Select Stars: A DBA's Guide to Azure Cosmos DB (Chicago Suburban SQL Server User Group)
- 2. Specialties / Focus Areas / Passions: • Performance Tuning & Troubleshooting • Very Large Databases • SQL Server Storage Engine • HA/DR • Cloud @sqlbob [email protected] heraflux.com bobpusateri
- 4. We were developing an IoT system …Which needed to ingest data from thousands/millions of devices … and that data needed to be queried within seconds?
- 5. We were building an e-commerce site Which needed guaranteed performance and availability … anywhere on Earth … and needed to be able to scale up/down in response to conditions?
- 8. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 9. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 10. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 11. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service Key-Value GraphColumn-Family Document
- 12. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service Has multiple APIs as well Table API MongoDB
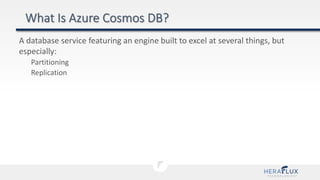
- 13. A database service featuring an engine built to excel at several things, but especially: Partitioning Replication
- 14. It’s a NoSQL offering! 3 DBAS WALKED INTO A NOSQL BAR…. A WHILE LATER THEY WALKED OUT BECAUSE THEY COULDN’T FIND A TABLE
- 15. • I often hear NoSQL == No Schema == No Design Not True • GENERALLY NoSQL schemas Do Exist Are somewhat enforced by the database Are fully enforced by the application • There are still design decisions that need to happen early on (And if they’re wrong you will pay for it later)
- 16. • Microsoft started having problems with internal large scale apps 2010 – “Project Florence” 2014 – Azure DocumentDB 2017 – Azure Cosmos DB • MS leverages this internally • Designed for the cloud • One of the fastest-growing services on Azure https://tinyurl.com/ycmhp6kd
- 17. • We’re developing an internal app for a global company • Thousands of users reading/updating data • How would we architect this?
- 23. • Cosmos DB is a Foundational Azure service • Put your data where the users are • Replication between regions is automatic • Multi-homing APIs Clients automatically connect to the nearest region • Adding or removing regions? No code changes! • Manual or automatic failovers • Designed from the ground up for HA
- 24. • Both storage and throughput can be scaled transparently • A single machine is never a bottleneck • Collections can scale from GB to PB across many machines and regions
- 25. • Requests are served from the nearest region • Database engine optimized for writes, latch-free • Indexing is synchronous and automatic • Single-digit millisecond latency at 99th Percentile Reads (1KB) Indexed Writes (1KB) 50th Percentile < 2ms < 6ms 99th Percentile < 10ms < 15ms
- 26. • 99.99% availability when in a single region • 99.999% availability in multiple regions • Highly-redundant storage architecture • Automatic or manual failover
- 28. • All data is encrypted, period. • In transit and at rest
- 29. • Two types of keys: • Master Keys Administrative Grant access to the entire account (not granular) Read-write and Read-only
- 30. • Resource Tokens • Used for application resources (Containers, docs, SPs, Triggers, UDF, etc.) Kinda like SQL Permissions • Tokens are specific to {user, resource, permission} • Tokens are time-sensitive (default 1 hour, max 5 hours)
- 31. • Resource Tokens DIRECT ACCESS
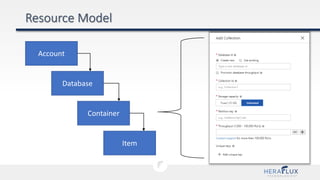
- 35. Account Item Database Container • Containers • Users • Permissions
- 36. Account Item Database Container • Data Model • Document (Collection) • Graph • Key-Value • Column-Value • Throughput
- 37. Account Item Database Container • Data Model • Document (Collection) • Graph • Key-Value • Column-Value • Throughput ATOM RECORD SEQUENCE (ARS) SYSTEM Atoms = primitives (string, bool, etc) Records = structs of atoms Sequences = arrays of {atom, record, sequence} Cosmos DB translates & projects all data models into an ARS model
- 39. Account Item Database Container • Depends on data model • Document • Node/Edge • Row/Item • Stored Procedures • Triggers • UDFs
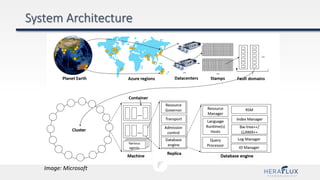
- 40. Image: Microsoft
- 41. • RU is the rate-based currency of Cosmos DB • Represents a combination of CPU, Memory, and IO • 1 RU = 1 read of 1KB • Every request is assigned a “cost” in RUs Reads, writes, stored procedures, etc
- 42. • Provisioned in units of RU/second • Can be changed at any time; metered hourly • Exceeding your RU budget = rate limiting • When quiescent, background tasks run Index Maintenance TTL Expiration Min RU/sec Max RU/sec RequestRate Rate Limiting No Limiting Replica Quiescent
- 44. • Define boundary values between partitions • Map partitions to physical locations (filegroups) • Similar values generally in the same partition Can lead to “hot” partitions Especially if on dates • Partition management is manual • Hard Limit: 15.000 partitions per table
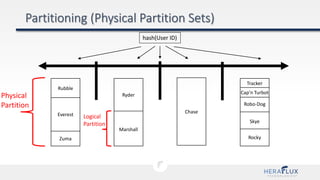
- 45. • There are no “ranges”, every partition key is hashed • Logical partitions (keys) are spread across physical partitions • Partition management is automatic! • No limit on number of partitions • Hard limit: 10GB max of data per partition key
- 46. • The most important design decision in Cosmos DB • Has a direct effect on How well it will scale How much you will pay • Think through partitioning during the design phase, it’s easier!
- 48. Partition Key: User ID Cosmos DB Container
- 49. Partition Key: User ID hash(User ID) Pseudo-random data distribution of hash values
- 52. hash(User ID) Chase Ryder Tracker Cap’n Turbot Everest Skye Rocky Rubble Zuma Marshall Robo-Dog What happens when it needs to grow?
- 53. Tracker Cap’n Turbot Skye Rocky Robo-Dog hash(User ID) Tracker Cap’n Turbot Robo-Dog Skye Rocky+ Partitions can be dynamically subdivided to grow the database without affecting availability This is done automatically.
- 54. • Plan to distribute both request and storage volume Remember the 10GB limit Adding dates after partition values can help with this • For greatest efficiency, queries should eliminate partitions • Queries can be routed/filtered via partition key • “Fan-Out” is something to try to avoid where possible
- 55. • Understand your workload! • Understand the most frequent/expensive queries • Understand insert vs update ratios • Remember partition keys are logical! Don’t be afraid of having too many More key values = better scalability
- 57. • This is huge because we have multiple replicas • If a change is replicated, what is seen elsewhere? • Why replicate, anyway? HA – multiple copies for failover Speed! • Bring the data closer to the user • “cheat” the speed of light!
- 58. Image: Microsoft
- 60. North Central US UK South Japan East
- 61. • Relational Databases: ACID Atomic Consistent Independent Durable • Distributed Systems: Brewer’s CAP Theorem Consistency Availability Partition tolerance (pick two)
- 62. • Problem: There’s no consistent definition of “consistent” in CS • Transactions (ACID) Each transaction moves from a single valid state to another • Replication (CAP) Getting a consistent view across replicated copies of data And CAP doesn’t even cover all cases….
- 63. • An extension of the CAP Theorem • Partitioning: Availability vs. Consistency ELSE Latency vs. Consistency • When partitioning a distributed system you have to choose between availability and consistency, but also when not partitioning one must choose between latency and consistency.
- 64. • Reader is far away from writer • Value gets updated by writer • Should the reader: See the old value? (prioritize latency) See the same result as the master? Wait for the new value (prioritize consistency)
- 65. • I love consistency models • I also love isolation levels
- 66. • Azure Cosmos DB has 5 of them • You can choose what gets prioritized • Can be overridden on a per-request basis Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 67. • Linearizability guarantee: reads will always return the most recent version of an item • (Like SERIALIZABLE [maybe?]) • Writes are only visible after committed by a majority quorum of replicas • If using this model, you are limited to a single Azure region Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 68. • Guarantees that “absence of any further writes, replicas will eventually converge” • No guarantee of order Client may get “new” values older than ones it had previously seen • Lowest latency for reads and writes …but it’s fast! Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 69. • Guarantees that readers will always see writes in order Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
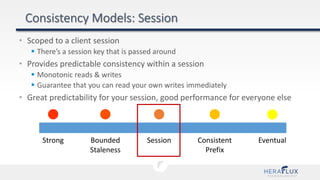
- 70. • Scoped to a client session There’s a session key that is passed around • Provides predictable consistency within a session Monotonic reads & writes Guarantee that you can read your own writes immediately • Great predictability for your session, good performance for everyone else Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 71. • Define a “window” of staleness in terms of # revisions or time • If a replica gets too far behind (is outside the “window”) Cosmos DB will prioritize consistency over all else May even rate limit writes until stale replica catches up Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 73. • What if you’re not doing geo-replication? Does this matter? • Yes it does! • Even in local regions there are still 4 replicas of your database 1 2 3 4
- 75. • Yeah, about that….
- 80. • Schema-agnostic • Automatic Every property of every record is indexed by default No latches involved (remember it’s highly write-optimized) • Customizable You can define what is indexed (and save space)
- 81. { "cars": [ { "make": "Hyundai", "model": "Santa Fe" }, { "make": "Subaru", "model": "Forester", “plate": "T SQL" } ], "city": "Chicago" } city Chicago0 1 make model make model license cars Hyundai Santa Fe Subaru Forester T SQL
- 82. { "cars": [ { "make": "Tesla", "model": "X" } ], "city": “Oslo" } city Oslo0 make model cars Tesla X
- 83. city Chicago0 1 make model make model license cars Hyundai Santa Fe Subaru Forester T SQL Oslo {1,2} {1,2}{1,2} {1} {2}{1,2} {1} Tesla X {1,2} {1,2} {1} {1}{2} {2} {1} {1} {1} {1} {1}{1} Term Postings $/cars/0 1,2 $/cars/0/make 1,2 $/cars/0/model 1,2 $/cars/1 1 ……
- 86. • Remember what I said about indexes?
- 87. • Backups are automatic • Snapshots taken and stored separately in Azure Blob Storage • For speed, it’s written to same region as current Cosmos DB write region • For safety, it’s replicated to another region as well
- 88. • Taken every 4 hours • Only the last 2 snapshots are retained • “If the data is accidentally dropped or corrupted, contact Azure support within eight hours.” • You can maintain your own backups Azure Cosmos DB Data Migration Tool “export to JSON” option • If you delete a container/database, backups retained for 30 days
- 92. • You Pay For: Storage ($0.25 per GB/month) Throughput ($0.008 per 100 RUs/hour) Data Transfer for geo-replication (varies by region) North Central US: $0.087 per GB • Check Azure Portal for most current pricing info • https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/cosmos-db/
- 93. • There’s a Cosmos DB Emulator! • Run locally on your machine for free • https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/local-emulator
- 94. • There’s a Cosmos DB Emulator! • Run locally on your machine for free • https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/local-emulator






























































![• Linearizability guarantee: reads will always return the most recent version
of an item
• (Like SERIALIZABLE [maybe?])
• Writes are only visible after committed by a majority quorum of replicas
• If using this model, you are limited to a single Azure region
Bounded
Staleness
Strong Consistent
Prefix
Session Eventual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb20180919-180919180557/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-Chicago-Suburban-SQL-Server-User-Group-67-320.jpg)












![{ "cars": [
{ "make": "Hyundai", "model": "Santa Fe" },
{ "make": "Subaru", "model": "Forester", “plate": "T SQL" }
],
"city": "Chicago"
}
city
Chicago0 1
make model make model license
cars
Hyundai
Santa
Fe
Subaru Forester T SQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb20180919-180919180557/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-Chicago-Suburban-SQL-Server-User-Group-81-320.jpg)
![{ "cars": [
{ "make": "Tesla", "model": "X" }
],
"city": “Oslo"
}
city
Oslo0
make model
cars
Tesla X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb20180919-180919180557/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-Chicago-Suburban-SQL-Server-User-Group-82-320.jpg)












