Single source Shortest path algorithm with example
- 1. Design and Analysis of Algorithm Greedy Methods (Single Source shortest path, Knapsack problem ) Lecture – 45 - 53
- 2. • A greedy algorithm always makes the choice that looks best at the moment. (i.e. it makes a locally optimal choice in the hope that this choice will lead to a globally optimal solution). • The objective of this section is to explores optimization problems that are solvable by greedy algorithms. Overview
- 3. Greedy Algorithm • In mathematics, computer science and economics, an optimization problem is the problem of finding the best solution from all feasible solutions. • Algorithms for optimization problems typically go through a sequence of steps, with a set of choices at each step. • Many optimization problems can be solved using a greedy approach. • Greedy algorithms are simple and straightforward.
- 4. Greedy Algorithm • A greedy algorithm always makes the choice that looks best at the moment. • That is, it makes a locally optimal choice in the hope that this choice will lead to a globally optimal solution. • Greedy algorithms do not always yield optimal solutions, but for many problems they do. • This algorithms are easy to invent, easy to implement and most of the time provides best and optimized solution.
- 5. Greedy Algorithm • Application of Greedy Algorithm: • A simple but nontrivial problem, the activity- selection problem, for which a greedy algorithm efficiently computes a solution. • In combinatorics,(a branch of mathematics), a ‘matroid’ is a structure that abstracts and generalizes the notion of linear independence in vector spaces. Greedy algorithm always produces an optimal solution for such problems. Scheduling unit-time tasks with deadlines and penalties is an example of such problem.
- 6. Greedy Algorithm • Application of Greedy Algorithm: • An important application of greedy techniques is the design of data-compression codes (i.e. Huffman code) . • The greedy method is quite powerful and works well for a wide range of problems. They are: • Minimum-spanning-tree algorithms (Example: Prims and Kruskal algorithm) • Single Source Shortest Path. (Example: Dijkstra's and Bellman ford algorithm)
- 7. Greedy Algorithm • Application of Greedy Algorithm: • A problem exhibits optimal substructure if an optimal solution to the problem contains within it optimal solutions to subproblems. • This property is a key ingredient of assessing the applicability of dynamic programming as well as greedy algorithms. • The subtleties between the above two techniques are illustrated with the help of two variants of a classical optimization problem known as knapsack problem. These variants are: • 0-1 knapsack problem (Dynamic Programming) • Fractional knapsack problem (Greedy Algorithm)
- 8. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • It is a shortest path problem where the shortest path from a given source vertex to all other remaining vertices is computed. • Dijkstra’s Algorithm and Bellman Ford Algorithm are the famous algorithms used for solving single-source shortest path problem.
- 9. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm • Dijkstra Algorithm is a very famous greedy algorithm. • It is used for solving the single source shortest path problem. • It computes the shortest path from one particular source node to all other remaining nodes of the graph.
- 10. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Feasible Condition) • Dijkstra algorithm works • for connected graphs. • for those graphs that do not contain any negative weight edge. • To provides the value or cost of the shortest paths. • for directed as well as undirected graphs.
- 11. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation) The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the following steps- • Step-01: • In the first step. two sets are defined- • One set contains all those vertices which have been included in the shortest path tree. • In the beginning, this set is empty. • Other set contains all those vertices which are still left to be included in the shortest path tree. • In the beginning, this set contains all the vertices of the given graph.
- 12. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation) The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the following steps- • Step-02: For each vertex of the given graph, two variables are defined as- • Π[v] which denotes the predecessor of vertex ‘v’ • d[v] which denotes the shortest path estimate of vertex ‘v’ from the source vertex.
- 13. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation) The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the following steps- • Step-02: Initially, the value of these variables is set as- • The value of variable ‘Π’ for each vertex is set to NIL i.e. Π[v] = NIL • The value of variable ‘d’ for source vertex is set to 0 i.e. d[S] = 0 • The value of variable ‘d’ for remaining vertices is set to ∞ i.e. d[v] = ∞
- 14. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation) The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the following steps- • Step-03: The following procedure is repeated until all the vertices of the graph are processed- • Among unprocessed vertices, a vertex with minimum value of variable ‘d’ is chosen. • Its outgoing edges are relaxed. • After relaxing the edges for that vertex, the sets created in step-01 are updated.
- 15. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 ∞ s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 16. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 17. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 18. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s ∞ x 10 t 5 y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 19. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s ∞ x 10 t 5 y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 20. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s ∞ x 10 t 5 y ∞ z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 21. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 14 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 22. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 14 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 23. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 14 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 24. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 13 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 25. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 13 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 26. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 9 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 27. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 9 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10
- 28. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- 4 0 s 9 x 8 t 5 y 7 z 2 9 7 1 6 2 3 5 10 Hence the shortest path to all the vertex from s are: 𝑠 → 𝑡 = 8 𝑠 → 𝑥 = 9 𝑠 → 𝑦 = 5 𝑠 → 𝑧 = 7
- 29. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Algorithm) DIJKSTRA(G, w, s) 1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) 2 S ← Ø 3 Q ← V[G] 4 while Q ≠ Ø 5 do u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q) 6 S ← 𝑆 ∈ {𝑢} 7 for each vertex 𝑣 ∈ 𝐴𝑑𝑗[𝑢] 8 do RELAX(u, v, w)
- 30. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Algorithm) INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) 1 for each vertex v V[G] 2 do d[v] ← ∞ 3 π[v] ← NIL 4 d[s] ← 0 RELAX(u, v, w) 1 if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) 2 then d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v) 3 π[v] ← u
- 31. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Complexity) CASE-01: • 𝐴[𝑖, 𝑗] stores the information about edge (𝑖, 𝑗). • Time taken for selecting 𝑖 with the smallest 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡 is 𝑂(𝑉). • For each neighbor of i, time taken for updating 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡[𝑗] is 𝑂(1) and there will be maximum V-1 neighbors. • Time taken for each iteration of the loop is O(V) and one vertex is deleted from Q. • Thus, total time complexity becomes O(𝑉2).
- 32. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Complexity) CASE-02: • With adjacency list representation, all vertices of the graph can be traversed using BFS in 𝑂(𝑉 + 𝐸) time. • In min heap, operations like extract-min and decrease-key value takes 𝑂(log 𝑉) time. • So, overall time complexity becomes 𝑂(𝐸 + 𝑉) 𝑥 𝑂(log 𝑉) which is 𝑂((𝐸 + 𝑉) 𝑥 log 𝑉) = 𝑂(𝐸 log 𝑉)
- 33. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Self Practice) Example 2: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Dijkstra’s Algorithm- s ∞ c ∞ a ∞ d ∞ b ∞ e ∞ 1 1 1 2 5 2 2 2
- 34. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm • Bellman-Ford algorithm solves the single-source shortest-path problem in the general case in which edges of a given digraph can have negative weight as long as G contains no negative cycles. • Like Dijkstra's algorithm, this algorithm, uses the notion of edge relaxation but does not use with greedy method. Again, it uses d[u] as an upper bound on the distance d[u, v] from u to v.
- 35. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm • The algorithm progressively decreases an estimate d[v] on the weight of the shortest path from the source vertex s to each vertex v ∈ V until it achieve the actual shortest-path. • The algorithm returns Boolean TRUE if the given digraph contains no negative cycles that are reachable from source vertex s otherwise it returns Boolean FALSE.
- 36. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path Bellman Ford Algorithm (Negative Cycle Detection) Assume: 𝑑[𝑢] ≤ 𝑑[𝑥] + 4 𝑑[𝑣] ≤ 𝑑[𝑢] + 5 𝑑[𝑥] ≤ 𝑑[𝑣] − 10 Adding: 𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑑[𝑣] + 𝑑[𝑥] ≤ 𝑑[𝑥] + 𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑑[𝑣] − 1 Because it’s a cycle, vertices on left are same as those on right. Thus we get 0 ≤ −1; a contradiction. So for at least one edge (𝑢, 𝑣), 𝑑[𝑣] > 𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑤(𝑢, 𝑣) This is exactly what Bellman-Ford checks for. u x v 4 5 -10
- 37. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm (Implementation) • Step 1: Start with the weighted graph. • Step 2: Choose the starting vertex by making the path value zero and assign infinity path values to all other vertices. • Step 3: Visit each edge and relax the path distances if they are inaccurate. • Step 4: Do step 3 V-1 times because in the worst case a vertex's path length might need to be readjusted V-1 times. • Step 5: After all vertices have their path lengths, check if a negative cycle is present or not.
- 38. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- ∞ s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 39. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- ∞ s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1
- 40. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 1 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 41. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 2 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 42. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 3 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 43. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 4 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 44. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 5 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 45. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 6 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 46. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 7 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 47. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 8 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 48. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no - 9 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 49. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 1 Edge no – 10 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 50. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 1 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 51. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 2 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 52. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y 16 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 3 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 53. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y 16 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 4 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 54. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y 16 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 5 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 55. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 11 x 6 t 7 y 16 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 6 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 56. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 11 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 7 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 57. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 11 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 8 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 58. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no - 9 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 59. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 2 Edge no – 10 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
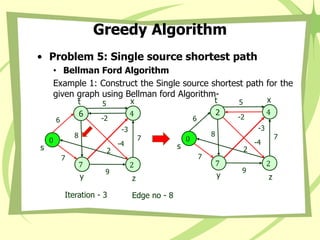
- 60. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 Iteration - 3 Edge no - 1 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 61. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 2 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 62. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 3 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 63. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 4 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 64. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 5 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 65. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 6 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 66. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 7 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 67. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 8 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 68. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no - 9 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 69. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 3 Edge no – 10 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 70. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 1 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 71. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 2 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 72. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 3 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 73. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 74. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 5 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 75. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 6 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 76. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 7 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y −2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 77. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 8 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y −2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 78. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no - 9 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y −2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 79. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- Iteration - 4 Edge no – 10 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y −2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4
- 80. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm Example 1: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman ford Algorithm- 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y −2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s ∞ x ∞ t ∞ y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s ∞ x 6 t 7 y ∞ z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 6 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 0 s 4 x 2 t 7 y 2 z 8 -3 2 5 7 9 -2 7 6 -4 After Iteration 1 After Iteration 3 After Iteration 2 After Iteration 4
- 81. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm (Algorithm) BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s) 1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) 2 for i ← 1 to |V[G]| - 1 3 do for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G] 4 do RELAX(u, v, w) 5 for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G] 6 do if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) 7 then return FALSE 8 return TRUE
- 82. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm (Algorithm) INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) 1 for each vertex v V[G] 2 do d[v] ← ∞ 3 π[v] ← NIL 4 d[s] ← 0 RELAX(u, v, w) 1 if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) 2 then d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v) 3 π[v] ← u
- 83. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm (Analysis) BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s) 1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) → Θ(𝑉) 2 for i ← 1 to |V[G]| - 1 3 do for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G] Ο(𝐸) 4 do RELAX(u, v, w) 5 for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G] 6 do if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) Ο(𝐸) 7 then return FALSE 8 return TRUE Ο(𝐸)
- 84. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Single source shortest path • Bellman Ford Algorithm(Self Practice) Example 2: Construct the Single source shortest path for the given graph using Bellman Ford Algorithm- s ∞ c ∞ a ∞ d ∞ b ∞ e ∞ 1 1 1 2 5 2 2 2
- 85. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Problem definition: • The Knapsack problem is an “combinatorial optimization problem”, a topic in mathematics and computer science about finding the optimal object among a set of object . • Given a set of items, each with a weight and a profit, determine the number of each item to include in a collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total profit is as large as possible.
- 86. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Versions of Knapsack: • Fractional Knapsack Problem: Items are divisible; you can take any fraction of an item and it is solved by using Greedy Algorithm. • 0/1 Knapsack Problem: Items are indivisible; you either take them or not and it is solved by using Dynamic Programming(DP).
- 87. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem • Fractional Knapsack Problem: Given n objects and a knapsack with a capacity “M” (weight) • Each object 𝑖 has weight 𝑤𝑖 and profit 𝑝𝑖. • For each object 𝑖, suppose a fraction 𝑥𝑖 , 0 ≤ 𝑥𝑖 ≤ 1, can be placed in the knapsack, then the profit earned is 𝑝𝑖. 𝑥𝑖 .
- 88. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem: The objective is to maximize profit subject to capacity constraints. 𝑖. 𝑒. 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑖=1 𝑛 𝑝𝑖𝑥𝑖 ------------------------------(1) Subject to 𝑖=1 𝑛 𝑤𝑖𝑥𝑖 ≤ 𝑀 ------------------------(2) Where, 0 ≤ 𝑥𝑖 ≤ 1, 𝑝𝑖 > 0, 𝑤𝑖 > 0. A feasible solution is any subset {𝑥1, 𝑥2, 𝑥3, … … , 𝑥𝑛} satisfying (1) & (2). An optimal solution is a feasible solution that maximize 𝑖=1 𝑛 𝑝𝑖𝑥𝑖.
- 89. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Fractional knapsack problem is solved using greedy method in the following steps- Step-01: • For each item, compute its (profit / weight) ratio.(i.e 𝑝𝑖/𝑥𝑖) Step-02: • Arrange all the items in decreasing order of their (profit / weight) ratio. Step-03: • Start putting the items into the knapsack beginning from the item with the highest ratio. • Put as many items as you can into the knapsack.
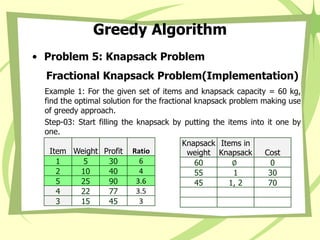
- 90. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-01: Compute the (profit / weight) ratio for each item-
- 91. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Algorithm) FRACTIONAL_KNAPSACK (p, 𝑤, 𝑀) 1 for i = 1 to n 2 do x[i] = 0 3 weight = 0 4 for i = 1 to n 5 if weight + w[i] ≤ M 6 then x[i] = 1 7 weight = weight + w[i] 8 else 9 x[i] = (M - weight) / w[i] 10 weight = M 11 break 12 return x
- 92. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Item Weight Profit 1 5 30 2 10 40 3 15 45 4 22 77 5 25 90
- 93. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-01: Compute the (profit / weight) ratio for each item- Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 3 15 45 3 4 22 77 3.5 5 25 90 3.6
- 94. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-02: Sort all the items in decreasing order of their value / weight ratio- Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3
- 95. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0
- 96. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0
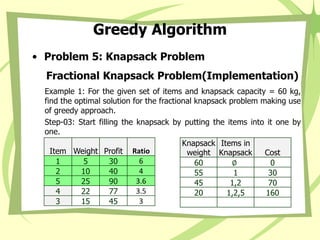
- 97. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30
- 98. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30
- 99. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30 45 1, 2 70
- 100. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30 45 1, 2 70
- 101. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30 45 1,2 70 20 1,2,5 160
- 102. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Step-03: Start filling the knapsack by putting the items into it one by one. Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30 45 1,2 70 20 1,2,5 160
- 103. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Implementation) Example 1: Now, Knapsack weight left to be filled is 20 kg but item-4 has a weight of 22 kg. Since in fractional knapsack problem, even the fraction of any item can be taken. So, knapsack will contain the fractional part of item 4.(20 out of 22) Total cost of the knapsack = 160 + (20/22) x 77 = 160 + 70 = 230 units Item Weight Profit Ratio 1 5 30 6 2 10 40 4 5 25 90 3.6 4 22 77 3.5 3 15 45 3 Knapsack weight Items in Knapsack Cost 60 ∅ 0 55 1 30 45 1,2 70 20 1,2,5 160 0 1,2,5, frac(4) 230
- 104. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(Algorithm) • The main time taking step is the sorting of all items in decreasing order of their (profit / weight) ratio. • If the items are already arranged in the required order, then while loop takes 𝑂(𝑛) time. • The average time complexity of Quick Sort is 𝑂(𝑛 log 𝑛). • Therefore, total time taken including the sort is 𝑂(𝑛 log 𝑛).
- 105. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(self practice) Example 2: For the given set of items and knapsack capacity = 60 kg, find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Item Weight Profit A 1 5 B 3 9 C 2 4 D 2 8
- 106. Greedy Algorithm • Problem 5: Knapsack Problem Fractional Knapsack Problem(self practice) Example 3: Find the optimal solution for the fractional knapsack problem making use of greedy approach. Consider- n = 3 M = 20 kg (w1, w2, w3) = (18, 15, 10) (p1, p2, p3) = (25, 24, 15)










![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation)
The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the
following steps-
• Step-02:
For each vertex of the given graph, two variables are defined
as-
• Π[v] which denotes the predecessor of vertex ‘v’
• d[v] which denotes the shortest path estimate of vertex ‘v’
from the source vertex.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-12-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Implementation)
The implementation of Dijkstra Algorithm is executed in the
following steps-
• Step-02:
Initially, the value of these variables is set as-
• The value of variable ‘Π’ for each vertex is set to NIL i.e.
Π[v] = NIL
• The value of variable ‘d’ for source vertex is set to 0 i.e. d[S]
= 0
• The value of variable ‘d’ for remaining vertices is set to ∞
i.e. d[v] = ∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-13-320.jpg)















![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Algorithm)
DIJKSTRA(G, w, s)
1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s)
2 S ← Ø
3 Q ← V[G]
4 while Q ≠ Ø
5 do u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q)
6 S ← 𝑆 ∈ {𝑢}
7 for each vertex 𝑣 ∈ 𝐴𝑑𝑗[𝑢]
8 do RELAX(u, v, w)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-29-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Algorithm)
INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s)
1 for each vertex v V[G]
2 do d[v] ← ∞
3 π[v] ← NIL
4 d[s] ← 0
RELAX(u, v, w)
1 if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v)
2 then d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v)
3 π[v] ← u](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-30-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Dijkstra’s Algorithm (Complexity)
CASE-01:
• 𝐴[𝑖, 𝑗] stores the information about edge (𝑖, 𝑗).
• Time taken for selecting 𝑖 with the smallest 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡 is 𝑂(𝑉).
• For each neighbor of i, time taken for updating 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡[𝑗] is 𝑂(1)
and there will be maximum V-1 neighbors.
• Time taken for each iteration of the loop is O(V) and one
vertex is deleted from Q.
• Thus, total time complexity becomes O(𝑉2).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-31-320.jpg)


![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Bellman Ford Algorithm
• Bellman-Ford algorithm solves the single-source
shortest-path problem in the general case in which
edges of a given digraph can have negative weight
as long as G contains no negative cycles.
• Like Dijkstra's algorithm, this algorithm, uses the
notion of edge relaxation but does not use with
greedy method. Again, it uses d[u] as an upper
bound on the distance d[u, v] from u to v.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-34-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Bellman Ford Algorithm
• The algorithm progressively decreases an estimate
d[v] on the weight of the shortest path from the
source vertex s to each vertex v ∈ V until it achieve
the actual shortest-path.
• The algorithm returns Boolean TRUE if the given
digraph contains no negative cycles that are
reachable from source vertex s otherwise it returns
Boolean FALSE.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-35-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
Bellman Ford Algorithm (Negative Cycle
Detection)
Assume:
𝑑[𝑢] ≤ 𝑑[𝑥] + 4
𝑑[𝑣] ≤ 𝑑[𝑢] + 5
𝑑[𝑥] ≤ 𝑑[𝑣] − 10
Adding:
𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑑[𝑣] + 𝑑[𝑥] ≤ 𝑑[𝑥] + 𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑑[𝑣] − 1
Because it’s a cycle, vertices on left are same as those on right. Thus
we get 0 ≤ −1; a contradiction.
So for at least one edge (𝑢, 𝑣),
𝑑[𝑣] > 𝑑[𝑢] + 𝑤(𝑢, 𝑣)
This is exactly what Bellman-Ford checks for.
u
x
v
4
5
-10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-36-320.jpg)











































![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Bellman Ford Algorithm (Algorithm)
BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s)
1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s)
2 for i ← 1 to |V[G]| - 1
3 do for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G]
4 do RELAX(u, v, w)
5 for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G]
6 do if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v)
7 then return FALSE
8 return TRUE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-81-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Bellman Ford Algorithm (Algorithm)
INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s)
1 for each vertex v V[G]
2 do d[v] ← ∞
3 π[v] ← NIL
4 d[s] ← 0
RELAX(u, v, w)
1 if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v)
2 then d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v)
3 π[v] ← u](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-82-320.jpg)
![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Single source shortest path
• Bellman Ford Algorithm (Analysis)
BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s)
1 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) → Θ(𝑉)
2 for i ← 1 to |V[G]| - 1
3 do for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G] Ο(𝐸)
4 do RELAX(u, v, w)
5 for each edge (u, v) ∈ E[G]
6 do if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) Ο(𝐸)
7 then return FALSE
8 return TRUE
Ο(𝐸)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-83-320.jpg)







![Greedy Algorithm
• Problem 5: Knapsack Problem
Fractional Knapsack Problem(Algorithm)
FRACTIONAL_KNAPSACK (p, 𝑤, 𝑀)
1 for i = 1 to n
2 do x[i] = 0
3 weight = 0
4 for i = 1 to n
5 if weight + w[i] ≤ M
6 then x[i] = 1
7 weight = weight + w[i]
8 else
9 x[i] = (M - weight) / w[i]
10 weight = M
11 break
12 return x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpath-240304040343-7fc336b9/85/Single-source-Shortest-path-algorithm-with-example-91-320.jpg)