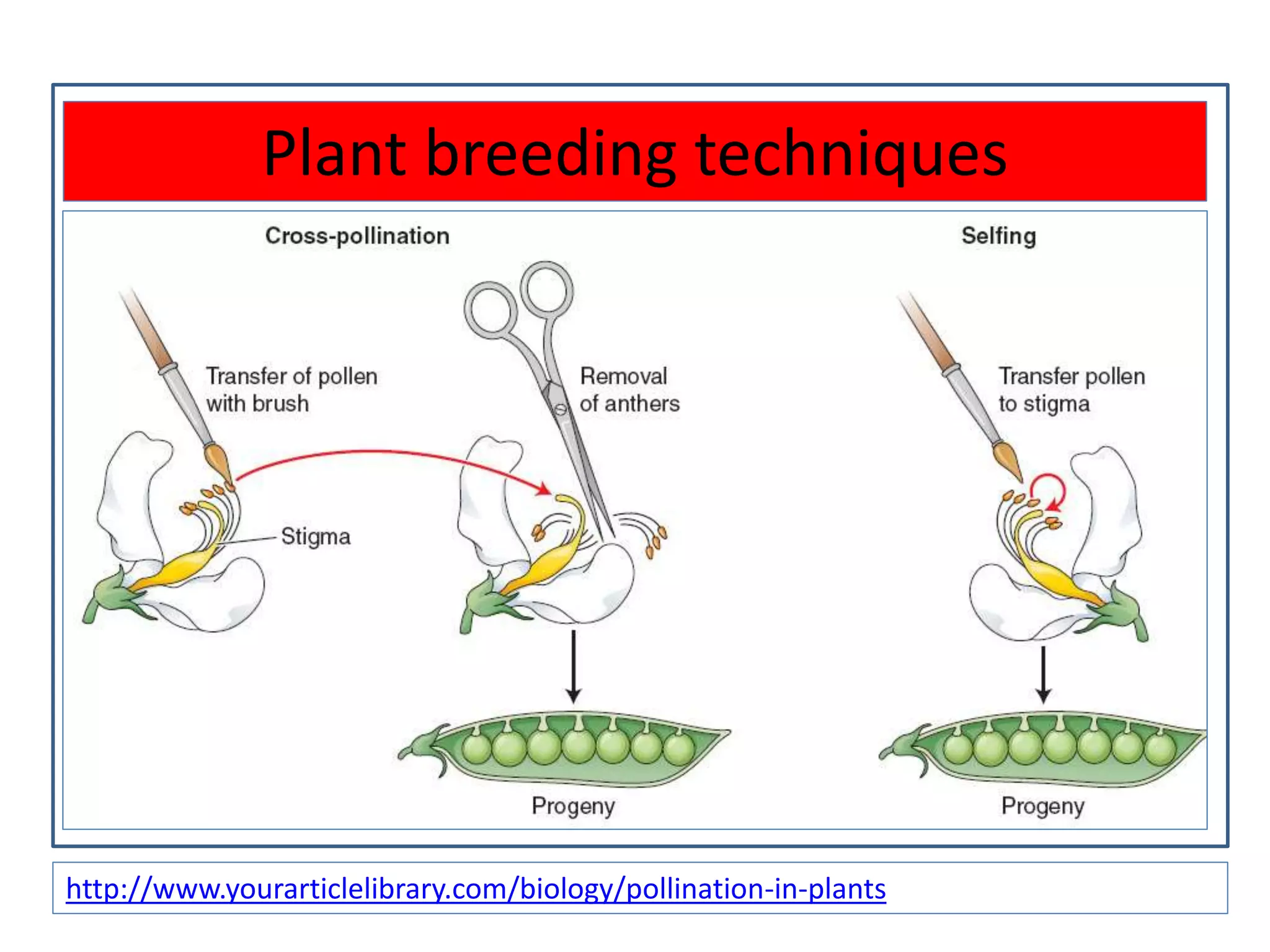
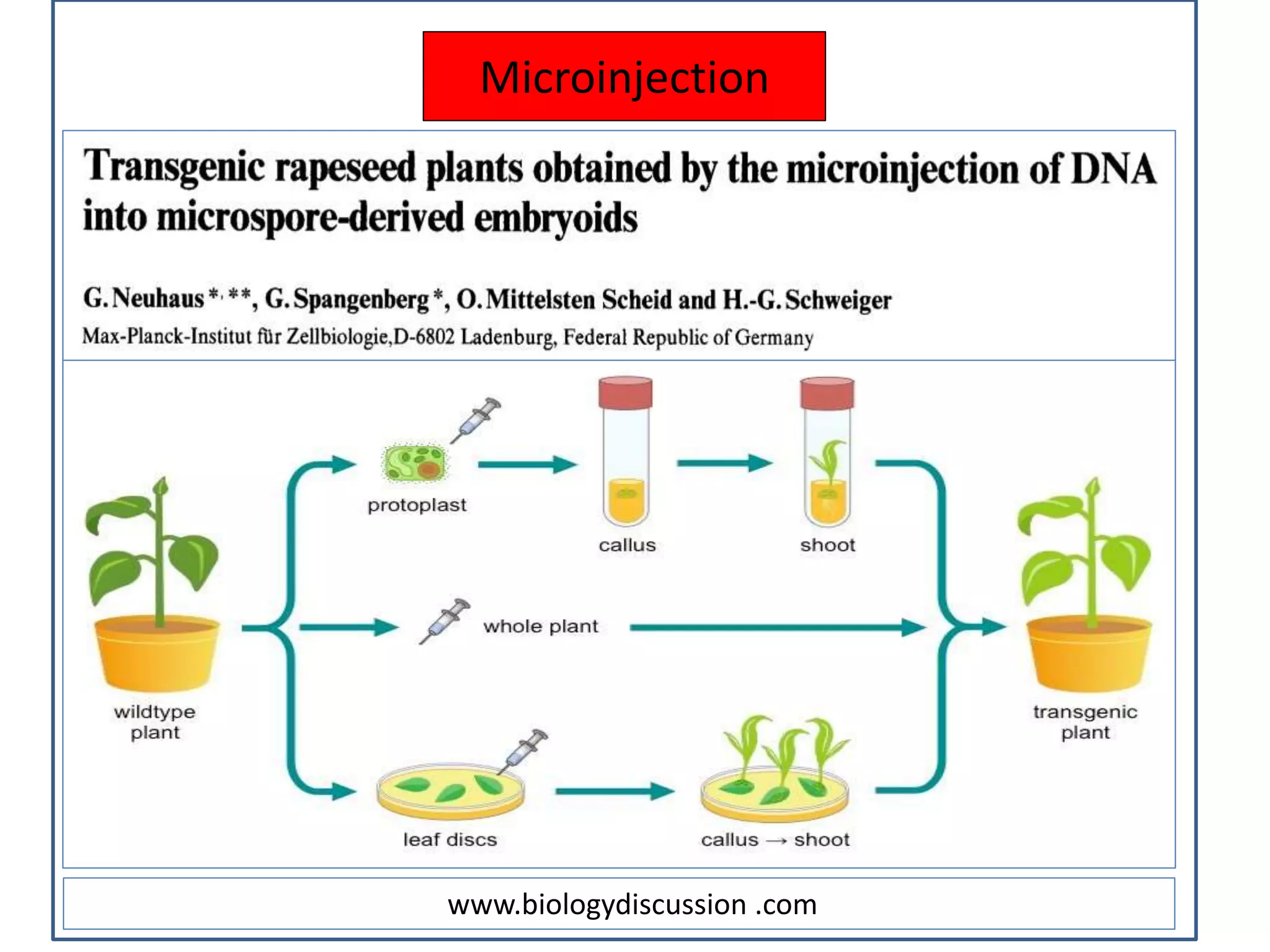
This document discusses various plant transformation systems. It describes direct transformation techniques like microinjection, electroporation, silicon carbide-mediated and gene gun/biolistic transformation. It also discusses indirect transformation techniques like Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated and virus-mediated gene transfer. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is able to transfer T-DNA from its Ti plasmid into the plant genome. Viral vectors like caulimoviruses and geminiviruses are also used for plant transformation. The document further explains in planta transformation techniques like meristem transformation and floral dip method. It provides examples of transgenic crops developed using these techniques.