Synapseindia mobile apps cellular networks and mobile computing part1
- 1. Cellular Networks and Mobile Computing COMS 6998-11, Fall 2012 1
- 2. Syllabus • Mobile App Development (lecture 2,3) – Mobile operating systems: iOS and Android – Development environments: Xcode, Eclipse with Android SDK – Programming: Objective-C and android programming • System Support for Mobile App Optimization (lecture 4,7) – Mobile device power models, energy profiling and ebug debugging – Core OS topics: virtualization, storage and OS support for power and context management • Interaction with Cellular Networks (lecture 1,5, 8) – Basics of 3G/LTE cellular networks – Mobile application cellular radio resource usage profiling – Measurement-based cellular network and traffic characterization • Interaction with the Cloud (lecture 6,9) – Mobile cloud computing platform services: push notification, iCloud and Google Cloud Messaging – Mobile cloud computing architecture and programming models • Mobile Platform Security and Privacy (lecture 10,11,12) – Mobile platform security: malware detection and characterization, attacks and defenses – Mobile data and location privacy: attacks, monitoring tools and defenses 2
- 3. Mobile App Development: iOS • iOS Overview • Objective C • Xcode • Model-View-Controller • Blocks and Multithreading • Core Data and Location • iCloud 3
- 4. Mobile App Development: Android • Android OS Overview • Eclipse and Android SDK • Application Framework – Activity, content provider, broadcast receiver, intent • Networking • Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) 4
- 5. System Support for Mobile App Optimization • Mobile device power models, energy profiler and ebug debugging • Core OS topics: – Virtualization – Storage 5
- 6. System Calls As Power Triggers Key observation: System call is the interface through which an application communicates with the underlying system (hardware) and outside world (Internet, GPS, etc.) Key Idea: Use System Calls as triggers in power modeling Advantages: – Encapsulates utilization based triggers • Parameters of system calls – Captures power behavior of ones that do not necessarily imply utilization – Can be traced back to process, thread, function • Eases energy accounting 6
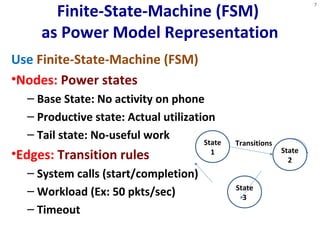
- 7. Finite-State-Machine (FSM) as Power Model Representation Use Finite-State-Machine (FSM) •Nodes: Power states – Base State: No activity on phone – Productive state: Actual utilization – Tail state: No-useful work •Edges: Transition rules – System calls (start/completion) – Workload (Ex: 50 pkts/sec) – Timeout 7 State 1 State 2 Transitions State 3
- 8. Virtualization: Device Namespace Linux Kernel VP 1 VP 2 VP 3 Power WiFi Cell Radio Framebuffer GPU RTC / Alarms ••• Sensors Input Android... Audio/Video ••• safely, correctly multiplex access to devices device namespaces 8
- 9. How Apps Use Storage? • Exactly what makes web browsing slow on Android? – Key lies in understanding how apps use SQLite and FS interface / data/data/com.necla.webvi ew lib (empty) cache webviewCac he 6aaa3f00, 03051d8d, … databases many files (5.5MB) webview.db (14KB) webviewCache.db (129KB) These files written to SQLite in sync These files written to FS in write-behind WebBench Storage Schema Apps typically store some data in FS (e.g., cache files) and some in a SQLite database (e.g., cache map) – All data through SQLite is written synchronously slow! – Apps often use SQLite oblivious to performance effects 9
- 10. Interaction with Cellular Networks • Basics of 3G/LTE cellular networks • Impact of radio access network on mobile apps – Radio resource usage profiling (ARO) • Impact of cellular network core on mobile applications – In-depth study of middleboxes in cellular networks – Cellular network architecture characterization and Implication to CDN 10
- 11. eNodeB 1 Cellular Core Network eNodeB 3 S-GW 2 P-GW 11 S-GW 1 eNodeB 2 Internet and Other IP Networks GTP Tunnels UE 1 UE 2 LTE Infrastructure MME/PCRF/HSS • UE: user equipment • eNodeB: base station • S-GW: serving gateway • P-GW: packet data network gateway • MME: mobility management entity • HSS: home subscriber server • PCRF: policy charging and rule function
- 12. 12 LTE Architecture (Cont’d) • eNodeB, S-GW and P-GW are involved in session setup, handoff, routing Control Plane Data Plane User Equipme nt (UE) Gateway BBaassee SSeerrvviningg PPaacckkeett D Daattaa (S-GW) Mobility Management Entity (MME) Network Gateway (P-GW) Home Subscriber Server (HSS) Policy Control and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) Station (eNodeB)
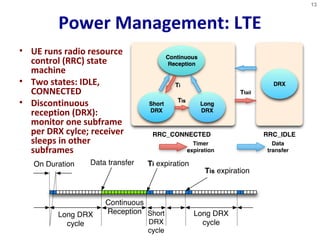
- 13. Power Management: LTE • UE runs radio resource control (RRC) state machine • Two states: IDLE, CONNECTED • Discontinuous reception (DRX): monitor one subframe per DRX cylce; receiver sleeps in other subframes 13
- 14. Power Management: UMTS • State promotions have promotion delay • State demotions incur tail times Tail Time Delay: 2s Delay: 1.5s Tail Time Channel Radio Power IDLE Not allocated Almost zero CELL_FACH Shared, Low Speed Low CELL_DCH Dedicated, High Speed High 14
- 15. Example: RRC State Machine for a Large Commercial 3G Network DCH Tail: 5 sec Promo Delay: 2 Sec FACH Tail: 12 sec Tail Time Waiting inactivity timers to expire DCH: High Power State (high throughput and power consumption) FACH: Low Power State (low throughput and power consumption) IDLE: No radio resource allocated 15
- 16. ARO: Mobile Application Resource Optimizer • Motivations: – Are developers aware of the RRC state machine and its implications on radio resource / energy? NO. – Do they need a tool for automatically profiling their prototype applications? YES. – If we provide that visibility, would developers optimize their applications and reduce the network impact? Hopefully YES. • ARO: Mobile Application Resource Optimizer – Provide visibility of radio resource and energy utilization. – Benchmark efficiencies of cellular radio resource and battery life for a specific application 16
- 17. RRC State Machine Inference • State promotion inference – Determine one of the two promotion procedures – P1: IDLEFACHDCH;P2:IDLEDCH A packet of min bytes never triggers FACHDCH promotion (we use 28B) A packet of max bytes always triggers FACHDCH promotion (we use 1KB) • State demotion and inactivity time inference – See paper for details P1: IDLEFACH, P2:IDLEDCH P1: FACHDCH, P2:Keep on DCH Normal RTT < 300ms RTT w/ Promo > 1500ms 17
- 18. ARO System Architecture 18
Editor's Notes
- #12: Verizon claims that, at its current rate of traffic growth, which is roughly doubling each year, it will reach the capacity thresholds on both its 3G EV-DO and LTE networks beginning in some markets by the end of 2013, and across its entire network by the end of 2015. Unless it can get new spectrum — i.e., the cable operators’ 20 MHz of AWS spectrum — its customers’ connection speeds and service quality will start suffering.
- #15: State machine – the standard for all UMTS carriers – transitions & paras can change