Spring One 2 GX 2014 - CACHING WITH SPRING: ADVANCED TOPICS AND BEST PRACTICES
- 1. Caching with Spring: Advanced Topics and Best Practices © 2014 SpringOne 2GX. All rights reserved. Do not distribute without permission. Michael Plöd @bitboss
- 2. I will talk about Caching Types / Topologies Best Practices for Caching in Enterprise Applications Caching with Spring JCache and Spring I will NOT talk about Latency / Synchronization discussion What is the best caching product on the market HTTP / Database Caching Caching in JPA, Hibernate or other ORMs
- 3. Cache! / kæʃ /! In computing, a cache is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. The data that is stored within a cache might be values that have been computed earlier or duplicates of original values that are stored elsewhere. If requested data is contained in the cache (cache hit), this request can be served by simply reading the cache, which is comparatively faster. Otherwise (cache miss), the data has to be recomputed or fetched from its original storage location, which is comparatively slower. Hence, the greater the number of requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the overall system performance becomes. Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_(computing)
- 4. That’s awesome. Let’s cache everything and everywhere and distribute it all in a Cluster in a transactional manner ohhh by the way: Twitter has been doing that for ages Are you crazy?
- 5. Business-Applications != Twitter / Facebook & co.
- 6. Many enterprise grade projects are adapting caching too defensive or too offensive and are running into consistency or performance issues because of that
- 7. But with a well adjusted caching strategy you will make your application more scalable, faster and cheaper to operate.
- 8. Local Cache, Data Grid, Document Store, JPA First Level Cache, JPA Second Level Cache, Types of Places CACHES for Hybrid Cache Database, Heap, HTTP Proxy, Browser, Prozessor, Disk, Off Heap, Persistence- Framework, Application
- 9. We will focus on local and distributed caching at the application level with the Spring Framework
- 10. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 11. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 12. 1 Identify suitable layers for caching
- 13. ComplaintManagementRestController ComplaintManagementBusinessService DataAggrgationManager Host! Commands SAP! Commands Spring Data Repository HTTP Caching Read Operations Read Operations Read Operations Read Operations Read and Write Operations Suitable Layers for Caching
- 14. 2 Stay local as long as possible
- 15. Lokal In-Memory JVM Cache
- 16. Clustered JVM Cache JVM Cache JVM Cache JVM Cache
- 17. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 18. Clustered - with sync JVM JVM JVM JVM Cache Cache Cache Cache
- 19. Clustered - with sync JVM JVM JVM JVM Cache Cache Cache Cache Invalidation Replication
- 20. 3 Avoid real replication where possible
- 21. Invalidation - Option 1 Cache Cache Cache Cache
- 22. Invalidation - Option 1 Cache Cache Cache #1 Cache PUT (Insert) PUT (Insert) #1 #1 PUT (Insert) PUT (Insert) #1
- 23. Invalidation - Option 1 Cache #1 #1 Cache Cache Cache #1 #1
- 24. Invalidation - Option 1 Cache #1 #1 Cache Cache Cache PUT (Update) #1 #1
- 25. Invalidation - Option 1 Cache Cache Cache Cache PUT (Update) #1
- 26. Invalidation - Option 2 Cache Cache Cache Cache
- 27. Invalidation - Option 2 Cache Cache Cache Cache PUT (Insert) #1
- 28. Replication Cache Cache Cache Cache
- 29. Replication Cache Cache Cache #1 Cache #1 #1 #1 PUT (Insert)
- 30. Replication Cache Cache Cache #1 Cache #1 #1 #1
- 31. Replication Cache Cache Cache #1 Cache #1 #1 #1 PUT (Update)
- 32. As of now every cache could potentially hold every data which consumes heap memory
- 33. Big Heap ?
- 34. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 35. 4 Avoid big heaps just for caching
- 36. Big heap leads to long major GCs Cache Application Data 32 GB
- 37. Long GCs can destabilize your cluster JVM Cache JVM Cache JVM Cache JVM Cache
- 38. Small caches are a bad idea! " Many evictions, fewer hits, no „hot data“. This is especially critical for replicating caches.
- 39. 5 Use a distributed cache for big amounts of data
- 40. Distributed Caches JVM JVM JVM JVM Cache Node 1 Cache Node 2 Cache Node 3
- 41. 1 Customer #23 Customer #30 Customer #27 Customer #32
- 42. 1 2 Customer #23 Customer #30 Customer #27 Customer #32 BACKUP #27 BACKUP #32 BACKUP #23 BACKUP #30 Data is being distributed and backed up
- 43. 1 2 3 Customer #23 Customer #30 Customer #27 Customer #32 BACKUP #27 BACKUP #32 BACKUP #23 BACKUP #30
- 44. 1 2 Customer #23 3 4 Customer #30 Customer #27 Customer #32 BACKUP #27 BACKUP #32 BACKUP #23 BACKUP #30
- 45. DEMO Hazelcast
- 46. A distributed cache leads to smaller heaps, more capacity and is easy to scale Application Data Cache 2 - 4 GB … Cache
- 47. 6 The operations specialist is your new best friend
- 48. Clustered caches are complex. Please make sure that operations and networking are involved as early as possible.
- 49. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 50. 7 Make sure that only suitable data gets cached
- 51. The best cache candidates are read-mostly data, which are expensive to obtain
- 52. If you urgently must cache write-intensive data make sure to use a distributed cache and not a replicated or invalidating one
- 53. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 54. 8 Only use existing cache implementations
- 55. NEVER write your own cache implementation EVER
- 56. Infinispan, EHCache, Hazelcast, Couchbase, Memcache, OSCache, SwarmCache, Xtreme Cache, Apache DirectMemory CACHE Implementations Terracotta, Coherence, Gemfire, Cacheonix, WebSphere eXtreme Scale, Oracle 12c In Memory Database
- 57. Which data shall I cache? Which cache shall I use? Where shall I cache? Which impact does it have on my infrastructure How about data-consistency How do I introduce caching? How about caching in Spring?
- 58. 9 Introduce Caching in three steps
- 59. Optimize your application Local Cache Distributed Cache Performance Boost Performance Loss
- 61. Example: Hazelcast putting and getting 10.000 objects locally GET Time PUT Time Payload Size Serializable ? ? ? Data Serializable ? ? ? Identifier Data Serializable ? ? ?
- 63. Example: Hazelcast putting and getting 10.000 objects locally GET Time PUT Time Payload Size Serializable 1287 ms 1220 ms 1164 byte Data Serializable 443 ms 408 ms 916 byte Identifier Data Serializable 264 ms 207 ms 882 byte
- 64. JAVA SERIALIZATION SUCKS for Caching if alternatives are present
- 65. 11 Use Off-Heap Storage for Cache instances with more than 4 GB Heap Size
- 66. Off Heap 30 GB RAM No Garbage Collection JVM Cache Runtime Cache Data 2 GB HEAP Very short Garbage Collections
- 67. 12 Mind the security gap
- 68. Application Security Security Security „CRM“ „Host“ DB Cache CRM Data SAP Data DB Data ? Mind security when reading data from the cache
- 69. I <3 Spring " Bot censored I’m at a Spring conference and this guy is 50 slides in and hasn’t yet mentioned Spring even if he advertised
- 70. 13 Abstract your cache provider
- 71. Tying your code to a cache provider is bad practice public Account retrieveAccount(String accountNumber) {! Cache cache = ehCacheMgr.getCache(„accounts“);! Account account = null;! Element element = cache.get(accountNumber);! if(element == null) {! //execute some business logic for retrieval! //account = result of logic above! cache.put(new Element(accountNumber, account));! } else {! account = (Account)element.getObjectValue();! }! return account;! }
- 72. Try switching from EHCache to Hazelcast public Account retrieveAccount(String accountNumber) {! Cache cache = ehCacheMgr.getCache(„accounts“);! Account account = null;! Element element = cache.get(accountNumber);! if(element == null) {! //execute some business logic for retrieval! //account = result of logic above! cache.put(new Element(accountNumber, account));! } else {! account = (Account)element.getObjectValue();! }! return account;! } You will have to adjust these lines of code to the Hazelcast API
- 73. You can’t switch cache providers between environments public Account retrieveAccount(String accountNumber) {! Cache cache = ehCacheMgr.getCache(„accounts“);! Account account = null;! Element element = cache.get(accountNumber);! if(element == null) {! //execute some business logic for retrieval! //account = result of logic above! cache.put(new Element(accountNumber, account));! } else {! account = (Account)element.getObjectValue();! }! return account;! } EHCache is tightly coupled to your code
- 74. You mess up your business logic with infrastructure public Account retrieveAccount(String accountNumber) {! Cache cache = ehCacheMgr.getCache(„accounts“);! Account account = null;! Element element = cache.get(accountNumber);! if(element == null) {! //execute some business logic for retrieval! //account = result of logic above! cache.put(new Element(accountNumber, account));! } else {! account = (Account)element.getObjectValue();! }! return account;! } This is all caching related code without any business relevance
- 75. Introducing Spring’s cache abstraction <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="ehCacheManager"/>! " <!-- EH Cache local -->! <bean id="ehCacheManager" ! class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"! p:cacheManager-ref="ehcache"/>! ! ! <bean id="ehcache" ! class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean"! ! p:configLocation="/ehcache.xml"/> @Cacheable("Customers")! public Customer getCustomer(String customerNumber) {! ! …! }
- 76. Spring’s Caching Annotations Annotation Description @Cacheable Demarcates cachable methods, can read and write to the cache(s) @CacheEvict Demarcates methods that perform cache eviction, that is methods that act as triggers for removing data from the cache. @CachePut Updates the cache with the annotated method’s return value. Will always execute the method. @Caching Allows multiple nested @Cacheable, @CacheEvict and @CachePut annotations to be used on the same method @CacheConfig Class-level annotation that allows to share the cache names, the custom KeyGenerator, the custom CacheManager and finally the custom CacheResolver. Does not enable caching.
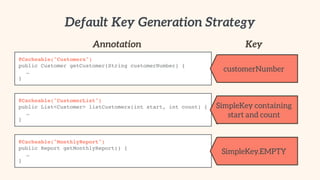
- 77. Default Key Generation Strategy Annotation Key @Cacheable("Customers")! public Customer getCustomer(String customerNumber) {! ! …! } @Cacheable("CustomerList")! public List<Customer> listCustomers(int start, int count) {! ! …! } @Cacheable("MonthlyReport")! public Report getMonthlyReport() {! ! …! } customerNumber SimpleKey containing start and count SimpleKey.EMPTY
- 78. public class MyOwnKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {! @Override! public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {! if (params.length == 0) {! return new SimpleKey("EMPTY");! }! if (params.length == 1) {! Object param = params[0];! if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {! return param;! }! }! return new SimpleKey(params);! }! } You need a custom default KeyGenerator? <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="hazelcastCacheManager" keyGenerator="myOwnKeyGenerator" />
- 79. SpEL in Caching Annotations Annotation Effect @Cacheable("concerts", key="#location.id")! public List<Concert> findConcerts(Location location) @Cacheable("concerts", key="T(someType).hash(#location)")! public List<Concert> findConcerts(Location location) @Cacheable("concerts", condition="#location.city == 'Dallas')", unless="#location.outOfBusiness")! public List<Concert> findConcerts(Location location) Key: id of location @CachePut("locations", key="#result.id")! public Location saveLocation(Location location) Key: hashCode of location Conditional Caching if Location is in Dallas in operating Key: generated id of result
- 80. I have multiple Caches and Cache Managers! @Cacheable("concerts", cacheManager="hazelCastCacheManager")! public List<Concert> findConcerts(Location location) @Cacheable("bands", cacheManager="gemfireCacheManager"))! public List<Band> listBand(int start, int count) @Cacheable("bands", cacheResolver="myOwnCacheResolver"))! public List<Band> listBand(int start, int count) Programmatic resolution through an implementation of the CacheResolver Interface Manual Assignment Manual Assignment
- 81. public class MyOwnCacheResolver extends AbstractCacheResolver {! @Autowired public MyOwnCacheResolver(CacheManager cacheManager) { super(cacheManager); } protected Collection<String> getCacheNames(CacheOperationInvocationContext<?> context) {! return getCacheNames(context.getTarget().getClass());! }! " private getCacheNames(Class<?> businessServiceClass) { ... }! } Working with CacheResolvers @Cacheable("bands", cacheResolver="myOwnCacheResolver"))! public List<Band> listBand(int start, int count)
- 82. You can use your own custom Annotations @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)! @Target({ElementType.METHOD})! @Cacheable("concerts", key="id")! public @interface DefaultConcertCacheable {! } @DefaultConcertCacheable! public Concert getConcert(Long id)
- 83. Spring 4.x is the first commerically supported container with JCache (JSR-107) Support! That’s years ahead of any JEE Server
- 84. Spring vs JCache Annotations Spring JCache Description @Cacheable @CacheResult Similar, but @CacheResult can cache Exceptions and force method execution @CacheEvict @CacheRemove Similar, but @CacheRemove supports eviction in the case of Exceptions @CacheEvict (removeAll=true) @CacheRemoveAll Same rules as for @CacheEvict vs @CacheRemove @CachePut @CachePut Different semantic: cache content must be annotated with @CacheValue. JCache brings Exception caching and caching before or after method execution @CacheConfig @CachePut Identical
- 85. Except for the dependencies JCache API and spring-context-support no further steps need to be taken to enable JCache Annotations in Spring Applications
- 86. ? Your Cache Provider has no integration for Spring or JCache
- 87. Code Walkthrough CacheManager & Cache API
- 88. How do I disable caching for Unit Tests? <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.CompositeCacheManager">! <property name="cacheManagers">! <list>! <ref bean="guavaCache"/>! <ref bean="ehCache"/>! </list>! </property>! <property name="fallbackToNoOpCache" value="true"/>! </bean>
- 89. Thank you! 82 Michael Plöd - Freelance Consultant https://github.com/mploed @bitboss http://slideshare.net/mploed













































































![public class MyOwnKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {!
@Override!
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {!
if (params.length == 0) {!
return new SimpleKey("EMPTY");!
}!
if (params.length == 1) {!
Object param = params[0];!
if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {!
return param;!
}!
}!
return new SimpleKey(params);!
}!
}
You need a custom default KeyGenerator?
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="hazelcastCacheManager"
keyGenerator="myOwnKeyGenerator" />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springone2gxcachingwithspring-140910132219-phpapp02/85/Spring-One-2-GX-2014-CACHING-WITH-SPRING-ADVANCED-TOPICS-AND-BEST-PRACTICES-78-320.jpg)










