Software design principles
- 2. Software Design Principles 1 Being presented by Mr. Ritesh Singh
- 3. Thanks. 1 Special thanks to Ms. Charu Jain for this initiave
- 4. Introduction 4 Software: A set of programs which helps user to execute its task using the system Design: creation of a plan to construct a system Principles: Rules or laws to be followed Demystifying the subjectDemystifying the subject
- 5. Objectives 5 • Clearly understand the software design principles • Follow the structured approach for the software design • Understand different models
- 6. System Models 6 System : A collection of components placed together to perform a task which is beyond components’ individual capability.
- 7. System Models 7 Types of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response • data flow diagram • entity relation diagram • object class/inheritance diagram • State transition diagram • Used to show the principal activities
- 8. System Models :: Data processing Model 8 Data-flow ModelsTypes of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response
- 9. System Models :: Data-flow Models 9 • Used to model the way data is processed in the system • Notation Used: Rounded corner rectangle -> Processing steps Rectangle -> Data Stores Arrows -> Flow of data
- 10. System Models 10 Types of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response
- 11. System Models :: Composition Model 11 Data-flow ModelsTypes of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response
- 12. System Models :: Semantic-data Model 12 • Semantics of data • Identifies entity in a database, their attributes and explicit relationship b/w them Notation Used: <Nam e> <name> An entity Input Cardinality Output Cardinality <name> An entity or Relation attribute
- 13. System Models 13 Types of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response
- 14. System Models :: Classification Model 14 Data-flow ModelsTypes of System Model Process Data-processing Classification Composition Stimulus-response
- 15. System Models :: Object Model 15 • Represent both data and its processing • Combination of some of uses of DFD and SDM Notation Used: <class name> <Attribute> <Service> Object Class
- 16. System Models :: Data Dictionaries 16 • List of name used by the systems, arranged alphabetically. Advantage: mechanism for name management store of organization information which can link analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation Names* -> entities, types, relations, attributes or services
- 17. Software Design 17 What is software design? "all the activities involved in conceptualizing, framing, implementing, commissioning, and ultimately modifying complex systems“ -Wikipedia
- 18. Software Design:: Activities 18 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
- 19. Software Design 19 To put it simply: "the activity following requirements specification and before programming." Design Requirement Specification Programming
- 20. Software Design:: Activities 20 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
- 22. Software Design :: Process 22 What is a process? A series of actions or steps taken to achieve an end. Action 1 Action 2 Action 3 Action 4 Action nPROCESS
- 23. Software Design :: Process 23 Design Activities (Actions): Architectural Design 1 Abstract Specification 2
- 24. Software Design :: Process 24 Interface Design 3 Component Specification 4
- 25. Software Design :: Process 25 Data Structure Design5 Algorithm Design 6
- 26. Software Design :: Process 26 Sub-systems making up the system and their relationships Architectural Design 1
- 27. Software Design :: Process 27 For each sub-system, an abstract specification of the services it provides and the constraints under which it must operate is produced. Abstract Specification 2
- 28. Software Design :: Process 28 Developing a method for two (or more) modules in a system to connect and communicate Interface Design 3
- 29. Software Design :: Process 29 Services are allocated to different components and the interfaces of these components are designed. Component Design 4
- 30. Software Design :: Process 30 The data structures used in the system implementation is designed in detail and specified. Data Structure Design5 *Data Structure : storing and organizing data
- 31. Software Design :: Process 31 A specific method to create a mathematical process in solving problems. Algorithm Design 6 *Algorithm : step-by-step procedure for calculations
- 32. Software Design:: Activities 32 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
- 34. Software Design :: Methods 34 1. Data flow model: data transformations 2. Entity relation model: logical data structures being used 3. Structural model: System components and their interactions are documented 4. Object oriented model: a model of how objects are composed of other objects and, usually, an object use model which shows how objects are used by other objects.
- 35. Software Design:: Activities 35 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
- 37. Software Design :: Description 37 Role: •Basis for detailed implementation •communication medium between designers of sub-systems •Info to system maintainers about the original intentions of the system designers Notations Used: Graphical notations Program description languages Informal text
- 38. Software Design :: Description 38 1. Graphical notations: • Display the relationships between the components making up the design and to relate the design to the real-world system. • Most useful for giving an overall picture of the system. 2. Program description languages: • use control and structuring constructs based on programming language constructs but also allow explanatory text and additional types of statement to be used. • intention of the designer is expressed rather than the details of how the design is to be implemented. 3. Informal text: 1. Information about design rationale or non-functional considerations may be expressed using natural language text. Continue..
- 39. Software Design:: Activities 39 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
- 41. Software Design :: Strategies 41 1. Functional design: • functional viewpoint, starting with a high-level view and progressively refining this into a more detailed design. • Example: Jackson Structured Programming and the Warnier-Orr method 2. Object oriented design: • system is viewed as a collection of objects rather than as functions. • JSD is a design method that falls somewhere between function oriented and object oriented design. *JSD : Jackson System Develpment
- 42. Software Design:: Activities 42 ProcessProcess MethodsMethods DescriptionDescription StrategiesStrategies QualityQuality
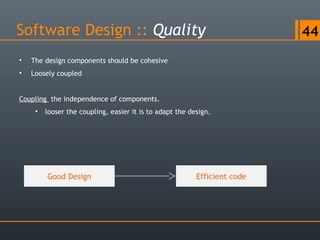
- 44. Software Design :: Quality 44 • The design components should be cohesive • Loosely coupled Coupling the independence of components. • looser the coupling, easier it is to adapt the design. Good Design Efficient code
- 45. Architectural Design 45 What is a it? Initial design process of identifying sub-system and establishing a framework for sub-system control and communication
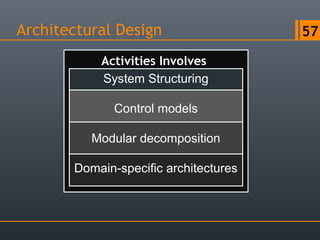
- 46. Architectural Design 46 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 47. Architectural Design :: System Structuring 47 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 48. Architectural Design :: System Structuring 48 • Decompose a system into a set of interacting sub-systems • Notations Used: • Box -> Sub system • Boxes within boxes -> sub-system has been decomposed to sub-systems • Arrow -> direction of data and/or control System structuring Repository model Client-server model Abstract machine model
- 49. Architectural Design :: System Structuring 49 System structuring Repository model Client-server model Abstract machine model • Data is held in a central database • Accessed by all sub-systems Project repository Design editor Code Generator Design analyzer Report Generator Program editor Design translator
- 50. Architectural Design :: System Structuring 50 System structuring Repository model Client-server model Abstract machine model • Distributed sys model • Standalone servers offer service to sub-sys (clients) • A network Network Catalog server Video server Client 1 Picture server Hypertext server Client 2 Client 4Client 3
- 51. Architectural Design :: System Structuring 51 System structuring Repository model Client-server model Abstract machine model • Layered • Layers provide a set of service to layer above • Supports incremental development • Changeable and portable Client 2Client 2Operating system Database Management Object Management Version Management
- 52. Architectural Design 52 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 53. Architectural Design :: Control Models 53 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 54. Architectural Design ::Control models 54 • Control flow b/w sub-system Control models Centralized control Event-based Control
- 55. Architectural Design ::Control models 55 Control models Centralized control Event-based Control • One sub-system designated as the system controller System Controller Computation Process Sensor Processes Actuator Processes Fault Handler Laser Interface
- 56. Architectural Design ::Control models 56 Control models Centralized control Event-based Control • Driven by externally generated events Broadcast models Interrupt-driven models • Broadcast to all, but particular sub-system responds to it • Used in Real time sys • Interrupt handler
- 57. Architectural Design 57 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 58. Architectural Design :: Control Models 58 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 59. Architectural Design ::Modular Decomposition 59 Modular Decomposition Object-oriented design Data-flow models • Sys is decomposed into a set of communicating objects • Sys is decomposed into functional modules • Also called Pipeline Approach
- 60. Architectural Design 60 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
- 61. Architectural Design :: Control Models 61 System Structuring Control models Modular decomposition Domain-specific architectures Activities Involves
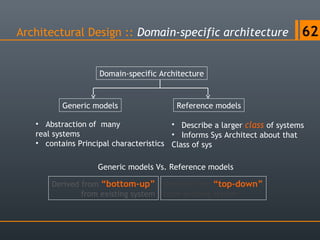
- 62. Architectural Design :: Domain-specific architecture 62 Domain-specific Architecture Generic models Reference models • Abstraction of many real systems • contains Principal characteristics • Describe a larger class of systems • Informs Sys Architect about that Class of sys Generic models Vs. Reference models Derived from “bottom-up” from existing system Derived from “top-down” from existing system
- 63. Summary 63 System Models Software Design Architecture Design
- 64. Thank you for your time. 1