Terraform – Infrastructure as Code (Kielux'18)
- 1. Terraform: Infrastructure as Code Martin Schütte 14 September 2018 Kieler Open Source und Linux Tage 2018
- 2. Concepts
- 3. by Rodzilla at Wikimedia Commons (CC-BY-SA-3.0) From Servers … Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 2/42
- 4. …to Services Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 3/42
- 5. Services have APIs • Starting servers is just a command line or function call • Add to build process (phoenix/immutable servers) • Replace “click paths” with source code in VCS • Fewer “black box” setup steps, better team handovers ⇒ Infrastructure as Code Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 4/42
- 6. Services also need Configuration Management • Lifecycle awareness, not just a setup.sh • Multiple stages/environments • Specification, documentation, policy enforcement ⇒ Tool support Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 5/42
- 7. TERRAFORM Build, Combine, and Launch Infrastructure
- 8. Example: Simple Webservice (part 1) ### AWS Setup provider ”aws” { profile = ”${var.aws_profile}” region = ”${var.aws_region}” } # Queue resource ”aws_sqs_queue” ”importqueue” { name = ”${var.app_name}-${var.aws_region}-importqueue” } # Storage resource ”aws_s3_bucket” ”importdisk” { bucket = ”${var.app_name}-${var.aws_region}-importdisk” acl = ”private” } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 7/42
- 9. Example: Simple Webservice (part 2) ### Heroku Setup provider ”heroku” { ... } # Importer resource ”heroku_app” ”importer” { name = ”${var.app_name}-${var.aws_region}-import” region = ”eu” config_vars { SQS_QUEUE_URL = ”${aws_sqs_queue.importqueue.id}” S3_BUCKET = ”${aws_s3_bucket.importdisk.id}” } } resource ”heroku_addon” ”mongolab” { app = ”${heroku_app.importer.name}” plan = ”mongolab:sandbox” } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 8/42
- 10. Example: Kubernetes on GCP (part 1) provider ”google” { region = ”us-central1” } resource ”google_container_cluster” ”cluster” { name = ”kielux-${terraform.workspace}” initial_node_count = 3 zone = ”us-central1-a” node_config { machine_type = ”g1-small” oauth_scopes = [ ... ] } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 9/42
- 11. Example: Kubernetes on GCP (part 2) provider ”kubernetes” { host = ”${google_container_cluster.cluster.endpoint}” client_certificate = ... } resource ”kubernetes_pod” ”test” { metadata { ... } spec { container { image = ”wordpress:4-apache” name = ”wordpress” port { container_port = 80 } } } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 10/42
- 12. Core Ideas in Terraform • Simple model of resource entities with attributes • Stateful lifecycle with CRUD operations • Declarative configuration • Dependencies by inference • Parallel execution Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 11/42
- 13. Core Concepts in Terraform • Provider: a source of resources (usually with an API endpoint & authentication) • Resource: every thing “that has a set of configurable attributes and a lifecycle (create, read, update, delete)” – implies ID and state • Data Source: information read from provider (e. g. lookup own account ID or AMI-ID) • Provisioner: initialize a resource with local or remote scripts Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 12/42
- 14. Design Choices in Terraform • Order: directed acyclic graph of all resources • Plan: generate an execution plan for review before applying a configuration • State: execution result is kept in state file (local or remote) • Lightweight: little provider knowledge, no error handling Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 13/42
- 15. Available services Providers: • AWS • Azure • Google Cloud • Alicloud • Heroku • DNSMadeEasy • OpenStack • Docker • … Resources: • aws_instance • aws_vpc • aws_iam_user • azurerm_subnet • azurerm_dns_zone • azure_instance • aws_iam_user • heroku_app • postgresql_schema • … Provisioners: • chef • file • local-exec • remote-exec Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 14/42
- 16. DSL Syntax • Hashicorp Configuration Language (HCL), think “JSON-like but human-friendly” • Variables • Interpolation, e. g. ”number ${count.index + 1}” • Attribute access with resource_type.resource_name • Few build-in functions, e. g. base64encode(string), format(format, args…) Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 15/42
- 17. HCL vs. JSON # An AMI variable ”ami” { description = ”custom AMI” } /* A multi line comment. */ resource ”aws_instance” ”web” { ami = ”${var.ami}” count = 2 source_dest_check = false connection { user = ”root” } } { ”variable”: { ”ami”: { ”description”: ”custom AMI” } }, ”resource”: { ”aws_instance”: { ”web”: { ”ami”: ”${var.ami}”, ”count”: 2, ”source_dest_check”: false, ”connection”: { ”user”: ”root” } } } } }Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 16/42
- 18. terraform graph | dot -Tpdf aws_s3_bucket.importdisk provider.aws aws_sqs_queue.importqueue heroku_addon.mongolab heroku_app.importer provider.heroku Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 17/42
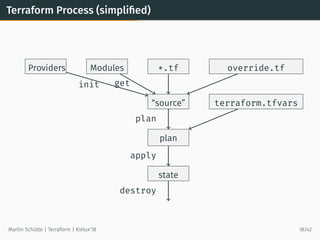
- 19. Terraform Process (simplified) *.tf override.tfModulesProviders “source” terraform.tfvars plan state init get plan apply destroy Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 18/42
- 20. Example: Add Provisioning # Importer resource ”heroku_app” ”importer” { name = ”${var.app_name}-${var.aws_region}-import” region = ”eu” config_vars { ... } provisioner ”local-exec” { command = <<EOT cd ~/projects/go-testserver && git remote add heroku ${heroku_app.importer.git_url} && git push heroku master EOT } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 19/42
- 21. Example: Add Outputs # Storage resource ”aws_s3_bucket” ”importdisk” { ... } # Importer resource ”heroku_app” ”importer” { ... } # Outputs output ”importer_bucket_arn” { value = ”${aws_s3_bucket.importdisk.arn}” } output ”importer_url” { value = ”${heroku_app.importer.web_url}” } output ”importer_gitrepo” { value = ”${heroku_app.importer.git_url}” } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 20/42
- 22. Example: Add Lifecycle Meta-Parameter # Storage resource ”aws_s3_bucket” ”importdisk” { bucket = ”${var.app_name}-${var.aws_region}-importdisk” acl = ”private” lifecycle { prevent_destroy = true } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 21/42
- 23. Demo $ terraform init $ terraform validate $ terraform plan -out=my.plan $ terraform show my.plan $ terraform apply my.plan $ terraform output $ terraform output -json $ terraform output importer_url $ curl -s $(terraform output importer_url) $ terraform graph | dot -Tpdf > graph.pdf && evince graph.pdf $ terraform plan -destroy $ terraform destroy Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 22/42
- 24. Features
- 25. Modules “Plain terraform code” lacks structure and reusability Modules • are subdirectories with self-contained terraform code • may be sourced from Git, Mercurial, HTTPS locations • use variables and outputs to pass data Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 23/42
- 26. Example Module module ”database” { source = ”github.com/terraform-community-modules/tf_aws_rds” # DB Instance Inputs rds_instance_identifier = ”${terraform.workspace}-${var.app}-db” rds_allocated_storage = ”${var.database_size}” database_name = ”${var.database_name}” database_user = ”${var.database_user}” database_password = ”${var.database_password}” # DB Subnet Inputs subnets = [”${aws_subnet.dbnet.*.id}”] rds_vpc_id = ”${data.aws_vpc.app.id}” tags { Name = ”${terraform.workspace} - ${var.app} - DB” } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 24/42
- 27. terraform.tfstate • Terraform keeps known state of resources • Defaults to local state in terraform.tfstate • Optional remote state with different backends (S3, Azure Storage, Consul, Atlas, …) • Useful to sync multiple team members • May need additional mutex mechanism (v0.9 added state locking for Local, S3, and Consul) • Remote state is a data source Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 25/42
- 28. Example: Using State Import $ terraform import azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account /subscriptions/e9b2ec19-ab6e-4547-a3ec-5a58e234ce5e/resourceGroups/ demo-res-group/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/demostorage20170418 azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account: Importing from ID ... azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account: Import complete! Imported azurerm_storage_account (ID: ...) azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account: Refreshing state... (ID: ...) Import success! The resources imported are shown above. These are now in your Terraform state. Import does not currently generate configuration, so you must do this next. If you do not create configuration for the above resources, then the next ‘terraform plan‘ will mark them for destruction. $ terraform state list azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account $ terraform state show azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account id = /subscriptions/e9b2ec19... account_kind = Storage account_type = Standard_LRS location = westeurope name = demostorage20170418 ... Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 26/42
- 29. Example: Use Remote State (with Workspaces) terraform { required_version = ”>= 0.10.0” environment = ”${terraform.workspace}” backend ”s3” { bucket = ”ms-terraform-state” key = ”infra/ms-tf-demo/state” region = ”eu-central-1” } } $ terraform workspace new prod $ terraform workspace new dev $ aws s3 ls --recursive ”s3://ms-terraform-state/” ... 282 workspace:/dev/infra/ms-tf-demo/state ... 282 workspace:/prod/infra/ms-tf-demo/state Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 27/42
- 30. Example: Use Remote State to Chain Projects data ”terraform_remote_state” ”infra” { backend = ”s3” config { bucket = ”ms-terraform-state” key = ”workspace:/${terraform.workspace}/infra/ ⌋ ms-tf-demo/state”→ region = ”eu-central-1” } } resource ”aws_instance” ”foo” { # use state from vpc_project subnet_id = ”${data.terraform_remote_state.infra.app_subnet_id}”→ instance_type = ”t2.micro” ami = ”ami-b968bad6” } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 28/42
- 31. Example: Using Data Source to Lookup Data # searches for most recent tagged AMI in own account data ”aws_ami” ”webami” { most_recent = true owners = [”self”] filter { name = ”tag:my_key” values = [”my_value”] } } # use AMI resource ”aws_instance” ”web” { instance_type = ”t2.micro” ami = ”${data.aws_ami.webami.id}” } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 29/42
- 32. Example: “External” Data Source data ”external” ”dyndns” { program = [”bash”, ”${path.module}/variomedia_dyndns.sh”] query = { hostname = ”aws-demo.martin-schuette.de” ipaddress = ”${aws_eip.foo.public_ip}” } } Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 30/42
- 33. How to Write Own Plugins Now: • Learn you some Golang • Use the schema helper lib • Adapt to model of Provider (setup steps, authentication) and Resources (arguments/attributes and CRUD methods) • Start reading of simple plugins like builtin/providers/mysql Future: • interface, support for Python, Ruby, C#, Java, … Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 31/42
- 34. Usage
- 35. General Problems for all Tools • Testing is inherently difficult • Provider coverage largely depends on community • Resource model mismatches, e. g. with Heroku apps • Ignorant of API rate limits, account ressource limits, etc. Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 32/42
- 36. Issues Under active development, current version 0.11.8 (August 15) • Modules are very simple • Lacking syntactic sugar (e. g. aggregations, common repetitions) • Big improvements in state management • Large variation in provider support, new project boundaries Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 33/42
- 37. Current Features Recently added features in 0.7–0.11 • State Import • Data Sources • Workspaces (previously: State Environments) • Separate sub-projects for providers terraform-providers Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 34/42
- 38. New Features in 0.12 “will be released later this summer” • First-Class Expressions i. e. instance_type = var.instance_type instead of instance_type = ”${var.instance_type}” • Conditionals …?…:… and null values • Rich Value Types module parameters and return objects • Template Syntax extended with conditionals and for expressions • remote operations Terraform Enterprise from CLI Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 35/42
- 39. Comparable Tools Configuration Management Tools: • SaltStack Salt Cloud • Ansible modules • Puppet modules Vendor Tools: • Azure Resource Manager Templates • AWS CloudFormation • OpenStack Heat Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 36/42
- 40. Workflow • Avoid user credentials in Terraform code, use e. g. profiles and assume-role wrapper scripts • At least use separate user credentials, know how to revoke them • To hold credentials in VCS use PGP encryption, e. g. with Blackbox Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 37/42
- 41. Workflow (contd.) • Use a VCS, i. e. git • Namespaces! – Always add some ”${var.shortname}-${var.env}” • per project • per region • per account • per provider • Use remote state and consider access locking, e. g. with a single build server • Take a look at Hashicorp Atlas and its workflow Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 38/42
- 42. Example: GitLab CI/CD Pipeline Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 39/42
- 43. Hashicorp Toolset Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 40/42
- 44. Links and Resources • Terraform.io and hashicorp/terraform • terraform-providers • terraform-community-modules • newcontext/kitchen-terraform • Terraforming – Export existing AWS resources • Terraform: Beyond the Basics with AWS • A Comprehensive Guide to Terraform • Terraform, VPC, and why you want a tfstate file per env • Infrastructure as Code by Kief Morris Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 41/42
- 45. The End Hopefully, deployments will become routine and boring–and in the world of operations, boring is a very good thing. — Terraform: Up & Running by Yevgeniy Brikman Thank You! — Questions? Martin Schütte @m_schuett [email protected] slideshare.net/mschuett/ noti.st/mschuett/ Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 42/42










![Example: Kubernetes on GCP (part 1)
provider ”google” {
region = ”us-central1”
}
resource ”google_container_cluster” ”cluster” {
name = ”kielux-${terraform.workspace}”
initial_node_count = 3
zone = ”us-central1-a”
node_config {
machine_type = ”g1-small”
oauth_scopes = [ ... ]
}
}
Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 9/42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180914-kielux-terraform-print-180914131625/85/Terraform-Infrastructure-as-Code-Kielux-18-10-320.jpg)














![Example Module
module ”database” {
source = ”github.com/terraform-community-modules/tf_aws_rds”
# DB Instance Inputs
rds_instance_identifier = ”${terraform.workspace}-${var.app}-db”
rds_allocated_storage = ”${var.database_size}”
database_name = ”${var.database_name}”
database_user = ”${var.database_user}”
database_password = ”${var.database_password}”
# DB Subnet Inputs
subnets = [”${aws_subnet.dbnet.*.id}”]
rds_vpc_id = ”${data.aws_vpc.app.id}”
tags {
Name = ”${terraform.workspace} - ${var.app} - DB”
}
}
Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 24/42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180914-kielux-terraform-print-180914131625/85/Terraform-Infrastructure-as-Code-Kielux-18-26-320.jpg)




![Example: Using Data Source to Lookup Data
# searches for most recent tagged AMI in own account
data ”aws_ami” ”webami” {
most_recent = true
owners = [”self”]
filter {
name = ”tag:my_key”
values = [”my_value”]
}
}
# use AMI
resource ”aws_instance” ”web” {
instance_type = ”t2.micro”
ami = ”${data.aws_ami.webami.id}”
}
Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 29/42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180914-kielux-terraform-print-180914131625/85/Terraform-Infrastructure-as-Code-Kielux-18-31-320.jpg)
![Example: “External” Data Source
data ”external” ”dyndns” {
program = [”bash”, ”${path.module}/variomedia_dyndns.sh”]
query = {
hostname = ”aws-demo.martin-schuette.de”
ipaddress = ”${aws_eip.foo.public_ip}”
}
}
Martin Schütte | Terraform | Kielux’18 30/42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180914-kielux-terraform-print-180914131625/85/Terraform-Infrastructure-as-Code-Kielux-18-32-320.jpg)












