Theory of computation complete 5th module
- 2. 2 Turing Machines are… Very powerful (abstract) machines that could simulate any modern day computer (although very, very slowly!) Why design such a machine? If a problem cannot be “solved” even using a TM, then it implies that the problem is undecidable Computability vs. Decidability For every input, answer YES or NO
- 3. 3 A Turing Machine (TM) M = (Q, ∑, Γ, δ, q0,B,F) B B B X1 X2 X3 … Xi … Xn B B … … Finite control Infinite tape with tape symbols B: blank symbol (special symbol reserved to indicate data boundary) Input & output tape symbols Tape head This is like the CPU & program counter Tape is the memory
- 4. 4 Transition function One move (denoted by |---) in a TM does the following: δ(q,X) = (p,Y,D) q is the current state X is the current tape symbol pointed by tape head State changes from q to p After the move: X is replaced with symbol Y If D=“L”, the tape head moves “left” by one position. Alternatively, if D=“R” the tape head moves “right” by one position. q p X / Y,D You can also use: for R for L
- 5. 5 ID of a TM Instantaneous Description or ID : X1X2…Xi-1qXiXi+1…Xn means: q is the current state Tape head is pointing to Xi X1X2…Xi-1XiXi+1…Xn are the current tape symbols δ(q,Xi) = (p,Y,R) is same as: X1…Xi-1qXi…Xn |---- X1…Xi-1YpXi+1…Xn δ(q,Xi) = (p,Y,L) is same as: X1…Xi-1qXi…Xn |---- X1…pXi-1YXi+1…Xn
- 6. 6 Way to check for Membership Is a string w accepted by a TM? Initial condition: The (whole) input string w is present in TM, preceded and followed by infinite blank symbols Final acceptance: Accept w if TM enters final state and halts If TM halts and not final state, then reject
- 7. 7 Example: L = {0n1n | n≥1} Strategy: w = 000111 0 1 1 1 0 0 B B B B … … 0 1 1 1 0 X B B B B … … … 0 Y 1 1 0 X B B B B … 0 Y 1 1 X X B B B B … … 0 Y Y 1 X X B B B B … … X Y Y 1 X X B B B B … X Y Y Y X X B B B B … Accept X Y Y Y X X B B B B … … … … … …
- 8. 8 TM for {0n1n | n≥1} q0 q1 0 / X,R 0 / 0,R q2 1 / Y,L Y / Y,L 0 / 0,L X / X,R q3 Y / Y,R Y / Y,R q4 B / B,R 1. Mark next unread 0 with X and move right 2. Move to the right all the way to the first unread 1, and mark it with Y 3. Move back (to the left) all the way to the last marked X, and then move one position to the right 4. If the next position is 0, then goto step 1. Else move all the way to the right to ensure there are no excess 1s. If not move right to the next blank symbol and stop & accept. Y / Y,R
- 9. 9 TM for {0n1n | n≥1} Next Tape Symbol Curr. State 0 1 X Y B q0 (q1,X,R) - - (q3,Y,R) - q1 (q1,0,R) (q2,Y,L) - (q1,Y,R) - q2 (q2,0,L) - (q0,X,R) (q2,Y,L) - q3 - - - (q3,Y,R) (q4,B,R) *q4 - -- - - - Table representation of the state diagram *state diagram representation preferred
- 10. 10 TMs for calculations TMs can also be used for calculating values Like arithmetic computations Eg., addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
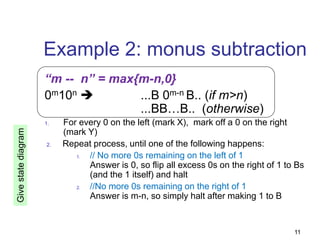
- 11. 11 Example 2: monus subtraction “m -- n” = max{m-n,0} 0m10n ...B 0m-n B.. (if m>n) ...BB…B.. (otherwise) 1. For every 0 on the left (mark X), mark off a 0 on the right (mark Y) 2. Repeat process, until one of the following happens: 1. // No more 0s remaining on the left of 1 Answer is 0, so flip all excess 0s on the right of 1 to Bs (and the 1 itself) and halt 2. //No more 0s remaining on the right of 1 Answer is m-n, so simply halt after making 1 to B Give state diagram
- 12. 12
- 13. 13
- 14. 14 Example 3: Multiplication 0m10n1 (input), 0mn1 (output) Pseudocode: 1. Move tape head back & forth such that for every 0 seen in 0m, write n 0s to the right of the last delimiting 1 2. Once written, that zero is changed to B to get marked as finished 3. After completing on all m 0s, make the remaining n 0s and 1s also as Bs Give state diagram
- 15. 16 Language of the Turing Machines Recursive Enumerable (RE) language Regular (DFA) Context- free (PDA) Context sensitive Recursively Enumerable
- 16. Variations of Turing Machines 17
- 17. 18 TMs with storage E.g., TM for 01* + 10* q storage Tape head 1 1 1 1 1 0 B B B B … Transition function δ: • δ([q0,B],a) = ([q1,a], a, R) • δ([q1,a],a) = ([q1,a], a, R) • δ([q1,a],B) = ([q2,B], B, R) [q,a]: where q is current state, a is the symbol in storage Are the standard TMs equivalent to TMs with storage? Yes Generic description Will work for both a=0 and a=1 Current state Current Storage symbol Tape symbol Next state New Storage symbol
- 18. 19
- 19. 21 Multi-track Turing Machines TM with multiple tracks, but just one unified tape head control … … … … … … Track 1 Track 2 Track k … One tape head to read k symbols from the k tracks at one step. …
- 20. 22 Multi-Track TMs TM with multiple “tracks” but just one head E.g., TM for {wcw | w∈ {0,1}* } but w/o modifying original input string control Tape head 0 c 0 1 1 0 0 B B B … … Track 1 X c Y Y X X Y B B B … … Track 2 AFTER control Tape head 0 c 0 1 1 0 0 B B B … … Track 1 B B B B B B B B B B … … Track 2 BEFORE Second track mainly used as a scratch space for marking
- 21. 23
- 22. L = {0n1n | n>=1} 24
- 23. Subroutine 25
- 24. 26
- 25. 27
- 26. 30 Multi-tape Turing Machines TM with multiple tapes, each tape with a separate head Each head can move independently of the others control … … … … … … Tape 1 Tape 2 Tape k … k separate heads
- 27. 31 On how a Multi-tape TM would operate Initially: The input is in tape #1 surrounded by blanks All other tapes contain only blanks The tape head for tape #1 points to the 1st symbol of the input The heads for all other tapes point at an arbitrary cell (doesn’t matter because they are all blanks anyway) A move: Is a function (current state, the symbols pointed by all the heads) After each move, each tape head can move independently (left or right) of one another
- 28. 32 Multitape TMs ≡ Basic TMs Theorem: Every language accepted by a k- tape TM is also accepted by a single-tape TM Proof by construction: Construct a single-tape TM with 2k tracks, where each tape of the k-tape TM is simulated by 2 tracks of basic TM k out the 2k tracks simulate the k input tapes The other k out of the 2k tracks keep track of the k tape head positions
- 29. 33 Multitape TMs ≡ Basic TMs … To simulate one move of the k-tape TM: Move from the leftmost marker to the rightmost marker (k markers) and in the process, gather all the input symbols into storage Then, take the action same as done by the k-tape TM (rewrite tape symbols & move L/R using the markers) control x … … A1 A2 … Ai … … … Track 1 Track 2 … x … … B1 B2 … Bi … Bj … … Track 3 Track 4 storage
- 31. 35 Non-deterministic TMs A TM can have non-deterministic moves: δ(q,X) = { (q1,Y1,D1), (q2,Y2,D2), … } Simulation using a multitape deterministic TM: Control ID1 ID2 ID3 ID4 * * * * Scratch tape Input tape Marker tape Non-deterministic TMs ≡ Deterministic TMs
- 32. 36
- 33. 37
- 34. 38 Summary TMs == Recursively Enumerable languages TMs can be used as both: Language recognizers Calculators/computers Basic TM is equivalent to all the below: 1. TM + storage 2. Multi-track TM 3. Multi-tape TM 4. Non-deterministic TM TMs are like universal computing machines with unbounded storage















![18
TMs with storage
E.g., TM for 01* + 10*
q
storage
Tape head
1 1 1 1
1
0 B B
B
B …
Transition function δ:
• δ([q0,B],a) = ([q1,a], a, R)
• δ([q1,a],a) = ([q1,a], a, R)
• δ([q1,a],B) = ([q2,B], B, R)
[q,a]: where q is current state,
a is the symbol in storage
Are the standard TMs
equivalent to TMs with storage?
Yes
Generic description
Will work for both a=0 and a=1
Current
state
Current
Storage
symbol
Tape
symbol
Next
state
New
Storage
symbol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5j8-250116075720-f5f421e2/85/Theory-of-computation-complete-5th-module-17-320.jpg)
















