System Programming :: Assembler
- 1. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I Introduction SPOS By
- 3. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I Course Outcome SPOS To analyze & synthesize various system software & understand the design of two pass assemblers.
- 4. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I Outline SPOS Introduction Software Assemblers
- 5. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS instruct Component System is Collection of eg. College Programming is Way to compute the Various Task To perform system programming is an art of designing and implementing system Programs. System introduction
- 6. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I System introduction SPOS Software Collection is of Many Programs Software System Software Application Software assist general user application Operating System Assembler software developed for the specific goal Media player Adobe Reader
- 7. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS System Program Required Effective Execution General user Programs Computer System are for of on System Programming designing and implementing system programs Is an art of System introduction
- 8. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I System Software SPOS Text Editor Editor Computer Program A user create and revise a document Text Editor Program Primary Elements Edited Character String is In which being are is That allows to Notepad Example
- 9. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Text Editor program Used for is Editing plain text files With the help Text Editor of Write Your Program You can C | Java Prog. Example System Software
- 10. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS System Software Loders Program Object Code As input is That takes Prepares and Execution Them for Initiates it Execution
- 11. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Relocation Linking Allocation Loading Functions
- 12. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Allocation Functions Loader allocates space for programs in main memory.
- 13. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Relocation Functions ● Adjusting all address dependent location. ● E.g. If we have two Programs Program A and Program B. ● Program A is saved at location 100. ● And user wants to save Program B on same location. That is physically not possible. ● So loader relocates program B to some another free location
- 14. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Linking Functions ● If we have different modules of our program. ● Loader links object modules with each other.
- 15. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Loading Functions Physically loading the machine instructions and data into main memory.
- 17. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Outline ❏ Review of previous session ❏ Assembler ❏ Macro Processor ❏ Compiler ❏ Debugger ❏ Assembly Language
- 18. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Loders System Software Relocation Linking Allocation Loading Functions
- 19. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembler Machine Lang. Assembly Lang. Program Assembler Translate
- 20. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Macro Processor Macro Sequence Source Lang. Code Referred many times Allows of Defined @ once To be
- 21. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Macro Macro Processor Syntax Macro name [ set of parameters ] // macro body Mend ★ A macro processor takes a source with macro definition and macro calls and replaces each macro call with its body
- 22. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Compiler Low Level Lang. High Level Lang. Compiler Converts
- 23. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Compiler Benefits of writing a program in a high level language Increases productivity Machine Independence It is very easy to write a program in a high level language A program written in a high level language is machine independent.
- 24. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Debugger Debugging tool helps programmer for testing and debugging programs It provides some facilities: •Setting breakpoints. •Displaying values of variables.
- 25. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language ● Assembly language is middle level language. ● An assembly language is machine dependent. ● It differs from computer to computer. ● Writing programs in assembly language is very easy as compared to machine(binary) language
- 27. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Assembly language programming Terms Location Counter points to the next instruction (LC) Literals Constant Values
- 28. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Assembly language programming Terms Symbols Name of variables and labels Procedures Methods | Function
- 29. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Assembly language Statements: Imperative Statements Declarative/Declaration Statements Assembler Directive
- 30. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Imperative Statements ❏ Imperative means mnemonics ❏ These are executable statements. ❏ Each imperative statement indicates an action to be taken during execution of the program
- 31. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Declarative/Declaration Statements ❏ Declaration statements are for reserving memory for variables. ❏ We can specify the initial value of a variable. Types DS DC Declare Storage Declare Constant
- 32. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Declare Storage Syntax [ Label ] DS < Constraint Specifying size > X DS 1 Example
- 33. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Declare Constant Syntax [ Label ] DC < Constraint Specifying values > X DC ‘ 5 ’ Example
- 34. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Assembler Directive ❏ Assembler directive instruct the assembler to perform certain actions during assembly of a program Some assembler directive are: START < Address Constant > END
- 35. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Advance Assembler Directive Origin EQU USING DROP LTORG
- 37. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Outline ❏ Review of previous session ❏ Identify Statement ❏ Pass 1 Assembler ❏ Machine Structure
- 38. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Sample Assembly language Code 1. START 100 2. MOVER A REG, X 3. MOVER B REG, Y 4. ADD A REG, Y 5. MOVEM A REG, X 6. X DC ‘10’ 7. Y DS 1 8. END
- 39. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Identify types of statement 1. START 100 IS DS AD Sr. No 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. MOVER B REG, Y 3. MOVER B REG, Y 4. ADD A REG, Y Code
- 40. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Identify types of statement 5. MOVEM A REG, X IS DS AD Sr. No 5. 6. 7. 8. 6. X DC ‘10’ 7. Y DS 1 8. End Code
- 41. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembly Language Some Definitions LC Symbol Literals Procedures
- 42. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Machine Structure
- 43. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Machine Structure Machine Instruction Format
- 44. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Assembler Assembler Pass 1 Assembler Pass 2 Assembler Separate Generate the machine code Determine Storage Requirement Build the Symbol Table Labels Operand Fields Mnemonic Opcode
- 45. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Pass 1 Assembler Uses How pass 1 assembler works? Machine opcode Table Symbol Table Pool Table Literal Table Data Structure Pass 1 Assembler ❏ Contents of MOT are fixed for an assembler.
- 46. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Apply LC Observe code Pass 1 Assembler
- 47. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Symbol Table Construct Pass 1 Assembler
- 48. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Construct Literal Table Pass 1 Assembler
- 49. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Pool table contains starting literal(index ) of each pool. Pool Table Pass 1 Assembler
- 50. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS | Construct Machine Code Intermediate Code Machine opcode Table needs Pass 1 Assembler
- 51. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Enhanced Machine Opcode Table Pass 1 Assembler
- 52. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Enhanced Machine Opcode Table Pass 1 Assembler
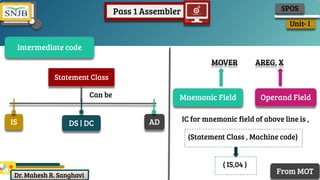
- 53. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Intermediate code ❏ For every line of assembly statement, one line of intermediate code is generated ❏ Each mnemonic field is represented as (Statement Class , Machine code) Pass 1 Assembler
- 54. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Intermediate code Statement Class Can be IS DS | DC AD MOVER AREG, X Mnemonic Field Operand Field IC for mnemonic field of above line is , (Statement Class , Machine code) ( IS,04 ) From MOT Pass 1 Assembler
- 55. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Intermediate code Operand Field S Symbol L Literal RG Register CC Condition Codes C Constant Operand Field ( operand Class , reference ) represented For a symbol or literal the reference field contains the index of the operands entry in symbol table or literal table. START 200 (AD, 01) (C, 200) E.g. MOVER AREG, X (IS, 04) (RG, 01) (S, 0) Mnemonic code Pass 1 Assembler
- 56. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Intermediate code
- 57. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Example 2 Assignment
- 60. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Outline ❏ Review of previous session ❏ Pass 2 Assembler
- 62. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Pass 2 Assembler Pass 2 Assembler Intermediate code Machine Code Pass 2 Assembler ❏ Processes the intermediate representation (IR) to synthesize the target program.
- 63. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Pass 2 Assembler Pass 2 Assembler Data Structure Pass I Pass II Intermediate code Source Program Target Program Data Access Control transfer
- 64. Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Unit- I SPOS Pass 2 Assembler Analysis Phase Synthesis Phase Vs
- 65. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi
- 66. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Pass 1 Pass 2 Intermediate Code Machine Code Output of Pass 1 | Pass 2 Assembler Generates Generates
- 67. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Variants Variants I Variants II Variants of Intermediate Code
- 68. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Variants I Variants of Intermediate Code In Variant I, each operand is represented by a pair of the form (operand class, code). The operand class is one of: 1. S for symbol 2. L for literal 3. C for constant 4. RG for register.
- 69. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Variants I Variants of Intermediate Code
- 70. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Variants II Variants of Intermediate Code In variant II, operands are processed selectively. Constants and literals are processed. Symbols, condition codes and CPU registers are not processed.
- 71. Unit- I SPOS Assembler Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi Variants II Variants of Intermediate Code




















![Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi
Unit- I
SPOS
Macro
Macro Processor
Syntax
Macro name [ set of parameters ]
// macro body
Mend
★ A macro processor takes a source with
macro definition and macro calls and
replaces each macro call with its body](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spos-uniti-210805054442/85/System-Programming-Assembler-21-320.jpg)










![Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi
Unit- I
SPOS
Assembly Language
Declare Storage
Syntax
[ Label ] DS < Constraint Specifying size >
X DS 1
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spos-uniti-210805054442/85/System-Programming-Assembler-32-320.jpg)
![Dr. Mahesh R. Sanghavi
Unit- I
SPOS
Assembly Language
Declare Constant
Syntax
[ Label ] DC < Constraint Specifying values >
X DC ‘ 5 ’
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spos-uniti-210805054442/85/System-Programming-Assembler-33-320.jpg)