Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication
- 1. TELKOMNIKA, Vol.16, No.6, December 2018, pp.2643~2650 ISSN: 1693-6930, accredited First Grade by Kemenristekdikti, Decree No: 21/E/KPT/2018 DOI: 10.12928/TELKOMNIKA.v16i6.10437 2643 Received June 27, 2018; Revised September 20, 2018; Accepted October 8, 2018 Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication Gregor Alexander Aramice*, Jaafar Qassim Kadhim, Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Mustansiriyah Universit, Baghdad, Iraq *Corresponding author, e-mail: [email protected] Abstract Any secured system requires one or more logging policies to make that system safe. Static passwords alone cannot be furthermore enough for securing systems, even with strong passwords illegal intrusions occur or it suffers the risk of forgotten. Authentication using many levels (factors) might complicate the steps when intruders try to reach system resources. Any person to be authorized for logging-in a secured system must provide some predefined data or present some entities that identify his/her authority. Predefined information between the client and the system help to get more secure level of logging-in. In this paper, the user that aims to log-in to a secured system must provide a recognized RFID card with a mobile number, which is available in the secured systems database, then the secured system with a simple algorithm generates a One-time Password that is sent via GSM Arduino compatible shield to the user announcing him/her as an authorized person. Keywords: multi factor authentication, secured system, password generation, PIN code, one-time password Copyright © 2018 Universitas Ahmad Dahlan. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Many secured systems require password for logging into the system, modern systems advise the user to provide a strong password in order to keep these passwords safe from being stolen or broken. System with only password as logging-in key (factor) is not strong enough, so many systems are improved to have another factor working with the password factor presenting the Two Factor Authentication (2FA) system, where the user must first know something (password) and at the same time he/she must have something to use (smart cards). Another security system provide three factors (levels) of authentication in addition to the above mentioned two factors, and the third factor is based on something the user is, as his/her fingerprint pattern. As illegal intrusions (loggings-in) are increased, security systems have to be more secure than before, many reasons caused an illegal logging-in to a system occurred. Even with strong passwords the illegal intrusion is possible. But with many permission factors making a series of what we can say they acts as a firewall, the illegal loggings-in can be decreased. Since the authentication is a process to prove who we are, Facebook corporation used the two factor authentication as an option for protecting its clients’ accounts from being stolen by someone trying to access any account from a computer or a mobile device that is not recognized by the Facebook servers, and this process requires a special Personal Identification Number (PIN) code (first factor) which is sent to the users mobile (second factor) to confirm the user logging-in. Logging-in or Access Control differs from one system to another, some systems request password from the user to provide authentication, another systems provide passwords to the user depending on some factors the system gets from the user (such as biometric features), all these systems are provided by a static passwords from the user. A fingerprint authentication system is designed to provide authentication depending on the user fingerprint, it is based on embedding fingerprint owner name as a binary label in the same extracted fingerprint using wavelet transformation for watermarking scheme, this method helps to provide “false matching” of fake fingerprint with the original one [1]. Alphanumeric password with Graphical password both are used as Two Factor Authentication steps, where the user must provide an alphanumeric password to pass the first security level, then he/she must provide a graphical password such as drawing a pattern lock to pass the second security level [2]. Banking area security has developed based on what is called by the Three Factor Authentication (3FA), here the system is based on un-programmable RFID card
- 2. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650 2644 (first authentication factor), the RFID card holds all information presented from the bank to the client, when a matched card is detected, the user must provide an authentication password (second authentication factor), if the password is matched then a web camera captures the client face and starts a face recognition process (third authentication factor), if client face is recognized a permission to the authenticating person (the client) is accepted to provide banking services [3]. A system is designed to open a garage door using (a password and a vehicle license plate), where the user must log into his own Local Area Network (LAN) and provide a password he/she knows (first factor), then a digital camera captures the vehicle license plate image (second factor) to analyse and recognize it and make an authority to log-in car pass by opening the garage door [4]. A secured data file accessing system is designed to make the accessing of a requested file more secure, this system is based on fingerprint biometric authentication to generate a secret code, where the user must provide his/her fingerprint to get connected to the system, then the system sends via Bluetooth a request to the file owner that sends back a permission to the user to get the data file [5]. The main problem of previous works is that the designed authenticating systems stand on a static password that is provided by the user, while a static password is easy to remember and is chosen by the user to indicate an event in his/her life (for example birthdate), but it still unsafe to use a static password since it is easy to be forgotten or maybe hacked by intruders. So for solving the problem of a static password, many systems started to use a one-time Password (OTP) that is generated to be used once. Such systems may utilize user biometric features to work; where the extracted features from the scanned fingerprint are used to generate a temporary one-time Password depending on special calculations [6]. Another special algorithm is used to generate one-time Password stands on MD5 Hash encryption algorithm depending on data extracted from Academic Information System for students, such as, Student ID, phone Number, and Time Stamp (date and hour of access), where the generated one-time Password is a random portion (six digits) of manipulated (32 digit) Hash [7]. Another banking system that provide transaction services uses the one-time Password authentication, where the user logs-in classically to the bank website using a username and password, after that an OTP is generated and sent to the users phone, then the user uses this OTP for officially be logged-in [8]. Less cost system also is designed depending on fingerprint features based on Arduino Yun and fingerprint scanners, the extracted features are manipulated and enhanced via steps of processes that end with Gabor filtration [9]. In this research three levels of authentication are used, (legal smart card, active mobile phone number and a generated PIN code). An OTP PIN code is generated using information presented by the user to the central server to perform the authentication process to achieve a legal logging-in. Arduino starter kit is used with RFID (card and reader) and the utilization of GSM technology to design this system, a simple method and less cost tools are produced to design the system. The research sections discuss briefly; the meaning of authentication, mutual authentication and access control; the concept of one-time password; and the rest sections are the description of the system and the proposed method of the OTP generation. 2. Access Control, Authentication and Authorization In general, Access means reaching resources or data for any secured system, while Control means the preparation of some conditions that permits the access to an authorized person. To make a good and a successful accessing, and to prevent access policies to be broken or destroyed, the controls that are managing the accessing should be able to provide the right rules (policies) to the authenticated users [10]. To achieve access control, authentication must occur to the right person, and this can be done by determining validity of the access control conditions. Authentication stands on the comparison method between data presented and data stored in a database, where an authenticating person provides authorized data (let’s say password) on any authentication system to access a destination or perform any other process, and when the (provided and stored) data are matched the authenticating person is authorized to access (logging-in). Authentication has many factors to be used, such as: 1. Something user knows; password, PIN code, etc. 2. Something user have; smart card, etc. 3. Something user is; physical characteristic, finger print, etc.
- 3. TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 1693-6930 Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication (Gregor Alexander Aramice) 2645 On the other hand; Authorization, is the concept that determines the above previous three factors to permit the user what to do, in order to satisfy full and complete authority and then to get a successeded access to the secured resources [11]. 3. One-time Password The concept or the method of One-time Password (OTP) is presented to avoid the drawbacks of the single static password, which is usually short or uses some personal information like (birth dates, relatives names), and this can be easily guessed and used to access to the client accounts or to the secured systems. This leads to the need of repeatedly changing the static password even if it is easy to remember. The OTP is a password that is used for one time to logging-in any secured system, it is generated by the authentication server and used once by the client and then removed. Two categories for OTP generation can be listed as: [12]. Time based category, where a time-synchronization is required between the authentications sever and the client, where the generated password is used for a short period of a time. Mathematical algorithm category, which can be generated either; “based on the previous password, where OTPs are effectively a chain and must be used in a predefined order”, or; “based on a challenge, where a random number chosen by the authentication server”. The generation of the OTPs is done using (Tokens) either hardware token or software token. Hardware tokens are easy handling devices and are capable of storing keys, PIN codes or biometric data, such as RFID tags. Software tokens are “programs that run on computers and generate password that is changed after a short period of a time” [13]. 4. Mutual Authentication Figure 1, shows the concept of mutual authentication in our research. In general, the Mutual Authentication can be considered as a security process in which both the authenticating client (that requests for authentication) and the secured system (that provides authentication code) are identifying each other (just like two persons are handshaking and introducing themselves to each other) before any access to the secured system resources [14]. Figure 1. Mutual authentication The client requests an authentication first, then the system sends generated PIN code to the client and waits for a specified period of time to give the client the chance of using that PIN code as a process of mutuality, or the PIN code is erased after that period of chance is finished. 5. System Main Idea The system generates OTP secure code depending on RFID card represented by a client that requires authentication, each RFID card has its own Unique IDentifier (UID), and the client with acceptable UID is presented by generated OTP code depending on an algorithm that generates a secure code. Each client with acceptable OTP code is authorized to use the secured system. Previous mentioned password systems have a main weakness, which is, the password that is presented to the user can be used many times to log-in the secured system, and as a solution for the risk of a static password is to use one-time password technique. In this paper, hardware token (RFID card) is used to start a software token (algorithm) that generates an OTP. Figure 2, shows the system hardware parts which are:
- 4. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650 2646 (a) Two Arduino UNO starter kits (b) GSM Arduino Compatible Shield (SIM900) (c) RFID (Card and Reader) (d) 4×4 Membrane Arduino Compatible Keypad (a) Arduino UNO (b) SIM900 GSM shield (c) RFID tag and reader (d) 4×4 keypad Figure 2. System hardware parts Two Arduino kits are used in this system of type (UNO), Arduino 1 is represented as the main brain of the system, since RFID reader is connected to it and at the same time this Arduino acts as the central unit that generates and accepts the PIN code. Arduino2 is used as transmitting centre that sends the generated PIN code to the user via GSM technology using Arduino compatible GSM shield of type (SIM900). Both Arduino1 and Arduino2 are connected to each other via serial connection using Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) communication protocol. This connection is used to send a copy of the generated PIN code from Arduino1 to Arduino 2 in order to send it to the client mobile via GSM as short message (SMS). Figure 3 shows the wiring connection between the two Arduinos for UART communication protocol. Figure 3. UART serial communication protocol wiring connection 5.1. UID Sensing A known client (classified as a user that can be presented an OTP code) has RFID card which its UID is predefined to the system. An UID is sensed by RFID reader, each UID is related previously with a mobile number, which belongs to the same client that intends to log-in using this RFID card, in a database. This process leads to generate the same secure code every time the user uses the same RFID card and this can be defined as disadvantage of the system, since the system depends on the related mobile number digits to generate the secure code, but still this disadvantage can be changed to an advantage, where the same password is kept for the same user, but, as mentioned before it is an one-time password, and it is removed after usage or after a short while. So the OTP is like a stamp (fixed but not always available). 5.2. OTP PIN Code Generation In general, PIN code generation is performed randomly, or performed depending on predefined different algorithms. In this paper, a simple algorithm is used as an example to generate an OTP secure code which is used for a specified period of time then it is removed. The system generates randomly a (4-digits) number (R) as a primary PIN code, this primary PIN code is multiplied by (10000) to provide (units, tens, hundreds and thousands) place values and get new code (X) with new four empty places from the units side. Then the system sorts the
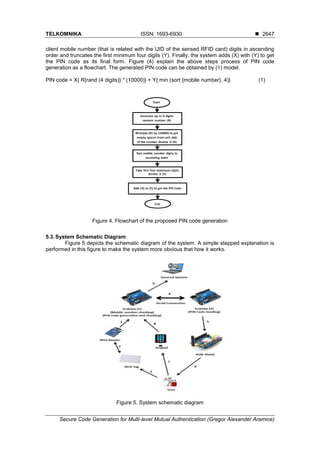
- 5. TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 1693-6930 Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication (Gregor Alexander Aramice) 2647 client mobile number (that is related with the UID of the sensed RFID card) digits in ascending order and truncates the first minimum four digits (Y). Finally, the system adds (X) with (Y) to get the PIN code as its final form. Figure (4) explain the above steps process of PIN code generation as a flowchart. The generated PIN code can be obtained by (1) model. PIN code = X{ R{rand (4 digits)} * (10000)} + Y{ min (sort {mobile number}, 4)} (1) Figure 4. Flowchart of the proposed PIN code generation 5.3.System Schematic Diagram Figure 5 depicts the schematic diagram of the system. A simple stepped explanation is performed in this figure to make the system more obvious that how it works. Figure 5. System schematic diagram
- 6. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650 2648 The proposed system operates due to the following steps: 1. The user presents its RFID card 2. RFID reader detects the RFID card 3. Arduino1 obtains RFID card UID, then starts to check the validity of this UID with the available UID’s in its Database, if the UID is available in the Database that’s means the user is a known person and must provide a PIN code to be an authorized client. Arduino1 starts to generate an OTP code to be sent to the user, and keeps a copy in another Database. 4. Arduino1 sends a copy of the generated OTP to Arduino2. 5. Arduino2 prepares the received OTP to load it to the GSM shield. 6. GSM shield sends the received OTP to the user as SMS. 7. The user inserts the received OTP using a Keypad connected to Arduino1. 8. Arduino1 detects the OTP from the Keypad and starts to check its validity. 9. If this OTP is available in the OTP’s Database then the user is declared as an authorized client. The system operation is explained in Figure 6 as a flowchart, it must be noticed again that the generated PIN code is an OTP code, which means that it is used once, so the system is designed to remove the generated OTP from its Database after usage or after a short period (30 second in our proposed system). Figure 6. Flowchart of the proposed system
- 7. TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 1693-6930 Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication (Gregor Alexander Aramice) 2649 5.4. The Proposed System Prototype After gathering and wiring all parts to work as a stand-alone unit (since two Alkaline batteries are used to switch ON/OFF the system), Figure 7 shows the proposed system prototype, all parts are wired and gathered in a plastic box, and a red LED is used as indication to the user that an authentication is approved. (a) (b) (c) Figure 7. The proposed system prototype (a) wiring parts (b) parts assembled in a box (c) system final prototype 6. Conclusion Because of the problems of using static passwords for logging-in any secured system or even reaching any resource or reaching any secured data, the use of a static password put the system under danger of intruders or under the risk of forgetting that static password. As a result, it is best to find another method of providing passwords that are used once and then deleted and become unavailable and useless. So many researchers provided the concept of one-time Password (OTP) and they used different methods to generate that OTP code. In this research, a simple design of a multi factor authentication system is performed for security purposes. More security is provided by using RFID card (with UID) as level one, mobile number of the person requesting an authorization as level two, and a generated OTP PIN code as level three, in order to give the authorization to use the secured system. RFID technology is utilized in this system for two reasons, cheaper and ease of use. For more security, An one-time Password concept is used instead of static password, the OTP is generated with a simple algorithm depending on the information received from the RFID card, and then this OTP code is sent using GSM technology as an SMS to the mobile number that is related with the RFID card. After the usage of the OTP or after a specified period of time, the generated OTP must be useless, so the system is designed to delete the generated OTP after usage or after a short period of time, and this make the system more secure. The system also is designed to match the received OTP from the client with the OTP saved in OTP’s Database, so removing it from Database terminates the acceptance of any password. The designed system can be used for any purpose as a security system, it can be used to log-in a banking system, or a smart house legal entrance, or a car parking systems. Since nothing is complete and perfect, this system doesn’t send any indication that the client didn’t received the generated OTP, but it informs the user after sending the generated OTP that the period allowed for accepting any OTP is over. Finally, as a comparison with other approaches which are using static passwords, our research based on two approaches; the first approach uses temporarily password that is generated on request for authorization and it is used once, so this reduced the risk of static password problems; the second important approach is that our system utilizes more than two authenticating levels rather than one static password as authenticating level.
- 8. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650 2650 References [1]. Chouhan, R, Mishra, A.,Khanna, P. Fingerprint Authentication by Wavelet-based Digital Watermarking, International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2012; 2(4). [2]. Vaithyasubramanian, S, Christy, A, Saravanan, D. Two Factor Authentications For Secured Login In Support Of Effective Information Preservation And Network Security. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences. 2015; 10(5). [3]. Lakshmi, S, Annapurna, N S, Sharmila Latha, T. Security Analysis of Three Factor Authentication Schemes For Banking. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences. 2015; 10(8). [4]. Aremice, G.A. Smart House Two Level Security System. Journal of Al-Turath University College. 2017; 23. [5]. Bastina, A, Rama, N. Biometric Identification and Authentication Providence using Fingerprint for Cloud Data Access. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2017; 7(1). [6]. Cha, B, Kim, C. Password Generation of OTP System using Fingerprint. IEEE International Conference on Information Security and Assurance, 2008 [7]. Sediyono, E, Santoso, K, Suhartono. Secure Login by Using one-time Password Authentication Based on MD5 Hash Encrypted SMS. IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), 2013 [8]. Nanda, A, Gupta, H. Anti-Phishing Techniques in Cryptography. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2015; 5(6). [9]. Martin, M, Štefan, K, L’ubor, F. Biometric Authentication of Fingerprint with Using Fingerprint Reader and Microcontroller Arduino. TELKOMNIKA Telecommunication, Computing, Electronics and Control. 2018; 16(2). [10]. Benantar, M. Access Control Systems (Security, Identity Management and Trust Models). Springer, USA. 2006: 1-10. [11]. Chapman, N , Chapman, J. Authentication and Authorization on the Web, MacAvon Media, 2012 [12]. Kalaikavitha, E, Phil, M, Gnanaselvi, J, Phil, M. Secure Login Using Encrypted One Time Password (Otp) and Mobile Based Login Methodology. International Journal Of Engineering And Science. 2013; 2(10). [13]. SOARE, C A. Internet Banking Two-Factor Authentication using Smartphones. Journal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems. 2012; 4(1). [14]. El Zouka, H A., Hosni, M M. Efficient and Timely Mutual Authentication Scheme for RFID. International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE), 2015; 9(10).
![TELKOMNIKA, Vol.16, No.6, December 2018, pp.2643~2650
ISSN: 1693-6930, accredited First Grade by Kemenristekdikti, Decree No: 21/E/KPT/2018
DOI: 10.12928/TELKOMNIKA.v16i6.10437 2643
Received June 27, 2018; Revised September 20, 2018; Accepted October 8, 2018
Secure Code Generation for Multi-level
Mutual Authentication
Gregor Alexander Aramice*, Jaafar Qassim Kadhim,
Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Mustansiriyah Universit, Baghdad, Iraq
*Corresponding author, e-mail: gregoralexander1977@uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
Abstract
Any secured system requires one or more logging policies to make that system safe. Static
passwords alone cannot be furthermore enough for securing systems, even with strong passwords illegal
intrusions occur or it suffers the risk of forgotten. Authentication using many levels (factors) might
complicate the steps when intruders try to reach system resources. Any person to be authorized for
logging-in a secured system must provide some predefined data or present some entities that identify
his/her authority. Predefined information between the client and the system help to get more secure level
of logging-in. In this paper, the user that aims to log-in to a secured system must provide a recognized
RFID card with a mobile number, which is available in the secured systems database, then the secured
system with a simple algorithm generates a One-time Password that is sent via GSM Arduino compatible
shield to the user announcing him/her as an authorized person.
Keywords: multi factor authentication, secured system, password generation, PIN code, one-time
password
Copyright © 2018 Universitas Ahmad Dahlan. All rights reserved.
1. Introduction
Many secured systems require password for logging into the system, modern systems
advise the user to provide a strong password in order to keep these passwords safe from being
stolen or broken. System with only password as logging-in key (factor) is not strong enough, so
many systems are improved to have another factor working with the password factor presenting
the Two Factor Authentication (2FA) system, where the user must first know something
(password) and at the same time he/she must have something to use (smart cards). Another
security system provide three factors (levels) of authentication in addition to the above
mentioned two factors, and the third factor is based on something the user is, as his/her
fingerprint pattern. As illegal intrusions (loggings-in) are increased, security systems have to be
more secure than before, many reasons caused an illegal logging-in to a system occurred. Even
with strong passwords the illegal intrusion is possible. But with many permission factors making
a series of what we can say they acts as a firewall, the illegal loggings-in can be decreased.
Since the authentication is a process to prove who we are, Facebook corporation used
the two factor authentication as an option for protecting its clients’ accounts from being stolen by
someone trying to access any account from a computer or a mobile device that is not
recognized by the Facebook servers, and this process requires a special Personal Identification
Number (PIN) code (first factor) which is sent to the users mobile (second factor) to confirm the
user logging-in. Logging-in or Access Control differs from one system to another, some systems
request password from the user to provide authentication, another systems provide passwords
to the user depending on some factors the system gets from the user (such as biometric
features), all these systems are provided by a static passwords from the user.
A fingerprint authentication system is designed to provide authentication depending on
the user fingerprint, it is based on embedding fingerprint owner name as a binary label in the
same extracted fingerprint using wavelet transformation for watermarking scheme, this method
helps to provide “false matching” of fake fingerprint with the original one [1]. Alphanumeric
password with Graphical password both are used as Two Factor Authentication steps, where
the user must provide an alphanumeric password to pass the first security level, then he/she
must provide a graphical password such as drawing a pattern lock to pass the second security
level [2]. Banking area security has developed based on what is called by the Three Factor
Authentication (3FA), here the system is based on un-programmable RFID card](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010437-200831081622/85/Secure-Code-Generation-for-Multi-level-Mutual-Authentication-1-320.jpg)
![ ISSN: 1693-6930
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650
2644
(first authentication factor), the RFID card holds all information presented from the bank to the
client, when a matched card is detected, the user must provide an authentication password
(second authentication factor), if the password is matched then a web camera captures the
client face and starts a face recognition process (third authentication factor), if client face is
recognized a permission to the authenticating person (the client) is accepted to provide banking
services [3]. A system is designed to open a garage door using (a password and a vehicle
license plate), where the user must log into his own Local Area Network (LAN) and provide a
password he/she knows (first factor), then a digital camera captures the vehicle license plate
image (second factor) to analyse and recognize it and make an authority to log-in car pass by
opening the garage door [4]. A secured data file accessing system is designed to make the
accessing of a requested file more secure, this system is based on fingerprint biometric
authentication to generate a secret code, where the user must provide his/her fingerprint to get
connected to the system, then the system sends via Bluetooth a request to the file owner that
sends back a permission to the user to get the data file [5].
The main problem of previous works is that the designed authenticating systems stand
on a static password that is provided by the user, while a static password is easy to remember
and is chosen by the user to indicate an event in his/her life (for example birthdate), but it still
unsafe to use a static password since it is easy to be forgotten or maybe hacked by intruders.
So for solving the problem of a static password, many systems started to use a one-time
Password (OTP) that is generated to be used once. Such systems may utilize user biometric
features to work; where the extracted features from the scanned fingerprint are used to
generate a temporary one-time Password depending on special calculations [6]. Another special
algorithm is used to generate one-time Password stands on MD5 Hash encryption algorithm
depending on data extracted from Academic Information System for students, such as, Student
ID, phone Number, and Time Stamp (date and hour of access), where the generated one-time
Password is a random portion (six digits) of manipulated (32 digit) Hash [7]. Another banking
system that provide transaction services uses the one-time Password authentication, where the
user logs-in classically to the bank website using a username and password, after that an OTP
is generated and sent to the users phone, then the user uses this OTP for officially be logged-in
[8]. Less cost system also is designed depending on fingerprint features based on Arduino Yun
and fingerprint scanners, the extracted features are manipulated and enhanced via steps of
processes that end with Gabor filtration [9].
In this research three levels of authentication are used, (legal smart card, active mobile
phone number and a generated PIN code). An OTP PIN code is generated using information
presented by the user to the central server to perform the authentication process to achieve a
legal logging-in. Arduino starter kit is used with RFID (card and reader) and the utilization of
GSM technology to design this system, a simple method and less cost tools are produced to
design the system. The research sections discuss briefly; the meaning of authentication, mutual
authentication and access control; the concept of one-time password; and the rest sections are
the description of the system and the proposed method of the OTP generation.
2. Access Control, Authentication and Authorization
In general, Access means reaching resources or data for any secured system, while
Control means the preparation of some conditions that permits the access to an authorized
person. To make a good and a successful accessing, and to prevent access policies to be
broken or destroyed, the controls that are managing the accessing should be able to provide the
right rules (policies) to the authenticated users [10]. To achieve access control, authentication
must occur to the right person, and this can be done by determining validity of the access
control conditions. Authentication stands on the comparison method between data presented
and data stored in a database, where an authenticating person provides authorized data
(let’s say password) on any authentication system to access a destination or perform any other
process, and when the (provided and stored) data are matched the authenticating person is
authorized to access (logging-in). Authentication has many factors to be used, such as:
1. Something user knows; password, PIN code, etc.
2. Something user have; smart card, etc.
3. Something user is; physical characteristic, finger print, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010437-200831081622/85/Secure-Code-Generation-for-Multi-level-Mutual-Authentication-2-320.jpg)
![TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 1693-6930
Secure Code Generation for Multi-level Mutual Authentication (Gregor Alexander Aramice)
2645
On the other hand; Authorization, is the concept that determines the above previous
three factors to permit the user what to do, in order to satisfy full and complete authority and
then to get a successeded access to the secured resources [11].
3. One-time Password
The concept or the method of One-time Password (OTP) is presented to avoid the
drawbacks of the single static password, which is usually short or uses some personal
information like (birth dates, relatives names), and this can be easily guessed and used to
access to the client accounts or to the secured systems. This leads to the need of repeatedly
changing the static password even if it is easy to remember. The OTP is a password that is
used for one time to logging-in any secured system, it is generated by the authentication server
and used once by the client and then removed. Two categories for OTP generation can be listed
as: [12]. Time based category, where a time-synchronization is required between the
authentications sever and the client, where the generated password is used for a short period of
a time. Mathematical algorithm category, which can be generated either; “based on the previous
password, where OTPs are effectively a chain and must be used in a predefined order”, or;
“based on a challenge, where a random number chosen by the authentication server”.
The generation of the OTPs is done using (Tokens) either hardware token or software
token. Hardware tokens are easy handling devices and are capable of storing keys, PIN codes
or biometric data, such as RFID tags. Software tokens are “programs that run on computers and
generate password that is changed after a short period of a time” [13].
4. Mutual Authentication
Figure 1, shows the concept of mutual authentication in our research. In general, the
Mutual Authentication can be considered as a security process in which both the authenticating
client (that requests for authentication) and the secured system (that provides authentication
code) are identifying each other (just like two persons are handshaking and introducing
themselves to each other) before any access to the secured system resources [14].
Figure 1. Mutual authentication
The client requests an authentication first, then the system sends generated PIN code
to the client and waits for a specified period of time to give the client the chance of using that
PIN code as a process of mutuality, or the PIN code is erased after that period of chance is
finished.
5. System Main Idea
The system generates OTP secure code depending on RFID card represented by a
client that requires authentication, each RFID card has its own Unique IDentifier (UID), and the
client with acceptable UID is presented by generated OTP code depending on an algorithm that
generates a secure code. Each client with acceptable OTP code is authorized to use the
secured system.
Previous mentioned password systems have a main weakness, which is, the password
that is presented to the user can be used many times to log-in the secured system, and as a
solution for the risk of a static password is to use one-time password technique. In this paper,
hardware token (RFID card) is used to start a software token (algorithm) that generates an OTP.
Figure 2, shows the system hardware parts which are:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010437-200831081622/85/Secure-Code-Generation-for-Multi-level-Mutual-Authentication-3-320.jpg)



![ ISSN: 1693-6930
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 16, No. 6, December 2018: 2643-2650
2650
References
[1]. Chouhan, R, Mishra, A.,Khanna, P. Fingerprint Authentication by Wavelet-based Digital
Watermarking, International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2012; 2(4).
[2]. Vaithyasubramanian, S, Christy, A, Saravanan, D. Two Factor Authentications For Secured Login In
Support Of Effective Information Preservation And Network Security. ARPN Journal of Engineering
and Applied Sciences. 2015; 10(5).
[3]. Lakshmi, S, Annapurna, N S, Sharmila Latha, T. Security Analysis of Three Factor Authentication
Schemes For Banking. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences. 2015; 10(8).
[4]. Aremice, G.A. Smart House Two Level Security System. Journal of Al-Turath University College.
2017; 23.
[5]. Bastina, A, Rama, N. Biometric Identification and Authentication Providence using Fingerprint for
Cloud Data Access. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2017;
7(1).
[6]. Cha, B, Kim, C. Password Generation of OTP System using Fingerprint. IEEE International
Conference on Information Security and Assurance, 2008
[7]. Sediyono, E, Santoso, K, Suhartono. Secure Login by Using one-time Password Authentication
Based on MD5 Hash Encrypted SMS. IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing,
Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), 2013
[8]. Nanda, A, Gupta, H. Anti-Phishing Techniques in Cryptography. International Journal of Electrical
and Computer Engineering (IJECE). 2015; 5(6).
[9]. Martin, M, Štefan, K, L’ubor, F. Biometric Authentication of Fingerprint with Using Fingerprint Reader
and Microcontroller Arduino. TELKOMNIKA Telecommunication, Computing, Electronics and Control.
2018; 16(2).
[10]. Benantar, M. Access Control Systems (Security, Identity Management and Trust Models). Springer,
USA. 2006: 1-10.
[11]. Chapman, N , Chapman, J. Authentication and Authorization on the Web, MacAvon Media, 2012
[12]. Kalaikavitha, E, Phil, M, Gnanaselvi, J, Phil, M. Secure Login Using Encrypted One Time Password
(Otp) and Mobile Based Login Methodology. International Journal Of Engineering And Science.
2013; 2(10).
[13]. SOARE, C A. Internet Banking Two-Factor Authentication using Smartphones. Journal of Mobile,
Embedded and Distributed Systems. 2012; 4(1).
[14]. El Zouka, H A., Hosni, M M. Efficient and Timely Mutual Authentication Scheme for RFID.
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE), 2015; 9(10).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010437-200831081622/85/Secure-Code-Generation-for-Multi-level-Mutual-Authentication-8-320.jpg)