Structured data type
- 2. ARRAY An array is collection of variable of same datatype that are referenced by a common name. Types of arrays- 1) SINGLE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS. 2) TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS.
- 3. SINGLE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS The simplest form of an array is a single dimentional array. The array is given a name and its elements are referred to by their subscripts or indices. C++ array’s index numbering starts with 0.
- 4. BASE DATATYPE The data type of array elements is known as the base type of the array. type array-name[size]; The above statement declared array marks has 50 elements, marks[0] to marks[49].
- 5. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> void main() { const int size = 50; float marks[size]; for(int i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<“Enter marks of students”<<i+1<<“n”; cin>>marks[i]; } cout<<n”; for(i=0; i<size; i++) cout<<“marks[“<<i<<“]=“<<marks[i]<<“n”; return 0; }
- 6. OUTPUT- Enter marks of student1 89 Enter marks of student2 98 Enter marks of student3 88 Marks[0] = 89 Marks[1] = 98 Marks[2] = 88
- 7. MEMORY REPRESENTATION OF SINGLE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Single dimension arrays are essentially lists of same information of the same type and their elements are stored in contiguous memory location in their index order. For example, an array grade of type char with 8 declared as char grade[8]; will have element grade[0] at 1st allocated memory location, grade[1] at the next, and so forth.
- 8. Since grade is a char type array, each element size of 1 byte(a character size is 1 byte) and it will be represented in the memory as shown below- GRADE ADDRESS 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 *An 8 element character array beginning at location 2000 . Total bytes = size of base datatype * no. of elements Grade [0] Grade [1] Grade [2] Grade[ 3] Grade [4] Grade [5] Grade [6] Grade [7]
- 9. ARRAY TRAVERSAL Traversal- Accessing each element of array. Example- #include<iostream.h> Void main() { float PER[10]; int c; for(c=0; c<10; c++) { cout<<“Enter percentage of student”<<c+1; cin>>PER[c]; } cout<<endl<<“Contents of array”<<endl; for(c=0; c<10; ++c) { cout<<“Percentage of student”<<c+1<<“=“<<PER[c]<<endl; } }
- 10. SEARCHING FOR AN ELEMENT IN A 1-D ARRAY Sometimes we need to search an element in an array. This can be only done by comparing the search-item with each and every element of the array. This process for searching for an element in an array is called linear search.
- 11. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> void main() { const int maxsize = 10; int ARR[maxsize],srch,ndx,found=0; cout<<endl<<“Enter array values”<<endl; for(int c=0; c<maxsize; ++c) cin>>ARR[c]; cout<<“Enter the value to be searched”; cin>>srch; for(c=0; c<maxsize; ++c) { if(ARR[c]==srch) { found=1; ndx=c; break; } } if(found==1) cout<<“First occurance is at index”<<ndx; else Cout<<“Value not found in the array”; }
- 12. CHARACTER ARRAY-STRINGS C++ stores sequence of characters I,e string into character arrays. In character arrays arrays C++ puts a special character after the last character within the string to mark the end of string. The special character is known as null character or 0. For reading spaces within a string gets() or getline() methods should be used and for reading one word only cin can be used.
- 13. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<ctype.h> void main() { char st[50]; int c; cout<<“Enter a string of characters”; gets(st); for(c=0; st[c]!=‘0’; c++) { if(c%2==0) st[c]=toupper(st[c]); else st[c]=tolower(st[c]); } cout<<“Converted string = “<<st; }
- 14. 2 DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS A 2-D array is an array in which each element is itself an array. For instance, an array A[m][n] is an M by N table with M rows and N columns containing M*N elements. No. of elements in 2-D array = No. of rows * No. of columns The simplest form of a multi dimensioned array is 2- D arrays, is an array having single dimensioned array as its elements. The general form of the 2-D array declaration is type array-name[rows][columns]
- 15. PROCESSING 2-D ARRAYS To read or process a 2-D array, you need to use nested loops. One loop processes the rows and other the columns. If outer loop is for rows and inner loop is for columns, then for each row index, all columns are processed and then the same process is repeated for next row index.
- 16. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> void main() { float marks[4][3],sum,avg; char grade[4]; int i,j; for(i=0; i<4; i++) { sum = avg = 0; cout<<“Enter 3 scores of student”<<i+1<<“:”; for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>marks[i][j]; sum+=marks[i][j]; } avg = sum3; if(avg<45.0) grade[i] = ‘D’; else if(avg<60.0) grade[i] = ‘C’; else if(avg<75.0) grade[i] = ‘B’; else grade[i] = ‘A’; } for(i=0; i<4; i++) { cout<<“student”<<i+1<<“tTotal Marks = “; cout<<marks[i][0] + marks[i][2] cout<<“tGrade=“<<grade[i]<<“n”; } return 0; }
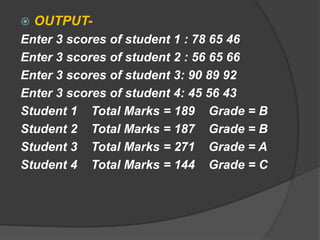
- 17. OUTPUT- Enter 3 scores of student 1 : 78 65 46 Enter 3 scores of student 2 : 56 65 66 Enter 3 scores of student 3: 90 89 92 Enter 3 scores of student 4: 45 56 43 Student 1 Total Marks = 189 Grade = B Student 2 Total Marks = 187 Grade = B Student 3 Total Marks = 271 Grade = A Student 4 Total Marks = 144 Grade = C
- 18. MEMORY REPRESENTATION OF 2 DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Two dimensional arrays are stored in a row- column matrix, where the first index indicates the row and second indicates the column. This means the second index changes faster than the first index when accessing the elements in the array in the order in which they are actually stored in memory.
- 19. 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 *A two dimensional array pay[5][7] in memory. Total bytes=no. of rows*no. of columns*size of base data type. Pay[2][3] Pay[3][1]
- 20. MATRICES AS 2-D ARRAYS Matrix is a useful concept of mathematics. A matrix is a set of mn numbers arranged in the form of a rectangular array of m rows and n columns. Such a matrix is called m*n(m by n) matrix. Matrices can be represented through 2- D arrays.
- 21. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> void main() { int A[3][3],B[3][3],r,c; //Read values in matrices cout<<“Enter first matrix row wisen”; for(r=0;r<3;r++) { for(c=0;c<3;c++) { cin>>B[r][c]; } } int flag=0; //loop to check equality for(r=0;r<3;r++) { for(c=0;c<3;c++) { if(A[r][c]!=B[r][c]) { flag=1; break; } if(flag==1) break; } if(flag!=0) cout<<“Matrices are unequaln”; else cout<<“Matrices are equaln”; return 0; }
- 22. OUTPUT- Enter first matrix row wise 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Enter second matrix row wise 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Matrices are equal
- 23. ARRAY INITIALIZATION C++ provides the facility of array initialization at the time of declaration. The arrays are initialized in the same way as other variables are. The general form of array initialization is Type array-name[size1]……[size N]={value-list}; Following code initializes an integer array with 12 elements: int days of month[12]={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
- 24. CALLING FUNCTIONS WITH ARRAYS When an arrays argument is passed to a function, C++, in most contexts treats the name of an array as if it were a pointer i,e., memory address of some element. That, if age is an int array to hold 10 integers then age stores the address of age[0], the first element of an array i,e., the array name age is a pointer to an integer which is the first element of an array age[10].
- 25. EXAMPLE- #include<iostream.h> void main() { float large(float arr[],intn); //Function prototype char ch; int i; float amount[50],big; for(i=0;i<50;i++) { cout<<“nEnter element no”<<i+1<<“n”; cin>>amount[i]; cout<<“nWant to enter more?(y/n)n”; cin>>ch; if(ch!=‘y’) break; } if(i<50) i++; //In case of incomplete loop big=large(amount,i); //Call function large() by passing the array and its number of elements cout<<“nThe largest element of the array is :”<<big<<“n”; return 0; } float large(float arr[],int n) { if(arr[j]>max) max=arr[j]; } return(max); }
- 26. EXAMPLE- Enter element no. 2 5 Want to enter more?(y/n) y Enter element no. 3 33 Want to enter more?(y/n) y Enter element no. 4 13 Want to enter more?(y/n) n The largest element of the array is :33
- 27. THANK YOU




![BASE DATATYPE
The data type of array elements is
known as the base type of the
array.
type array-name[size];
The above statement declared
array marks has 50 elements,
marks[0] to marks[49].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-4-320.jpg)
![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
const int size = 50;
float marks[size];
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
{
cout<<“Enter marks of students”<<i+1<<“n”;
cin>>marks[i];
}
cout<<n”;
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
cout<<“marks[“<<i<<“]=“<<marks[i]<<“n”;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-5-320.jpg)
![ OUTPUT-
Enter marks of student1
89
Enter marks of student2
98
Enter marks of student3
88
Marks[0] = 89
Marks[1] = 98
Marks[2] = 88](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-6-320.jpg)
![MEMORY
REPRESENTATION OF
SINGLE DIMENSIONAL
ARRAYS Single dimension arrays are essentially lists of
same information of the same type and their
elements are stored in contiguous memory
location in their index order.
For example, an array grade of type char with 8
declared as
char grade[8];
will have element grade[0] at 1st allocated
memory location, grade[1] at the next, and so
forth.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-7-320.jpg)
![Since grade is a char type array, each
element size of 1 byte(a character size is 1 byte)
and it will be represented in the memory as shown
below-
GRADE
ADDRESS 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
*An 8 element character array beginning at
location 2000 .
Total bytes = size of base datatype * no. of elements
Grade
[0]
Grade
[1]
Grade
[2]
Grade[
3]
Grade
[4]
Grade
[5]
Grade
[6]
Grade
[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-8-320.jpg)
![ARRAY
TRAVERSAL Traversal- Accessing each element of array.
Example-
#include<iostream.h>
Void main()
{
float PER[10];
int c;
for(c=0; c<10; c++)
{
cout<<“Enter percentage of student”<<c+1;
cin>>PER[c];
}
cout<<endl<<“Contents of array”<<endl;
for(c=0; c<10; ++c)
{
cout<<“Percentage of student”<<c+1<<“=“<<PER[c]<<endl;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-9-320.jpg)

![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
const int maxsize = 10;
int ARR[maxsize],srch,ndx,found=0;
cout<<endl<<“Enter array values”<<endl;
for(int c=0; c<maxsize; ++c)
cin>>ARR[c];
cout<<“Enter the value to be searched”;
cin>>srch;
for(c=0; c<maxsize; ++c)
{
if(ARR[c]==srch)
{
found=1;
ndx=c;
break;
}
}
if(found==1)
cout<<“First occurance is at index”<<ndx;
else
Cout<<“Value not found in the array”;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-11-320.jpg)

![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void main()
{
char st[50];
int c;
cout<<“Enter a string of characters”;
gets(st);
for(c=0; st[c]!=‘0’; c++)
{
if(c%2==0)
st[c]=toupper(st[c]);
else
st[c]=tolower(st[c]);
}
cout<<“Converted string = “<<st;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-13-320.jpg)
![2 DIMENSIONAL
ARRAYS
A 2-D array is an array in which each element is
itself an array.
For instance, an array A[m][n] is an M by N table
with M rows and N columns containing M*N
elements.
No. of elements in 2-D array = No. of rows * No. of
columns
The simplest form of a multi dimensioned array is 2-
D arrays, is an array having single dimensioned
array as its elements.
The general form of the 2-D array declaration is
type array-name[rows][columns]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-14-320.jpg)

![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
float marks[4][3],sum,avg;
char grade[4];
int i,j;
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
sum = avg = 0;
cout<<“Enter 3 scores of student”<<i+1<<“:”;
for(j=0; j<3; j++)
{
cin>>marks[i][j];
sum+=marks[i][j];
}
avg = sum3;
if(avg<45.0)
grade[i] = ‘D’;
else if(avg<60.0)
grade[i] = ‘C’;
else if(avg<75.0)
grade[i] = ‘B’;
else
grade[i] = ‘A’;
}
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{ cout<<“student”<<i+1<<“tTotal Marks = “;
cout<<marks[i][0] + marks[i][2]
cout<<“tGrade=“<<grade[i]<<“n”;
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-16-320.jpg)

![0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
*A two dimensional array pay[5][7] in
memory.
Total bytes=no. of rows*no. of
columns*size of base data type.
Pay[2][3]
Pay[3][1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-19-320.jpg)

![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
int A[3][3],B[3][3],r,c; //Read values in matrices
cout<<“Enter first matrix row wisen”;
for(r=0;r<3;r++)
{ for(c=0;c<3;c++)
{ cin>>B[r][c];
}
}
int flag=0; //loop to check equality
for(r=0;r<3;r++)
{
for(c=0;c<3;c++)
{ if(A[r][c]!=B[r][c])
{ flag=1; break;
}
if(flag==1) break;
}
if(flag!=0)
cout<<“Matrices are unequaln”;
else
cout<<“Matrices are equaln”;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-21-320.jpg)

![ARRAY
INITIALIZATION
C++ provides the facility of array initialization at
the time of declaration.
The arrays are initialized in the same way as other
variables are.
The general form of array initialization is
Type array-name[size1]……[size N]={value-list};
Following code initializes an integer array with 12
elements:
int days of month[12]={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-23-320.jpg)
![CALLING
FUNCTIONS WITH
ARRAYS When an arrays argument is passed to a
function, C++, in most contexts treats the
name of an array as if it were a pointer i,e.,
memory address of some element.
That, if age is an int array to hold 10
integers then age stores the address of
age[0], the first element of an array i,e., the
array name age is a pointer to an integer
which is the first element of an array
age[10].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-24-320.jpg)
![ EXAMPLE-
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
float large(float arr[],intn); //Function prototype
char ch;
int i;
float amount[50],big;
for(i=0;i<50;i++)
{
cout<<“nEnter element no”<<i+1<<“n”;
cin>>amount[i];
cout<<“nWant to enter more?(y/n)n”;
cin>>ch;
if(ch!=‘y’)
break;
}
if(i<50)
i++; //In case of incomplete loop
big=large(amount,i); //Call function large() by passing the array and its number of elements
cout<<“nThe largest element of the array is :”<<big<<“n”;
return 0;
}
float large(float arr[],int n)
{
if(arr[j]>max)
max=arr[j];
}
return(max);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureddatatype-150917134329-lva1-app6891/85/Structured-data-type-25-320.jpg)

