=AnnotationConstants.TRUE, min=3, max=32) private String name; public void validate (){ if( description.contains(“sex”) ) throw new ValidationException(this, “sex”, “Banned word”); } @ViewAction(validation=AnnotationConstants.TRUE) public void save(){ ... } } Before to call the save() method Roma controller will execute the validation for name field and then the custom validate() method. If anything is ok the save() method will be invoked, otherwise a ValidationException will be thrown.
- 23. MVC Controller: 100% POJO based Controller Invoking “ OK ” Action POJO Binds changes form fields to the POJO Calls ok () method against the POJO @FlowAction(next=HomePage.class) public void ok (){ sendMessageToRemoteService(); } @ViewField( required =true, min =2) private String name; public void validate (){ if( name == null || name.trim().length() == 0){ throw new ValidationException( this, “name”, “ Please insert the name!”); } } Validates POJO's rules + validate () method if any HomePage.java Follows the flow declared using Java5 Annotation
- 24. Accessing to Aspects and Components Roma allows to access to each registered component and aspect by ObjectContext singleton class. Get by class type. Convention wants each aspect's implementation is registered in the IoC system with the name of the interface : ObjectContext.getInstance(). getComponent (ViewAspect.class).show(employee) Get the component by the registered name: ObjectContext.getInstance(). getComponent (“MyComponent”) Get the component in context. Useful for PersistenceAspect to work with the same transaction. ObjectContext.getInstance(). getContextComponent (PersistenceAspect.class).updateObject(employee)
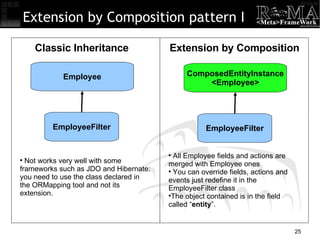
- 25. Extension by Composition pattern I ComposedEntityInstance <Employee> EmployeeFilter Employee EmployeeFilter Classic Inheritance Extension by Composition All Employee fields and actions are merged with Employee ones You can override fields, actions and events just redefine it in the EmployeeFilter class The object contained is in the field called “ entity ”. Not works very well with some frameworks such as JDO and Hibernate: you need to use the class declared in the ORMapping tool and not its extension.
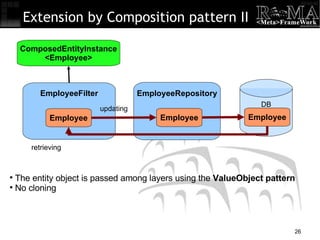
- 26. Extension by Composition pattern II ComposedEntityInstance <Employee> EmployeeFilter The entity object is passed among layers using the ValueObject pattern No cloning Employee EmployeeRepository DB Employee Employee updating retrieving
- 27. Dirty approach: dirty you hands when required EmployeeRepository EmployeeRepository JDO Roma wants cover the most common use cases . It's utopian to imagine covering all user requirements since they are so many and frameworks can be so much differents between their. So if you need to access directly to the tool and framework in the behind you had to know that you can do it. Just remember that piece of code will be not portable across implementation when, and if, you'll decide to migrate to another one. Aseptic class. It doesn't contain any references to tool and framework used. = 100% portable :-) Extension of theportable class. It's a best practice to name it with the technology it depends as suffix. So you'll had to search all JDO classes when you need to migrate to another one Persistence Aspect. = Not portable :-(
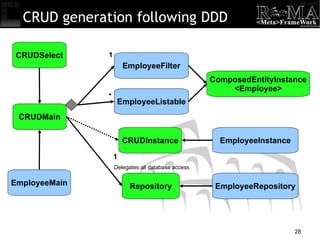
- 28. CRUD generation following DDD CRUDMain EmployeeMain ComposedEntityInstance <Employee> CRUDInstance CRUDSelect EmployeeInstance EmployeeListable EmployeeFilter Repository EmployeeRepository Delegates all database access * 1 1 1
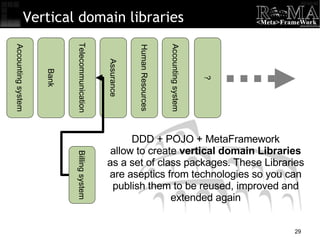
- 29. Vertical domain libraries Accounting system Bank Telecommunication Assurance Human Resources Accounting system Billing system ? DDD + POJO + MetaFramework allow to create vertical domain Libraries as a set of class packages. These Libraries are aseptics from technologies so you can publish them to be reused, improved and extended again
- 30. Available modules now - reporting-jr - users - monitoring-mx4j - view-echo2 - designer - project-web - web-jetty - workflow-pojo - etl-xpath - project-simple - portal-solo - project-webready - workflow-tevere-gui - persistence-jpox - scheduler-quartz - admin - workflow-tevere-engine - monitoring-jmx - messaging Community is developing: - persistence-jpa - view-html-css - view-swing - wiki
- 31. Conclusions Save your investment : Application is finally portable across tools and frameworks because your business code and model doesn't contain any references to its Huge gain of productivity : save at least 50% of effort in comparison to conventional MVC approaches. Up to 90% for very CRUD based applications Average skill required is lower and constant in the time Much less code to write, test, maintain and learn Part of the code is generated High quality of application: state of the art for technology used (JPox, Echo2, etc.) 100% POJO based: easy to handle Use your brain mainly for the Domain True Open Source project with commercial friendly license (Apache 2.0) Once tried you never will go back!
- 32. Summary 16 available modules, a lot of others coming... 9 committers 9.500+ downloads 2.676 SVN commits 207.000+ page viewed www.romaframework.org

![Let's think to the application domain , then model it in simple Java Classes, write the business logic and Roma will make all the rest “ ” www.RomaFramework.org Luca Garulli Roma Meta Framework Project Leader CTO AssetData [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/romaframework-tutorial-basics-1201300791131474-2/85/RomaFramework-Tutorial-Basics-1-320.jpg)






![Roma: look to the source directory tutorial-basic/src/ commons-logging.properties // Apache Commons logging cfg (use Log4J) jetty.xml // Jetty Web Server cfg jpox-log4j.properties // JPOX's log cfg log4j.xml // Log4J logging configuration org/romaframework/tutorial/basic domain // Where to place all domain entities i18n // I18N aspect: language mapping repository // DDD Repository pattern view // View Aspect domain // Where to place all presentation related domain classes screen // Where to place screen cfgs [CRUD] // Any CRUD is generated as package here containing all CRUD classes for the entity image // All images used by Echo2 style // Echo2 stylesheets (as XML files) CustomApplicationConfiguration.java // Handle user session](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/romaframework-tutorial-basics-1201300791131474-2/85/RomaFramework-Tutorial-Basics-8-320.jpg)