TimeComplexity important topic of Algorithm analysis .pptx
- 1. Analysis of Algorithms: time & space Dr. Jeyakesavan Veerasamy [email protected] The University of Texas at Dallas, USA
- 2. Program running time When is the running time (waiting time for user) noticeable/important?
- 3. Program running time – Why? When is the running time (waiting time for user) noticeable/important? • web search • database search • real-time systems with time constraints
- 4. Factors that determine running time of a program
- 5. Factors that determine running time of a program • problem size: n • basic algorithm / actual processing • memory access speed • CPU/processor speed • # of processors? • compiler/linker optimization?
- 6. Running time of a program or transaction processing time • amount of input: n min. linear increase • basic algorithm / actual processing depends on algorithm! • memory access speed by a factor • CPU/processor speed by a factor • # of processors? yes, if multi-threading or multiple processes are used. • compiler/linker optimization? ~20%
- 7. Running time for a program: a closer look time (clock cycles) CPU memory access disk I/O access
- 8. Time Complexity • measure of algorithm efficiency • has a big impact on running time. • Big-O notation is used. • To deal with n items, time complexity can be O(1), O(log n), O(n), O(n log n), O(n2 ), O(n3 ), O(2n ), even O(nn ).
- 9. Coding example #1 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) m += i;
- 10. Coding example #2 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ ) sum[i] += entry[i][j];
- 11. Coding example #3 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j<i ; j++ ) m += j;
- 12. Coding example #4 i = 1; while (i < n) { tot += i; i = i * 2; }
- 13. Example #4: equivalent # of steps? i = n; while (i > 0) { tot += i; i = i / 2; }
- 14. Coding example #5 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ ) for( k=0 ; k<n ; k++ ) sum[i][j] += entry[i][j][k];
- 15. Coding example #6 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ ) sum[i] += entry[i][j][0]; for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( k=0 ; k<n ; k++ ) sum[i] += entry[i][0][k];
- 16. Coding example #7 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j< sqrt(n) ; j++ ) m += j;
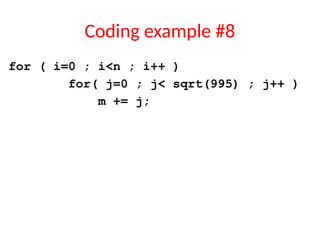
- 17. Coding example #8 for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) for( j=0 ; j< sqrt(995) ; j++ ) m += j;
- 18. Coding example #8 : Equivalent code for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) { m += j; m += j; m += j; … m += j; // 31 times }
- 19. Coding example #9 int total(int n) for( i=0 ; i < n; i++) subtotal += i; main() for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) tot += total(i);
- 20. Coding example #9: Equivalent code for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ) { subtotal = 0; for( j=0 ; j < i; j++) subtotal += j; tot += subtotal; }
- 21. Compare running time growth rates
- 22. Time Complexity maximum N? http://www.topcoder.com/tc?module=Static&d1=tutorials&d2=complexity1
- 24. Example #1: carry n items from one room to another room
- 25. Example #1: carry n items from one room to another room • How many operations? • n pick-ups, n forward moves, n drops and n reverse moves 4 n operations • 4n operations = c. n = O(c. n) = O(n) • Similarly, any program that reads n inputs from the user will have minimum time complexity O(n).
- 26. Example #2: Locating patient record in Doctor Office What is the time complexity of search?
- 27. Example #2: Locating patient record in Doctor Office What is the time complexity of search? • Binary Search algorithm at work • O(log n) • Sequential search? • O(n)
- 28. Example #3: Store manager gives gifts to first 10 customers • There are n customers in the queue. • Manager brings one gift at a time.
- 29. Example #3: Store manager gives gifts to first 10 customers • There are n customers in the queue. • Manager brings one gift at a time. • Time complexity = O(c. 10) = O(1) • Manager will take exactly same time irrespective of the line length.
- 30. Example #4: Thief visits a Doctor with Back Pain
- 31. Example #4: Thief visits a Doctor with Back Pain • Doctor asks a few questions: – Is there a lot of stress on the job? – Do you carry heavy weight?
- 32. Example #4: Thief visits a Doctor with Back Pain • Doctor asks a few questions: – Is there a lot of stress on the job? – Do you carry heavy weight? • Doctor says: Never carry > 50 kgs
- 33. Knapsack problems • Item weights: 40, 10, 46, 23, 22, 16, 27, 6 • Instance #1: Target : 50 • Instance #2: Target: 60 • Instance #3: Target: 70
- 34. Knapsack problem : Simple algorithm
- 35. Knapsack problem : Greedy algorithm
- 36. Knapsack problem : Perfect algorithm
- 37. Example #5: Hanoi Towers
- 38. Hanoi Towers: time complexity
- 39. Hanoi Towers: n pegs?
- 40. Hanoi Towers: (log n) pegs?
- 41. A few practical scenarios
- 42. Game console • Algorithm takes longer to run requires higher-end CPU to avoid delay to show output & keep realism.
- 43. Web server • Consider 2 web-server algorithms: one takes 5 seconds & another takes 20 seconds.
- 44. Database access Since the database load & save operations take O(n), why bother to optimize database search operation?
- 45. Daily data crunching • Applicable for any industry that collects lot of data every day. • Typically takes couple of hours to process. • What if it takes >1 day?
- 46. Data crunching pseudocode • initial setup • loop – read one tuple – open db connection – send request to db – get response from db – close db • post-processing
- 47. Data crunching pseudocode • initial setup • loop – read one tuple – open db connection – send request to db – get response from db – close db • post-processing • Equation for running time = c1. n + d1 • Time complexity is O(n)
- 48. Data crunching pseudocode • initial setup • open db connection • loop – read one tuple – send request to db – get response from db • close db • post-processing • Equation for running time = c2. n + d2 • Time complexity is still O(n), but the constants are different. • c2 < c1 • d2> d1
- 49. Search algorithms • Sequential search • Binary search • Hashing
- 50. Summary • Time complexity is a measure of algorithm efficiency • Efficient algorithm plays the major role in determining the running time. Q: Is it possible to determine running time based on algorithm’s time complexity alone? • Minor tweaks in the code can cut down the running time by a factor too. • Other items like CPU speed, memory speed, device I/O speed can help as well. • For certain problems, it is possible to allocate additional space & improve time complexity.









![Coding example #2
for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ )
sum[i] += entry[i][j];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timecomplexity-250516032908-cdc3f643/85/TimeComplexity-important-topic-of-Algorithm-analysis-pptx-10-320.jpg)



![Coding example #5
for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ )
for( k=0 ; k<n ; k++ )
sum[i][j] += entry[i][j][k];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timecomplexity-250516032908-cdc3f643/85/TimeComplexity-important-topic-of-Algorithm-analysis-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Coding example #6
for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
for( j=0 ; j<n ; j++ )
sum[i] += entry[i][j][0];
for ( i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
for( k=0 ; k<n ; k++ )
sum[i] += entry[i][0][k];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timecomplexity-250516032908-cdc3f643/85/TimeComplexity-important-topic-of-Algorithm-analysis-pptx-15-320.jpg)