Two graph data models : RDF and Property Graphs
- 1. Two graph data models RDF and Property Graphs Andy Seaborne Paolo Castagna [email protected], [email protected]
- 2. Introduction This talk is about two graph data models (RDF and Property Graphs), example of a couple of Apache projects using such data models, and a few lessons learned along the way.
- 3. Graph Data Models ➢ RDF ● W3C Standard ➢ Property Graphs ● Industry standard
- 4. RDF ➢ IRIs (=URIs), literals (strings, numbers, …), blank nodes ➢ Triple => subject-predicate-object ● Predicate (or property) is the link name : an IRI ➢ Graph => set of triples
- 5. prefix : <http://example/myData/> prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> # foaf:name is a short form of <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name> :alice rdf:type foaf:Person ; foaf:name "Alice Smith" ; # ; means “same subject” foaf:knows :bob . :alice foaf:knows "Alice Smith" foaf:name foaf:Person rdf:type :bob
- 6. prefix : <http://example/myData/> prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> :bob rdf:type foaf:Person ; foaf:name "Bob Brown" . "Bob Brown" foaf:Person rdf:type :bob
- 7. prefix : <http://example/myData/> prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> :alice rdf:type foaf:Person ; foaf:name "Alice Smith" ; foaf:knows :bob . :bob rdf:type foaf:Person ; foaf:name "Bob Brown" . :alice foaf:knows "Alice Smith" foaf:name foaf:Person rdf:type "Bob Brown" foaf:Person rdf:type :bob
- 8. RDFS prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> foaf:Person rdfs:subClassOf foaf:Agent . foaf:Person rdfs:subClassOf <http://www.w3.org/2003/01/geo/wgs84_pos#SpatialThing> . foaf:skypeID rdfs:domain foaf:Agent ; rdfs:label "Skype ID" ; rdfs:range rdfs:Literal ; rdfs:subPropertyOf foaf:nick .
- 9. RDF : Access ➢ SPARQL : Query language ➢ Protocol : over HTTP PREFIX : <http://example/myData/> PREFIX rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> ## Names of people Alice knows. SELECT * { :alice foaf:knows ?X . ?X foaf:name ?name . }
- 10. RDF : Access ➢ SPARQL : Query language ➢ Protocol : over HTTP PREFIX rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> SELECT ?name ?numFriends { { SELECT ?person (count(*) AS ?numFriends) { ?person foaf:knows ?X . } GROUP BY ?person } ?person foaf:name ?name . } ORDER BY ?numFriends
- 11. RDF : Access ➢ SPARQL : Update language ➢ Protocol : over HTTP PREFIX : <http://example/myData/> PREFIX rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> INSERT DATA { :bob foaf:name "Bob Brown" ; foaf:knows :alice } ; INSERT { :alice knows ?B } } WHERE { :bob knows ?B }
- 12. Apache Jena TLP: April 2012 ➢ Involvement in standards ➢ RDF 1.1, SPARQL 1.1 ➢ RDF database ➢ SPARQL server Other RDF@ASF: ➢ Any23, Marmotta, Clerezza, Stanbol, Rya
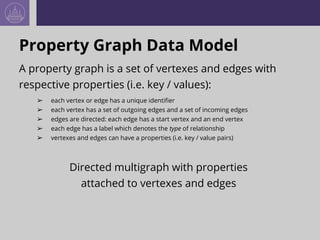
- 13. Property Graph Data Model A property graph is a set of vertexes and edges with respective properties (i.e. key / values): ➢ each vertex or edge has a unique identifier ➢ each vertex has a set of outgoing edges and a set of incoming edges ➢ edges are directed: each edge has a start vertex and an end vertex ➢ each edge has a label which denotes the type of relationship ➢ vertexes and edges can have a properties (i.e. key / value pairs) Directed multigraph with properties attached to vertexes and edges
- 14. Property Graph: Example id = 1 id = 2 name = “Alice” surname = “Smith” age = 32 email = [email protected] ... name = “Bob” surname = “Brown” age = 45 email = [email protected] ... since = 01/01/1970 ... id = 3 knows
- 15. Apache Spark: GraphX* // Creating a Graph val vertexes: RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] = sc.parallelize (Array((1L,("Alice", "[email protected]")), (2L,("Bob", "[email protected]")))) val edges: RDD[Edge[String]] = sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(1L, 2L, "knows")) val graph = Graph(vertexes, edges) ... Example of parallel graph algorithms available: // Find the triangle count for each vertex val triCounts = graph.triangleCount().vertices // Find the connected components val cc = graph.connectedComponents().vertices // Run PageRank val ranks = graph.pageRank(0.0001).vertices * GraphX is in the alpha stage
- 16. Property Graphs @ASF ➢ Apache Tinkerpop (incubating) ➢ Apache Spark > GraphX ➢ Apache Giraph ➢ Apache Flink > Gelly
- 17. Use Case for Graphs ➢ Analytics ● Social networks and recommendation engines ● Data center infrastructure management ➢ Knowledge Graphs ● Happenings: people, places, events ● Customer databases / products catalogues
- 18. Some Conclusions ➢ Data Graphs are (still) new to many people ➢ RDF emphasizes information modelling → Knowledge graphs → SQL-like query ➢ Property Graph emphasizes data processing → Data capture → Graph analytic algorithms ➢ Naive layering of data models leads dissatisfaction → Can only mix toolsets by knowing it’s layered ➢ Could share technology → Storage, data access, query algebra
- 19. Thanks and Q&A ?













![Apache Spark: GraphX*
// Creating a Graph
val vertexes: RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] =
sc.parallelize (Array((1L,("Alice", "alice@example.com")), (2L,("Bob", "bob@example.com"))))
val edges: RDD[Edge[String]] =
sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(1L, 2L, "knows"))
val graph = Graph(vertexes, edges)
...
Example of parallel graph algorithms available:
// Find the triangle count for each vertex
val triCounts = graph.triangleCount().vertices
// Find the connected components
val cc = graph.connectedComponents().vertices
// Run PageRank
val ranks = graph.pageRank(0.0001).vertices
* GraphX is in the alpha stage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015apacheconeupgrdf-151020205431-lva1-app6892/85/Two-graph-data-models-RDF-and-Property-Graphs-15-320.jpg)



