Segment Routing Lab
- 1. Segment Routing Lab Santiago Alvarez Maan Al Bachari Thierry Couture
- 2. Thank you for attending Cisco Connect Toronto 2015, here are a few housekeeping notes to ensure we all enjoy the session today. § Please ensure your cellphones / laptops are set on silent to ensure no one is disturbed during the session § A power bar is available under each desk in case you need to charge your laptop (Labs only) House Keeping Notes
- 3. § Source Routing: source chooses a path and encodes it in packet header as an ordered list of segments. § Segment: an identifier for any type of instruction § Service § Context § Locator § IGP-based forwarding construct § BGP-based forwarding construct § Local value or Global Index Segment Routing Key Concepts Segment = Instructions such as "go to node N using the shortest path"
- 4. § MPLS: an ordered list of segments is represented as a stack of labels § SR re-uses MPLS data plane without any change § IPv6: an ordered list of segments is represented as a routing extension header Segment Routing This lab focuses on MPLS data plane IPv6 IPv6 IPv6 Control Plane IPv4 MPLS Data Plane
- 5. § Locally significant to node allocating it § Node processes SID and switches packet towards adjacency § Advertised as an absolute value IGP Segment Identifiers § Globally significant within SR domain § All nodes switch packet towards prefix/node via shortest path § Advertised as a relative (index) value § Make use of a per-node reserved block (SR Global Block or SRGB) B C N O Z D P A 9101 9105 9107 9103 9105 B C N O Z D P A 65 65 65 65 Prefix/Node SID Adjacency SID
- 6. MPLS Control and Forwarding Operation with Segment Routing PE1 PE2 IGPPE1 PE2 Services IPv4 IPv6 IPv4 VPN IPv6 VPN VPWS VPLS Packet Transport LDP MPLS Forwarding RSVP BGP Static IS-IS OSPF No changes to control or forwarding plane IGP label distribution for IPv4 and IPv6, same forwarding plane BGP / LDP
- 7. § Prefix SID § SID encoded as an index § Index represents an offset from SRGB base § Index globally unique § SRGB may vary across LSRs § SRGB (base and range) advertised with router capabilities § Adjacency SID § SID encoded as absolute (i.e. not indexed) value § Locally significant § Automatically allocated for each adjacency SID Encoding SRGB = [ 16000 - 23999 ]. Advertised as base = 16,000, range = 7999 Prefix SID = 16041. Advertised as Prefix SID Index = 41 Adjacency SID = 24000. Advertised as Adjacency SID = 24000 SR-enabled Node
- 8. § Each pod has a dedicated test bed that has been partially pre- configured § The devices dedicated to a pod are isolated from the devices assigned to other pods § Follow the tasks and steps in the order provided § Explore the entire test bed and verify operation beyond the sample output provided Lab General Instructions
- 9. Lab Testbed Topology g0/0/0/1 g0/0/0/1 g0/0/0/0 g0/0/0/2 lo0 lo0 g0/0/0/0 lo0 lo0 IS-IS Area 49.0002 IS-IS Area 49.0001 P1 IS-IS L1-L2 P2 IS-IS L1-L2 PE1 IS-IS L1 PE2 IS-IS L2
- 10. P1 IS-IS L1-L2 P2 IS-IS L1-L2 PE1 IS-IS L1 PE2 IS-IS L2 192.168.255.2 /32 (VRF RED) g0/0/0/0 172.16.1.0/31 Lab Testbed Topology (IPv4 Addressing) g0/0/0/1 172.16.2.2/31 g0/0/0/1 172.16.1.2/31 g0/0/0/0 172.16.2.0/31 g0/0/0/2 172.16.2.4/31 lo0 172.16.255.1/32 lo0 172.16.255.2/32 172.16.255.101/32 lo0 lo0 172.16.255.102/32 .4 .5 .0 .1 .2 .3 .2 .3 .0 .1 IS-IS Area 49.0002 IS-IS Area 49.0001 2001:db8:a::ff:2 /128 (VRF GREEN) 192.168.255.1 /32 (VRF RED) 2001:db8:a::ff:1 /128 (VRF GREEN)
- 11. Lab Testbed Topology (IPv6 Addressing) g0/0/0/0 2001:db8::1:0/127 g0/0/0/1 2001:db8::1:2/127 g0/0/0/2 2001:db8::2:4/127 Lo0 2001:db8::ff:1/128 2001:db8::ff:101/128 lo0 lo0 2001:db8::ff: 102/128 :4 :5 :0 :1 :2 :3 :2 :3 :0 :1 g0/0/0/1 2001:db8::2:2/127 g0/0/0/0 2001:db8::2:0/127 IS-IS Area 49.0002 IS-IS Area 49.0001 lo0 2001:db8::ff:2/128 2001:db8:b::ff:2 /128 (Global) 2001:db8:b::f:1 /128 (Global) P1 IS-IS L1-L2 P2 IS-IS L1-L2 PE1 IS-IS L1 PE2 IS-IS L2
- 12. § When a node is LDP capable but its next-hop along the SPT to the destination is not LDP capable § no LDP outgoing label § In this case, the LDP LSP is connected to the prefix segment § C installs the following LDP-to-SR FIB entry: § incoming label: label bound by LDP for FEC Z § outgoing label: prefix segment bound to Z § outgoing interface: D § This entry is derived automatically at the routing layer LDP/SR Interworking - LDP to SR A CB D Z 16066 LDP SR Input Label (LDP) Out Label (SID), Interface 32 16066, 1 Prefix Out Label (LDP), Interface Z 16, 0
- 13. § When a node is SR capable but its next-hop along the SPT to the destination is not SR capable § no SR outgoing label available § In this case, the prefix segment is connected to the LDP LSP § Any node on the SR/LDP border installs SR-to-LDP FIB entry(ies) LDP/SR Interworking - SR to LDP A CB D Z 16066 SR LDP Input Label (SID) Out Label (LDP), Interface ? 16, 1 Prefix Out Label (SID), Interface Z ?, 0
- 14. § A wants to send traffic to Z, but § Z is not SR-capable, Z does not advertise any prefix- SID à which label does A have to use? § The Mapping Server advertises the SID mappings for the non-SR routers § for example, it advertises that Z is 16066 § A and B install a normal SR prefix segment for 16066 § C realizes that its next hop along the SPT to Z is not SR capable hence C installs an SR-to-LDP FIB entry § incoming label: prefix-SID bound to Z (16066) § outgoing label: LDP binding from D for FEC Z § A sends a frame to Z with a single label: 16066 LDP/SR Interworking - Mapping Server A CB D ZZ(16066) Input Label (SID) Out Label (LDP), Interface 16066 16, 1 Prefix Out Label (SID), Interface Z 16066, 0 SR LDP
- 15. Lab Testbed Topology (Mapping Server) g0/0/0/1 g0/0/0/1 g0/0/0/0 g0/0/0/2 lo0 lo0 g0/0/0/0 lo0 lo0 IS-IS Area 49.0002 IS-IS Area 49.0001 LDP-Only LSR SR Mapping Server SR Mapping Server SR Mapping Client P1 IS-IS L1-L2 P2 IS-IS L1-L2 PE1 IS-IS L1 PE2 IS-IS L2
- 16. § Leverages existing and proven LFA technology § P space - set of nodes reachable from node S (PLR) without using protected link L § Q space - set of nodes that can reach destination D without using protected link L § Enforcing loop-freeness on post-convergence path § Where can I release the packet? At the intersection between the post-convergence shortest path and the Q space § How do I reach the release point? By chaining intermediate segments that are assessed to be loop-free Topology Independent LFA – Implementation
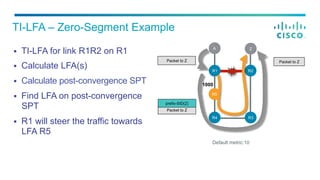
- 17. 1000 § TI-LFA for link R1R2 on R1 § Calculate LFA(s) § Calculate post-convergence SPT § Find LFA on post-convergence SPT § R1 will steer the traffic towards LFA R5 TI-LFA – Zero-Segment Example Packet to Z Default metric:10 R5 R2R1 A Z R3 Packet to Z R4 R5 Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z)
- 18. § TI-LFA for link R1R2 on R1 § Calculate P and Q spaces § They overlap in this case § Calculate post-convergence SPT § Find PQ node on post- convergence SPT § R1 will push the prefix-SID of R4 on the backup path TI-LFA – Single-Segment Example Q-space P-space Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z) Packet to Z Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z) prefix-SID(R4) Default metric:10 R5 R2R1 A Z R3 Packet to Z R4
- 19. § TI-LFA for link R1R2 on R1 § Calculate P and Q spaces § Calculate post-convergence SPT § Find Q and adjacent P node on post-convergence SPT § R1 will push the prefix-SID of R4 and the adj-SID of R4-R3 link on the backup path TI-LFA – Double-Segment Example P-space Q-space 1000 Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z) Packet to Z Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z) adj-SID(R4-R3) prefix-SID(R4) Packet to Z prefix-SID(Z) adj-SID(R4-R3) Default metric:10 R5 R2R1 A Z R3R4 R3R4 Packet to Z
- 20. g0/0/0/1 Metric=10 (default) Testbed Topology (TI LFA) g0/0/0/1 g0/0/0/0 g0/0/0/2 Metric=30 lo0 lo0 Metric=10 (default) g0/0/0/0 lo0 IS-IS Area 49.0002 IS-IS Area 49.0001 lo0 LDP-Only LSR P1 IS-IS L1-L2 P2 IS-IS L1-L2 PE1 IS-IS L1 PE2 IS-IS L2
- 21. § Give us your feedback and you could win a Plantronics headset. Complete the session survey on your Cisco Connect Toronto Mobile app at the end of your session for a chance to win § Winners will be announced and posted at the Information desk and on Twitter at the end of the day (You must be present to win!) Complete your session evaluation
- 22. § Cisco dCloud is a self-service platform that can be accessed via a browser, a high-speed Internet connection, and a cisco.com account § Customers will have direct access to a subset of dCloud demos and labs § Restricted content must be brokered by an authorized user (Cisco or Partner) and then shared with the customers (cisco.com user). § Go to dcloud.cisco.com, select the location closest to you, and log in with your cisco.com credentials § Review the getting started videos and try Cisco dCloud today: https://dcloud-cms.cisco.com/help dCloud Customers now get full dCloud experience!
- 23. #CiscoSpark Let’s continue this conversation on… Spark Cisco’s mobile collaboration team application Visit the Collaboration booth in the World of Solutions to join the Connect Spark room
- 24. Thank you







![§ Prefix SID
§ SID encoded as an index
§ Index represents an offset from SRGB base
§ Index globally unique
§ SRGB may vary across LSRs
§ SRGB (base and range) advertised with router
capabilities
§ Adjacency SID
§ SID encoded as absolute (i.e. not indexed)
value
§ Locally significant
§ Automatically allocated for each adjacency
SID Encoding
SRGB = [ 16000 - 23999 ]. Advertised as base = 16,000, range = 7999
Prefix SID = 16041. Advertised as Prefix SID Index = 41
Adjacency SID = 24000. Advertised as Adjacency SID = 24000
SR-enabled Node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ts-sp-03-ialvarez-saalvare-cct2015-sr-lab-v4-150520182614-lva1-app6892/85/Segment-Routing-Lab-7-320.jpg)