Apache Spark & Hadoop
- 1. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 1 ® © 2014 MapR Technologies Apache Spark Keys Botzum Senior Principal Technologist, MapR Technologies June 2014
- 2. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 2 Agenda • MapReduce • Apache Spark • How Spark Works • Fault Tolerance and Performance • Examples • Spark and More
- 3. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 3 MapR: Best Product, Best Business & Best Customers Top Ranked Exponential Growth 500+ Customers Cloud Leaders 3X bookings Q1 ‘13 – Q1 ‘14 80% of accounts expand 3X 90% software licenses <1% lifetime churn >$1B in incremental revenue generated by 1 customer
- 4. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 4© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Review: MapReduce
- 5. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 5 MapReduce: A Programming Model • MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters (published 2004) • Parallel and Distributed Algorithm: • Data Locality • Fault Tolerance • Linear Scalability
- 6. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 6 MapReduce Basics • Assumes scalable distributed file system that shards data • Map – Loading of the data and defining a set of keys • Reduce – Collects the organized key-based data to process and output • Performance can be tweaked based on known details of your source files and cluster shape (size, total number)
- 7. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 7 MapReduce Processing Model • Define mappers • Shuffling is automatic • Define reducers • For complex work, chain jobs together
- 8. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 8 MapReduce: The Good • Built in fault tolerance • Optimized IO path • Scalable • Developer focuses on Map/Reduce, not infrastructure • simple? API
- 9. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 9 MapReduce: The Bad • Optimized for disk IO – Doesn’t leverage memory well – Iterative algorithms go through disk IO path again and again • Primitive API – Developer’s have to build on very simple abstraction – Key/Value in/out – Even basic things like join require extensive code • Result often many files that need to be combined appropriately
- 10. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 10© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Apache Spark
- 11. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 11 Apache Spark • spark.apache.org • github.com/apache/spark • [email protected] • Originally developed in 2009 in UC Berkeley’s AMP Lab • Fully open sourced in 2010 – now at Apache Software Foundation - Commercial Vendor Developing/Supporting
- 12. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 12 Spark: Easy and Fast Big Data • Easy to Develop – Rich APIs in Java, Scala, Python – Interactive shell • Fast to Run – General execution graphs – In-memory storage 2-5× less code
- 13. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 13 Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD) • Spark revolves around RDDs • Fault-tolerant read only collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel • Cached in memory or on disk http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~matei/papers/2012/nsdi_spark.pdf
- 14. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 14 RDD Operations - Expressive • Transformations – Creation of a new RDD dataset from an existing • map, filter, distinct, union, sample, groupByKey, join, reduce, etc… • Actions – Return a value after running a computation • collect, count, first, takeSample, foreach, etc… Check the documentation for a complete list http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/scala-programming-guide.html#rdd- operations
- 15. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 15 Easy: Clean API • Resilient Distributed Datasets • Collections of objects spread across a cluster, stored in RAM or on Disk • Built through parallel transformations • Automatically rebuilt on failure • Operations • Transformations (e.g. map, filter, groupBy) • Actions (e.g. count, collect, save) Write programs in terms of transformations on distributed datasets
- 16. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 16 Easy: Expressive API • map • reduce
- 17. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 17 Easy: Expressive API • map • filter • groupBy • sort • union • join • leftOuterJoin • rightOuterJoin • reduce • count • fold • reduceByKey • groupByKey • cogroup • cross • zip sample take first partitionBy mapWith pipe save ...
- 18. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 18 Easy: Example – Word Count • Spark• Hadoop MapReduce public static class WordCountMapClass extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word = new Text(); public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { String line = value.toString(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line); while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { word.set(itr.nextToken()); output.collect(word, one); } } } public static class WorkdCountReduce extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { int sum = 0; while (values.hasNext()) { sum += values.next().get(); } output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum)); } } val spark = new SparkContext(master, appName, [sparkHome], [jars]) val file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...") val counts = file.flatMap(line => line.split(" ")) .map(word => (word, 1)) .reduceByKey(_ + _) counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")
- 19. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 19 Easy: Example – Word Count • Spark• Hadoop MapReduce public static class WordCountMapClass extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word = new Text(); public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { String line = value.toString(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line); while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { word.set(itr.nextToken()); output.collect(word, one); } } } public static class WorkdCountReduce extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values, OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { int sum = 0; while (values.hasNext()) { sum += values.next().get(); } output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum)); } } val spark = new SparkContext(master, appName, [sparkHome], [jars]) val file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...") val counts = file.flatMap(line => line.split(" ")) .map(word => (word, 1)) .reduceByKey(_ + _) counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")
- 20. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 20 Easy: Works Well With Hadoop • Data Compatibility • Access your existing Hadoop Data • Use the same data formats • Adheres to data locality for efficient processing • Deployment Models • “Standalone” deployment • YARN-based deployment • Mesos-based deployment • Deploy on existing Hadoop cluster or side-by-side
- 21. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 21 Easy: User-Driven Roadmap • Language support – Improved Python support – SparkR – Java 8 – Integrated Schema and SQL support in Spark’s APIs • Better ML – Sparse Data Support – Model Evaluation Framework – Performance Testing
- 22. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 22 Example: Logistic Regression data = spark.textFile(...).map(readPoint).cache() w = numpy.random.rand(D) for i in range(iterations): gradient = data .map(lambda p: (1 / (1 + exp(-p.y * w.dot(p.x)))) * p.y * p.x) .reduce(lambda x, y: x + y) w -= gradient print “Final w: %s” % w
- 23. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 23 Fast: Logistic Regression Performance 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 1 5 10 20 30 RunningTime(s) Number of Iterations Hadoop Spark 110 s / iteration first iteration 80 s further iterations 1 s
- 24. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 24 Easy: Multi-language Support Python lines = sc.textFile(...) lines.filter(lambda s: “ERROR” in s).count() Scala val lines = sc.textFile(...) lines.filter(x => x.contains(“ERROR”)).count() Java JavaRDD<String> lines = sc.textFile(...); lines.filter(new Function<String, Boolean>() { Boolean call(String s) { return s.contains(“error”); } }).count();
- 25. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 25 Easy: Interactive Shell Scala based shell % /opt/mapr/spark/spark-0.9.1/bin/spark-shell scala> val logs = sc.textFile("hdfs:///user/keys/logdata”)" scala> logs.count()" …" res0: Long = 232681 scala> logs.filter(l => l.contains("ERROR")).count()" …." res1: Long = 205 Python based shell as well - pyspark
- 26. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 26© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Fault Tolerance and Performance
- 27. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 27 Fast: Using RAM, Operator Graphs • In-memory Caching • Data Partitions read from RAM instead of disk • Operator Graphs • Scheduling Optimizations • Fault Tolerance = cached partition = RDD join filter groupBy Stage 3 Stage 1 Stage 2 A: B: C: D: E: F: map
- 28. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 28 Directed Acylic Graph (DAG) • Directed – Only in a single direction • Acyclic – No looping • This supports fault-tolerance
- 29. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 29 Easy: Fault Recovery RDDs track lineage information that can be used to efficiently recompute lost data msgs = textFile.filter(lambda s: s.startsWith(“ERROR”)) .map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) HDFS File Filtered RDD Mapped RDD filter (func = startsWith(…)) map (func = split(...))
- 30. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 30 RDD Persistence / Caching • Variety of storage levels – memory_only (default), memory_and_disk, etc… • API Calls – persist(StorageLevel) – cache() – shorthand for persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY) • Considerations – Read from disk vs. recompute (memory_and_disk) – Total memory storage size (memory_only_ser) – Replicate to second node for faster fault recovery (memory_only_2) • Think about this option if supporting a time sensitive client http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/scala-programming-guide.html#rdd- persistence
- 31. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 31 PageRank Performance 171 80 23 14 0 50 100 150 200 30 60 Iterationtime(s) Number of machines Hadoop Spark
- 32. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 32 Other Iterative Algorithms 0.96 110 0 25 50 75 100 125 Logistic Regression 4.1 155 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 K-Means Clustering Hadoop Spark Time per Iteration (s)
- 33. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 33 Fast: Scaling Down 69 58 41 30 12 0 20 40 60 80 100 Cache disabled 25% 50% 75% Fully cached Execution time (s) % of working set in cache
- 34. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 34 Comparison to Storm • Higher throughput than Storm – Spark Streaming: 670k records/sec/node – Storm: 115k records/sec/node – Commercial systems: 100-500k records/sec/node 0 10 20 30 100 1000 Throughput per node (MB/s) Record Size (bytes) WordCount Spark Storm 0 20 40 60 100 1000 Throughput per node (MB/s) Record Size (bytes) Grep Spark Storm
- 35. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 35© 2014 MapR Technologies ® How Spark Works
- 36. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 36 Working With RDDs
- 37. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 37 Working With RDDs RDD textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 38. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 38 Working With RDDs RDD RDD RDD RDD Transformations linesWithSpark = textFile.filter(lambda line: "Spark” in line)! textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 39. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 39 Working With RDDs RDD RDD RDD RDD Transformations Action Value linesWithSpark = textFile.filter(lambda line: "Spark” in line)! linesWithSpark.count()! 74! ! linesWithSpark.first()! # Apache Spark! textFile = sc.textFile(”SomeFile.txt”)!
- 40. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 40© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Example: Log Mining
- 41. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 41 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns
- 42. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 42 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver
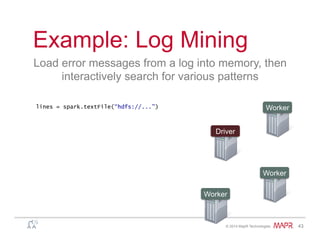
- 43. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 43 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
- 44. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 44 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns Worker Worker Worker Driver lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) Base RDD
- 45. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 45 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) Worker Worker Worker Driver
- 46. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 46 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) Worker Worker Worker Driver Transformed RDD
- 47. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 47 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
- 48. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 48 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Action
- 49. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 49 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker Driver messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3
- 50. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 50 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver tasks tasks tasks
- 51. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 51 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Read HDFS Block Read HDFS Block Read HDFS Block
- 52. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 52 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 Process & Cache Data Process & Cache Data Process & Cache Data
- 53. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 53 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 results results results
- 54. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 54 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Driver Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
- 55. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 55 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() tasks tasks tasks Driver
- 56. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 56 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver Process from Cache Process from Cache Process from Cache
- 57. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 57 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver results results results
- 58. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 58 Example: Log Mining Load error messages from a log into memory, then interactively search for various patterns lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”) errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”)) messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2]) messages.cache() Worker Worker Worker messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count() Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Cache 1 Cache 2 Cache 3 messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count() Driver Cache your data è Faster Results Full-text search of Wikipedia • 60GB on 20 EC2 machines • 0.5 sec from cache vs. 20s for on-disk
- 59. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 59© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Example: Page Rank
- 60. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 60 Example: PageRank • Good example of a more complex algorithm – Multiple stages of map & reduce • Benefits from Spark’s in-memory caching – Multiple iterations over the same data
- 61. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 61 Basic Idea Give pages ranks (scores) based on links to them • Links from many pages è high rank • Link from a high-rank page è high rank Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PageRank-‐hi-‐res-‐2.png
- 62. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 62 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
- 63. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 63 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1 0.5 0.5 0.5 1 0.5
- 64. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 64 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 0.58 1.0 1.85 0.58
- 65. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 65 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 0.58 0.29 0.29 0.5 1.85 0.58 1.0 1.85 0.58 0.5
- 66. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 66 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 0.39 1.72 1.31 0.58 . . .
- 67. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 67 Algorithm 1. Start each page at a rank of 1 2. On each iteration, have page p contribute rankp / |neighborsp| to its neighbors 3. Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 × contribs 0.46 1.37 1.44 0.73 Final state:
- 68. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 68 Scala Implementation val links = // load RDD of (url, neighbors) pairs var ranks = // give each url rank of 1.0 for (i <- 1 to ITERATIONS) { val contribs = links.join(ranks).values.flatMap { case (urls, rank)) => urls.map(dest => (dest, rank/urls.size)) } ranks = contribs.reduceByKey(_ + _) .mapValues(0.15 + 0.85 * _) } ranks.saveAsTextFile(...) https://github.com/apache/spark/blob/master/examples/src/main/scala/org/ apache/spark/examples/SparkPageRank.scala
- 69. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 69© 2014 MapR Technologies ® Spark and More
- 70. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 70 Easy: Unified Platform Spark SQL (SQL) Spark Streaming (Streaming) MLLib (Machine learning) Spark (General execution engine) GraphX (Graph computation) Continued innovation bringing new functionality, e.g.,: • BlinkDB (Approximate Queries) • SparkR (R wrapper for Spark) • Tachyon (off-heap RDD caching)
- 71. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 71 Spark on MapR • Certified Spark Distribution • Fully supported and packaged by MapR in partnership with Databricks – mapr-spark package with Spark, Shark, Spark Streaming today – Spark-python, GraphX and MLLib soon • YARN integration – Spark can then allocate resources from cluster when needed
- 72. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 72 References • Based on slides from Pat McDonough at • Spark web site: http://spark.apache.org/ • Spark on MapR: – http://www.mapr.com/products/apache-spark – http://doc.mapr.com/display/MapR/Installing+Spark +and+Shark
- 73. ® © 2014 MapR Technologies 73 Q&A @mapr maprtech [email protected] Engage with us! MapR maprtech mapr-technologies


















![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 18
Easy: Example – Word Count
• Spark• Hadoop MapReduce
public static class WordCountMapClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class WorkdCountReduce extends MapReduceBase
implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
val spark = new SparkContext(master, appName, [sparkHome], [jars])
val file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...")
val counts = file.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-18-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 19
Easy: Example – Word Count
• Spark• Hadoop MapReduce
public static class WordCountMapClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class WorkdCountReduce extends MapReduceBase
implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
val spark = new SparkContext(master, appName, [sparkHome], [jars])
val file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...")
val counts = file.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-19-320.jpg)









![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 29
Easy: Fault Recovery
RDDs track lineage information that can be used to
efficiently recompute lost data
msgs = textFile.filter(lambda s: s.startsWith(“ERROR”))
.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
HDFS File Filtered RDD Mapped RDD
filter
(func
=
startsWith(…))
map
(func
=
split(...))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-29-320.jpg)
















![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 47
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-47-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 48
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Action](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-48-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 49
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
Driver
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-49-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 50
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Driver
tasks
tasks
tasks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-50-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 51
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Driver
Read
HDFS
Block
Read
HDFS
Block
Read
HDFS
Block](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-51-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 52
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Driver
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
Process
& Cache
Data
Process
& Cache
Data
Process
& Cache
Data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-52-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 53
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Driver
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
results
results
results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-53-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 54
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Driver
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-54-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 55
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
tasks
tasks
tasks
Driver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-55-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 56
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
Process
from
Cache
Process
from
Cache
Process
from
Cache](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-56-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 57
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
results
results
results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-57-320.jpg)
![®
© 2014 MapR Technologies 58
Example: Log Mining
Load error messages from a log into memory, then
interactively search for various patterns
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
Worker
Worker
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Cache 1
Cache 2
Cache 3
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Driver
Cache your data è Faster Results
Full-text search of Wikipedia
• 60GB on 20 EC2 machines
• 0.5 sec from cache vs. 20s for on-disk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-june2014-140711131800-phpapp01/85/Apache-Spark-Hadoop-58-320.jpg)














