structure and union from c programming language.ppt
- 2. Objective Definition of Structure Declaring structure variable Accessing Structure members Structure initialization Array of structure Array within structure Structure within structure Union Union vs. Structure
- 3. Definition of structure 1. A collection of variables that are functionally related to each other. 2. Each variable that is a member of the structure has a specific type. 3. Different members of the structure may have either the same or different types. Cf. the elements of an array, which must all be of one type. 4. A structure is a derived data type, constructed from two or more objects of one or more individual types. 5. The entire structure may bear a name. 6. Each member of the structure must [also] have a name. 7. The scope of the name of a structure member is limited to the structure itself and also to any variable declared to be of the structure's type.
- 4. Continue… 8. THEREFORE, different structures may contain members having the same name; these may be of the same or of different types. 9. A self-referential structure contains a member which is a pointer to the same structure type. 10. Declaration of the structure merely defines the new data type; space is NOT reserved in memory as a result of the declaration. (However, declaration of the structure does define how much memory is needed to store each variable subsequently declared to be of the type of the defined structure.)
- 5. Example Struct book { char name; float price; int page; }; name price page Memory representation name price page Char float int
- 6. Structure declaration -1 struct nameOfThisStructureType { typeOfFirstMember nameOfFirstMember; typeOfSecondMember nameOfSecondMember; typeOfThirdMember nameOfThirdMember; . . . }; Struct nameOfThisStructureType variable1OfThisStructureType, variable2ofThisStructureType, … ; Example Struct book { char name; float price; int page; }; Struct book b1,b2,b3;
- 7. Structure declaration -2 struct nameOfThisStructureType { typeOfFirstMember nameOfFirstMember; typeOfSecondMember nameOfSecondMember; typeOfThirdMember nameOfThirdMember; . . . } variable1OfThisStructureType, variable2OfThisStructureType, . . .; Example Struct book { char name; float price; int page; } b1,b2,b3;
- 8. Structure declaration -3 struct /* NO NAME ASSIGNED TO THE TYPE */ { typeOfFirstMember nameOfFirstMember; typeOfSecondMember nameOfSecondMember; typeOfThirdMember nameOfThirdMember; . . . } variable1OfThisStructureType, variable2OfThisStructureType, . . .; Example Struct { char name; float price; int page; } b1,b2,b3;
- 9. Accessing Structure members To access structure members we have to (.)operator. variable1OfTheStructureType.nameOfTheMember Example b1.page b2.price
- 10. Structure initialization A structure can be initialize by the following way, Watch this example. Example struct book { char name; float price; int pages; }; struct book b1={‘B’, 130.00, 550 }; //structure initialization
- 11. Simple structure program #include<stdio.h> void main() { struct book { char name; float price; int pages; }; struct book b1={‘B’, 130.00, 550 }; printf(“n book name is:%c”,b1.name); printf(“n book price is: %f”,b1.price); printf(“n book pages are: %d”,b1.pages); }
- 12. Array of structure Array of structure is possible in c language. If you declare a array of structure then the variables of the structure type will be stored in continuous memory locations. An example of declaring an array of structure is given below. struct book { char name; float price; int pages; }; struct book b[100]; //declaration of array of structure
- 13. Sample program of array of structure #include<stdio.h> void main() { struct book { char name; float price; int pages; }; struct book b[100]; int i; for(i=0;i<=99;i++) { printf(“n Enter name, price and pages”); scanf(“%c %f %d”, &b [i].name,&b[i].price,&b[i].pages); } for(i=0;i<=99;i++) printf(“n %c %f %d”, b[i].name,b[i].price,b[i].pages); }
- 14. Array within structure Array can exist as a member of structure. A simple example is given below. struct book { char name[100]; //Array within structure float price; int pages; }; struct book b1;
- 15. Structure within structure A structure itself can be member of another structure. This is given in the following example. Struct employee { char name[100]; char department[20]; struct { int dearness; int house_rent; int city; }allowance; }emp1,emp2,emp3;
- 16. Union What is union? 1. Like a structure, a union is also a derived data type. 2. The members of a union share a single storage space. 3. Only ONE member of each union can be referenced t a time. 4. Amount of space allocated for storage is the amount needed for the largest member of the union.
- 17. Example of union union book { char name; float price; int pages; }; This will take memory space of 4 bytes, since price(datatype is float which is of 4 bytes) is the largest member in this union. This 4 byte is shared by all the members in the union. Only 1 member of this union can be referenced at a time
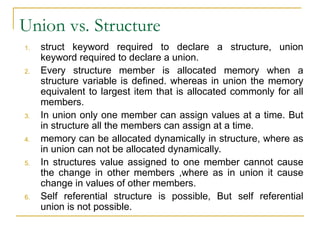
- 18. Union vs. Structure 1. struct keyword required to declare a structure, union keyword required to declare a union. 2. Every structure member is allocated memory when a structure variable is defined. whereas in union the memory equivalent to largest item that is allocated commonly for all members. 3. In union only one member can assign values at a time. But in structure all the members can assign at a time. 4. memory can be allocated dynamically in structure, where as in union can not be allocated dynamically. 5. In structures value assigned to one member cannot cause the change in other members ,where as in union it cause change in values of other members. 6. Self referential structure is possible, But self referential union is not possible.
- 19. Thank You END


![Definition of structure
1. A collection of variables that are functionally related to each
other.
2. Each variable that is a member of the structure has a specific
type.
3. Different members of the structure may have either the same
or different types. Cf. the elements of an array, which must all
be of one type.
4. A structure is a derived data type, constructed from two or
more objects of one or more individual types.
5. The entire structure may bear a name.
6. Each member of the structure must [also] have a name.
7. The scope of the name of a structure member is limited to the
structure itself and also to any variable declared to be of the
structure's type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion-241207181837-97d7ae44/85/structure-and-union-from-c-programming-language-ppt-3-320.jpg)








![Array of structure
Array of structure is possible in c language. If
you declare a array of structure then the
variables of the structure type will be stored in
continuous memory locations. An example of
declaring an array of structure is given below.
struct book
{
char name;
float price;
int pages;
};
struct book b[100]; //declaration of array of structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion-241207181837-97d7ae44/85/structure-and-union-from-c-programming-language-ppt-12-320.jpg)
![Sample program of array of structure
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
struct book
{
char name;
float price;
int pages;
};
struct book b[100];
int i;
for(i=0;i<=99;i++)
{
printf(“n Enter name, price and pages”);
scanf(“%c %f %d”, &b [i].name,&b[i].price,&b[i].pages);
}
for(i=0;i<=99;i++)
printf(“n %c %f %d”, b[i].name,b[i].price,b[i].pages);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion-241207181837-97d7ae44/85/structure-and-union-from-c-programming-language-ppt-13-320.jpg)
![Array within structure
Array can exist as a member of structure. A
simple example is given below.
struct book
{
char name[100]; //Array within structure
float price;
int pages;
};
struct book b1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion-241207181837-97d7ae44/85/structure-and-union-from-c-programming-language-ppt-14-320.jpg)
![Structure within structure
A structure itself can be member of another structure.
This is given in the following example.
Struct employee
{
char name[100];
char department[20];
struct
{
int dearness;
int house_rent;
int city;
}allowance;
}emp1,emp2,emp3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandunion-241207181837-97d7ae44/85/structure-and-union-from-c-programming-language-ppt-15-320.jpg)