Select Stars: A DBA's Guide to Azure Cosmos DB (SQL Saturday Oslo 2018)
- 2. Specialties / Focus Areas / Passions: • Performance Tuning & Troubleshooting • Very Large Databases • SQL Server Storage Engine • HA/DR • Cloud @sqlbob [email protected] heraflux.com bobpusateri
- 5. We were developing an IoT system …Which needed to ingest data from thousands/millions of devices … and that data needed to be queried within seconds?
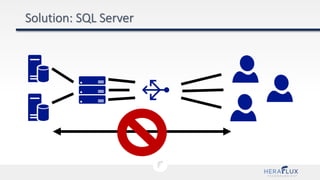
- 6. We were building an e-commerce site Which needed guaranteed performance and availability … anywhere on Earth … and needed to be able to scale up/down in response to conditions?
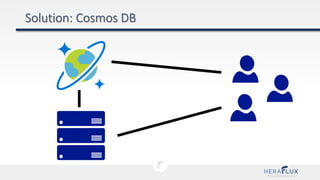
- 9. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 10. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 11. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service
- 12. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service Key-Value GraphColumn-Family Document
- 13. A globally distributed, massively scalable, multi-model database service Has multiple APIs as well Table API MongoDB
- 14. A database service featuring an engine built to excel at several things, but especially: Partitioning Replication
- 15. It’s a NoSQL offering! 3 DBAS WALKED INTO A NOSQL BAR…. A WHILE LATER THEY WALKED OUT BECAUSE THEY COULDN’T FIND A TABLE
- 16. • I often hear NoSQL == No Schema == No Design ▪ Not True • GENERALLY NoSQL schemas ▪ Do Exist ▪ Are somewhat enforced by the database ▪ Are fully enforced by the application • There are still design decisions that need to happen early on ▪ (And if they’re wrong you will pay for it later)
- 17. • Microsoft started having problems with internal large scale apps ▪ 2010 – “Project Florence” ▪ 2014 – Azure DocumentDB ▪ 2017 – Azure Cosmos DB • MS leverages this internally • Designed for the cloud • One of the fastest-growing services on Azure https://tinyurl.com/ycmhp6kd
- 18. • We’re developing an internal app for a global company • Thousands of users reading/updating data • How would we architect this?
- 24. • Cosmos DB is a Foundational Azure service • Put your data where the users are • Replication between regions is automatic • Multi-homing APIs ▪ Clients automatically connect to the nearest region • Adding or removing regions? No code changes! • Manual or automatic failovers • Designed from the ground up for HA
- 25. • Both storage and throughput can be scaled transparently • A single machine is never a bottleneck • Collections can scale from GB to PB across many machines and regions
- 26. • Requests are served from the nearest region • Database engine optimized for writes, latch-free • Indexing is synchronous and automatic • Single-digit millisecond latency at 99th Percentile Reads (1KB) Indexed Writes (1KB) 50th Percentile < 2ms < 6ms 99th Percentile < 10ms < 15ms
- 27. • 99.99% availability when in a single region • 99.999% availability in multiple regions • Highly-redundant storage architecture • Automatic or manual failover
- 28. • Will give you money back if they’re not met! • https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/support/legal/sla/cosmos-db/
- 29. • All data is encrypted, period. • In transit and at rest
- 30. • Two types of keys: • Master Keys ▪ Administrative ▪ Grant access to the entire account (not granular) ▪ Read-write and Read-only
- 31. • Resource Tokens • Used for application resources (Containers, docs, SPs, Triggers, UDF, etc.) ▪ Kinda like SQL Permissions • Tokens are specific to {user, resource, permission} • Tokens are time-sensitive (default 1 hour, max 5 hours)
- 32. • Resource Tokens DIRECT ACCESS
- 36. Account Item Database Container • Containers • Users • Permissions
- 37. Account Item Database Container • Data Model • Document (Collection) • Graph • Key-Value • Column-Value • Throughput
- 38. Account Item Database Container • Data Model • Document (Collection) • Graph • Key-Value • Column-Value • Throughput ATOM RECORD SEQUENCE (ARS) SYSTEM Atoms = primitives (string, bool, etc) Records = structs of atoms Sequences = arrays of {atom, record, sequence} Cosmos DB translates & projects all data models into an ARS model
- 40. Account Item Database Container • Depends on data model • Document • Node/Edge • Row/Item • Stored Procedures • Triggers • UDFs
- 41. Image: Microsoft
- 42. • RU is the rate-based currency of Cosmos DB • Represents a combination of CPU, Memory, and IO • 1 RU = 1 read of 1KB • Every request is assigned a “cost” in RUs ▪ Reads, writes, stored procedures, etc
- 43. • Provisioned in units of RU/second • Can be changed at any time; metered hourly • Exceeding your RU budget = rate limiting • When quiescent, background tasks run ▪ Index Maintenance ▪ TTL Expiration Min RU/sec Max RU/sec RequestRate Rate Limiting No Limiting Replica Quiescent
- 45. • Define boundary values between partitions • Map partitions to physical locations (filegroups) • Similar values generally in the same partition ▪ Can lead to “hot” partitions ▪ Especially if on dates • Partition management is manual • Hard Limit: 15.000 partitions per table
- 46. • There are no “ranges”, every partition key is hashed • Logical partitions (keys) are spread across physical partitions • Partition management is automatic! • No limit on number of partitions • Hard limit: 10GB max of data per partition key
- 47. • The most important design decision in Cosmos DB • Has a direct effect on ▪ How well it will scale ▪ How much you will pay • Think through partitioning during the design phase, it’s easier!
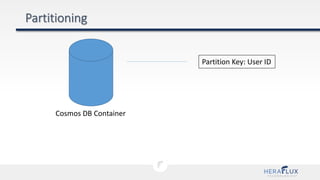
- 49. Partition Key: User ID Cosmos DB Container
- 50. Partition Key: User ID hash(User ID) Pseudo-random data distribution of hash values
- 53. hash(User ID) Chase Ryder Tracker Cap’n Turbot Everest Skye Rocky Rubble Zuma Marshall Robo-Dog What happens when it needs to grow?
- 54. Tracker Cap’n Turbot Skye Rocky Robo-Dog hash(User ID) Tracker Cap’n Turbot Robo-Dog Skye Rocky+ Partitions can be dynamically subdivided to grow the database without affecting availability This is done automatically.
- 55. • Plan to distribute both request and storage volume ▪ Remember the 10GB limit ▪ Adding dates after partition values can help with this • For greatest efficiency, queries should eliminate partitions • Queries can be routed/filtered via partition key • “Fan-Out” is something to try to avoid where possible
- 56. • Understand your workload! • Understand the most frequent/expensive queries • Understand insert vs update ratios • Remember partition keys are logical! ▪ Don’t be afraid of having too many ▪ More key values = better scalability
- 58. • This is huge because we have multiple replicas • If a change is replicated, what is seen elsewhere? • Why replicate, anyway? ▪ HA – multiple copies for failover ▪ Speed! • Bring the data closer to the user • “cheat” the speed of light!
- 59. Image: Microsoft
- 61. North Central US UK South Japan East
- 62. North Central US UK South Japan East
- 64. North Central US UK South Japan East X
- 65. • Do we keep all the replicas online? ▪ One of them will be wrong? • Do we shut down the stale replica? ▪ Sacrifice availability for correctness? • Do we shut down everything? ▪ All or nothing?
- 66. • Relational Databases: ACID ▪ Atomic ▪ Consistent ▪ Independent ▪ Durable • Distributed Systems: Brewer’s CAP Theorem ▪ Consistency ▪ Availability ▪ Partition tolerance ▪ (pick two)
- 67. • Problem: There’s no consistent definition of “consistent” in CS • Transactions (ACID) ▪ Each transaction moves from a single valid state to another • Replication (CAP) ▪ Getting a consistent view across replicated copies of data ▪ And CAP doesn’t even cover all cases….
- 68. • An extension of the CAP Theorem • Partitioning: Availability vs. Consistency ELSE Latency vs. Consistency • When partitioning a distributed system you have to choose between availability and consistency, but also when not partitioning one must choose between latency and consistency.
- 69. • Reader is far away from writer • Value gets updated by writer • Should the reader: ▪ See the old value? (prioritize latency) ▪ See the same result as the master? ▪ Wait for the new value (prioritize consistency)
- 70. • I love consistency models • I also love isolation levels
- 71. • Azure Cosmos DB has 5 of them • You can choose what gets prioritized • Can be overridden on a per-request basis Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 72. • Linearizability guarantee: reads will always return the most recent version of an item • (Like SERIALIZABLE [maybe?]) • Writes are only visible after committed by a majority quorum of replicas • If using this model, you are limited to a single Azure region Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 73. • Guarantees that “absence of any further writes, replicas will eventually converge” • No guarantee of order ▪ Client may get “new” values older than ones it had previously seen • Lowest latency for reads and writes ▪ …but it’s fast! Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 74. • Guarantees that readers will always see writes in order Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 75. • Scoped to a client session ▪ There’s a session key that is passed around • Provides predictable consistency within a session ▪ Monotonic reads & writes ▪ Guarantee that you can read your own writes immediately • Great predictability for your session, good performance for everyone else Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 76. • Define a “window” of staleness in terms of # revisions or time • If a replica gets too far behind (is outside the “window”) ▪ Cosmos DB will prioritize consistency over all else ▪ May even rate limit writes until stale replica catches up Bounded Staleness Strong Consistent Prefix Session Eventual
- 78. • What if you’re not doing geo-replication? Does this matter? • Yes it does! • Even in local regions there are still 4 replicas of your database 1 2 3 4
- 80. • Yeah, about that….
- 85. • Schema-agnostic • Automatic ▪ Every property of every record is indexed by default ▪ No latches involved (remember it’s highly write-optimized) • Customizable ▪ You can define what is indexed (and save space)
- 86. { "cars": [ { "make": "Hyundai", "model": "Santa Fe" }, { "make": "Subaru", "model": "Forester", “plate": "T SQL" } ], "city": "Chicago" } city Chicago0 1 make model make model license cars Hyundai Santa Fe Subaru Forester T SQL
- 87. { "cars": [ { "make": "Tesla", "model": "X" } ], "city": “Oslo" } city Oslo0 make model cars Tesla X
- 88. city Chicago0 1 make model make model license cars Hyundai Santa Fe Subaru Forester T SQL Oslo {1,2} {1,2}{1,2} {1} {2}{1,2} {1} Tesla X {1,2} {1,2} {1} {1}{2} {2} {1} {1} {1} {1} {1}{1} Term Postings $/cars/0 1,2 $/cars/0/make 1,2 $/cars/0/model 1,2 $/cars/1 1 ……
- 91. • Remember what I said about indexes?
- 92. • Backups are automatic • Snapshots taken and stored separately in Azure Blob Storage • For speed, it’s written to same region as current Cosmos DB write region • For safety, it’s replicated to another region as well
- 93. • Taken every 4 hours • Only the last 2 snapshots are retained • “If the data is accidentally dropped or corrupted, contact Azure support within eight hours.” • You can maintain your own backups ▪ Azure Cosmos DB Data Migration Tool “export to JSON” option • If you delete a container/database, backups retained for 30 days
- 97. • You Pay For: ▪ Storage (2,0286 kr per GB/month) ▪ Throughput (0,065 kr per 100 RUs/hour) ▪ Data Transfer for geo-replication (varies by region) ▪ West Europe: 0,706 kr per GB • Check Azure Portal for most current pricing info • https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/cosmos-db/
- 98. • There’s a Cosmos DB Emulator! • Run locally on your machine for free • https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/local-emulator
- 99. • There’s a Cosmos DB Emulator! • Run locally on your machine for free • https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/local-emulator




































































![• Linearizability guarantee: reads will always return the most recent version
of an item
• (Like SERIALIZABLE [maybe?])
• Writes are only visible after committed by a majority quorum of replicas
• If using this model, you are limited to a single Azure region
Bounded
Staleness
Strong Consistent
Prefix
Session Eventual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb-180901124445/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-SQL-Saturday-Oslo-2018-72-320.jpg)













![{ "cars": [
{ "make": "Hyundai", "model": "Santa Fe" },
{ "make": "Subaru", "model": "Forester", “plate": "T SQL" }
],
"city": "Chicago"
}
city
Chicago0 1
make model make model license
cars
Hyundai
Santa
Fe
Subaru Forester T SQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb-180901124445/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-SQL-Saturday-Oslo-2018-86-320.jpg)
![{ "cars": [
{ "make": "Tesla", "model": "X" }
],
"city": “Oslo"
}
city
Oslo0
make model
cars
Tesla X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selectstarscosmosdb-180901124445/85/Select-Stars-A-DBA-s-Guide-to-Azure-Cosmos-DB-SQL-Saturday-Oslo-2018-87-320.jpg)












