Understanding Computers - Introduction to Computers
- 1. What is a computer? A computer is a programmable, electronic device that accepts data, performs operations on that data, presents the results, and stores the data or results as needed
- 2. What does a computer do? A computer can perform four general operations: Input (entering data into a computer) Processing (performing operations on the data) Output (presenting the results) Storage (saving data, programs, or output)
- 3. Data vs. Information Data: almost any kind of fact or set of facts Information Processing: the conversion of data into information Information: processed data into a meaningful form Data • Raw, unorganized, unprocessed facts Information Processing Information • Data that has been processed into a meaningful form
- 4. What is hardware? Hardware is the physical part of a computer, that you can touch Examples: Keyboard Mouse Monitor Printer Scanner speaker
- 5. What is software? Software refers to the programs or instructions used to tell the computer hardware what to do
- 6. Types of software: 1. System Software The programs that allow a computer to operate are collectively referred to as system software. Examples: Windows, Mac LINUX, UNIX Android, Symbian
- 7. Types of software: 2. Application Software Application software consists of programs designed to allow people to perform specific task Examples: Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Access) Adobe Photoshop, Acrobat Internet explorer
- 8. Types of Users Computer Users (End Users) -- People who use computers to perform tasks or obtain information Programmers – Computer Professionals who write, test, and maintain computer programs System Analysts – Computer Professionals who analyze and design computer systems to solve business problems Operations Personnel – Computer Professionals who are responsible for the day-to-day computer operations
- 9. Types of computers: 1. Embedded Computers A tiny computer embedded into a product and designed to perform specific tasks or functions Examples: Washing machine Microwave Televisions Cars
- 10. Types of computers: 2. Mobile Devices A very small communication device with built-in computing or internet capability Examples: Smart phones Smart watches Handheld gaming devices Portable digital media players
- 11. Types of computers: 3. Personal Computers A computer designed to be used by one person at a time Examples: Desktop Computers Portable Computers (Notebook/Laptop, Tablet, Netbook, Ultra-mobile PC/Handheld Computer)
- 12. Types of computers: 4. Midrange Server/Computer A medium-sized computer used to host programs and data for a small network Example: Medical or dental offices School computer lab Home & small business servers
- 13. Types of computers: 5. Mainframe Computer A powerful computer used by many large organizations to manage large amounts of centralized data and programs Examples: Hospitals Universities Banks Government offices
- 14. Types of computers: 6. Supercomputer The most powerful and most expensive computer for complex computations and processing Examples: Space Missions and Satellite Controls Weather forecasting Oil exploration Scientific research
- 15. Basic types of data Multimedia Integration of multiple forms of media Computer information represented through audio, video, animation, in addition to, text, image Data Text Number Image Audio Video
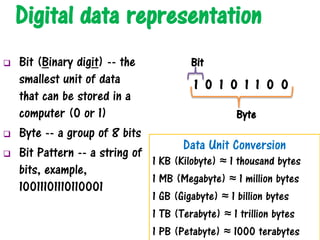
- 16. Digital data representation Bit (Binary digit) -- the smallest unit of data that can be stored in a computer (0 or 1) Byte -- a group of 8 bits Bit Pattern -- a string of bits, example, 10011101110110001 Data Unit Conversion 1 KB (Kilobyte) ≈ 1 thousand bytes 1 MB (Megabyte) ≈ 1 million bytes 1 GB (Gigabyte) ≈ 1 billion bytes 1 TB (Terabyte) ≈ 1 trillion bytes 1 PB (Petabyte) ≈ 1000 terabytes 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 Byte Bit
- 17. Coding Standards for Text-based Data (Characters) ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) uses 7-bit code to represent each character Each 7-bit code can represent up to 128 characters (27 unique combinations) Extended ASCII uses 8-bit code to represent each character Each 8-bit code can represent up to 256 characters (28 unique combinations) EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Information Code) uses 8-bit code to represent each character Each 8-bit code can represent up to 256 characters (28 unique combinations) Unicode Universal international coding standard to represent text-based data in any language uses (8-bit to 32-bit) code to represent each character ISO (International Organization for Standardization) uses 32-bit code to represent each character Each 32-bit code can represent up to 232 characters
- 18. Types of images: 1. Bitmap Graphic made of a grid or matrix of small dots (pixels; picture elements) The color at each pixel is represented by binary code/number 0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 11 1 1 1 1 0 0 011 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 For monochrome (Black & White) graphic image
- 19. Types of images: 2. Vector Graphic made of lines, curves and shapes based on vectors (paths) that lead through locations (control points or nodes) all lines, curves, or shapes are represented by mathematical formulas
- 20. Audio The procedure to convert analog sound to digital sound 1) analog signal is sampled 2) samples are quantized 3) The quantized values are coded into binary patterns
- 21. Video A collection of frames (images) that are projected in sequence dynamically Each image data is converted to a set of bit patterns and stored
- 22. Numerical data representation Decimal number system – based on 10 symbols (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) Binary number system – based 2 symbols (0, 1) Octal number system – based on 8 symbols (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) Each octal number is represented in binary form as 3-bit pattern Hexadecimal number -- based on 16 symbols (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F) Each hexadecimal number is represented in binary form as 4-bit pattern 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
- 23. Conversion: Decimal to Binary Decimal (25)10 = binary (11001)2 2512631 101 1 0 Procedure: Divide the decimal number by 2 and write down remainders successively
- 24. Conversion: Decimal to Binary Decimal (35)10 = binary (100011)2 35178421 1101 0 0 Procedure: Divide the decimal number by 2 and write down remainders successively
- 25. Conversion: Binary to Decimal Binary (11001)2 = Decimal (25)10 16 8 0 0 1 25 16 8 4 2 1 1 1 0 0 1 Procedure: Multiply the binary number by multiple of 2 respectively and add all
- 26. Conversion: Binary to Decimal Binary (100011)2 = Decimal (35)10 32 0 0 0 2 1 35 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 Procedure: Multiply the binary number by multiple of 2 respectively and add all
- 28. Motherboard– main electronic circuit board inside system unit that contains computer chips and other connected components Central Processing Unit (CPU)/Processor– chip located on motherboard of computer that performs processing for the computer o Multi-core CPU– CPU that contains processing components or core of more than one processor in a single CPU o Dual-core CPU– CPU that contains two separate processing cores o Quad-core CPU– CPU that contains four separate processing cores
- 29. Inside CPU
- 30. Bus– electronic path on motherboard along which data is transferred Example: Memory bus, Front-side bus, PCI and PCI Express bus, USB bus, FireWire/IEEE 1394 bus
- 31. Port– the exterior of the computer to which A device may be attached using a connector Example: Monitor port, Network port, Modem port, USB port, FireWire(IEEE 1394) port, Keyboard port, SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) port, MIDI port, Audio port, etc.
- 32. Volatile memory (Primary Storage) Memory refers to chip-based storage RAM (Random Access Memory) – This main-memory integrated- chip of computer provides temporary location to hold data and programs. Generally, it is volatile (the memory content is erased when the computer is powered down), except nonvolatile-RAM SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) – This volatile memory is faster but expensive. It uses electronic flip – flop gates (a gate with two states: 0 and 1) to hold data. It doesn’t need memory refreshing. DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)– This volatile memory is slower but inexpensive. It uses electronic capacitors (charged or discharged states as 1 or 0) to hold data. It needs constant memory refreshing. Cache Memory– group of fast memory circuitry located on or near CPU to help speed up processing Register– high-speed memory built into CPU that temporarily stores data during processing
- 33. ROM (Read Only Memory) -- nonvolatile memory chip that permanently stores data or programs in general. PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory) – nonvolatile memory chip that can be programmed/written only once (one-time). EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) – nonvolatile memory chip that can be erased and reprogrammed/rewritten many times. Non-volatile memory
- 34. Storage systems Floppy Disk -- low-capacity, removable disk made of flexible plastic Hard Drive – are used to store programs and data Magnetic Hard Drive/Disk – contains metal hard disks that are tracked with magnetic spots representing 0s and 1s Solid State Drive (SSD) – uses flash memory technology to store data and programs Hybrid Hard drive – a combination of magnetic hard drive and solid-state drive (contains flash memory together with magnetic hard disks)
- 35. Optical Disc – thin circular disc that stores and reads data using laser beam (optically) CD (Compact Disc) – low capacity (typically 650 MB) optical disc that uses infrared laser for data storage DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) – medium capacity (typical 4.7 GB to 8.5 GB) optical disc that uses red laser for data storage BD (Blue-ray Disc) – high-capacity (typically 25 GB to 50 GB) disc that uses blue-violet laser for data storage
- 36. CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, and BD-ROM discs These discs are read-only optical discs that come prerecorded and user can not write CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R, and BD-R discs These discs are recordable optical discs (write-once discs) but can not be erased afterward CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and BD-RE discs These discs are rewritable optical discs that can be written to, erased, and overwritten many times
- 37. Flash Memory -- a chip-based storage medium that stores data using electrons (electrical charge trapped or not, i.e., 0 or 1) within flash memory cell Flash Memory Cards – small, rectangular flash memory medium containing chips, such as a Compact Flash (CF) or Secure Digital (SD) card USB Flash Drive (Universal Serial Bus Drive) -- small storage device that plugs into USB port and contains flash memory media
- 38. Input Devices Keyboard -- input device containing numerous keys that can be used to input letters, numbers, and other symbols Mouse -- common pointing device that user slides along a flat surface to move pointer Electronic pen -- input device that is used to write electronically on the display screen Scanner -- input device that reads printed text and graphics and transfers them to a computer in digital form Examples: Flatbed Scanner, Handheld Scanner, Integrated Scanner Touch Screen– display device that is touched with finger to issue commands
- 39. Readers – input devices that read different types of codes and marks as well as individual’s biometric characteristics 1. Barcode Reader-- an input device that reads barcode (optical code) 5. RFID(Radio Frequency Identification) Reader— device used to read RFID tags (tiny chip with radio antenna to be identified using RFID technology) 2. OMR(Optical Mark Readers)– an input device to input data from special forms to score or tally exams, questionnaires, ballots, etc.) 3. OCR(Optical Character Recognition) Reader– used to recognize scanned text characters (from monthly bills for credit cards or utilities companies, etc.) and convert into electronic form as text 4. MICR(Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) Reader– used to read and add magnetic-inked MICR characters primarily during bank check/cheque processing 6. Biometric Reader— device used to input biometric data, such as fingerprint, voice, face
- 40. Output Devices Display device— an output device that contains a viewing screen Monitor-- display device for desktop computer Display Screen– display device built into a notebook computer, netbook, UMPC etc. Flat-panel display– slim type of display device that uses electronically charged chemicals or gases
- 41. Display Device Characteristics Color vs. Monochrome Display Devices– display devices form images by lighting up the proper configurations of pixels (the dots or the smallest colorable areas on a display device); picture elements Color Display Device-- each pixel can display a combination of three colors (red, green, and blue) Monochrome Display Device-- Each pixel can only be one of two colors (Black or White) CRT Monitors vs. Flat-Panel Displays CRT Monitor Display -- uses cathode-ray tube technology (electron gun projects an electron beam at a screen coated with red, green, and blue phosphor dots) Flat-Panel Display-- uses electronically charged chemicals or gases filled in between thin panes of glass or other transparent material
- 42. Audio Output -- includes voice, music, and other audible sounds Types of audio output devices: -- Computer Speaker-- output device connected to computers that provide audio output -- Headphone– personal audio output device used by an individual to hear sound -- Headset– headphone with a built-in microphone Flat-Panel Display Technologies -- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) – uses charged liquid crystals located between two sheets of glass or plastic -- Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Display– uses emissive organic material to display brighter and sharper images -- Plasma Display– uses layered technology (a layer of gas between two plates of glass) to display images -- Data Projector– display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen
- 43. Printer– output device that produces output on paper Printer Characteristics– technology used, size, speed, print quality, etc. Printing Technology– Printers produce images through either impact or nonimpact technologies Impact Printer– have a print mechanism that actually strikes the paper to transfer ink to the paper Example: dot-matrix printer Nonimpact Printer– have a print mechanism that does not strike/touch the paper to transfer ink to paper Example: Laser printer, ink-jet printer Color vs. Black & White Printers ─ Color printer uses black, blue, red, yellow ink to print a document ─ often used in homes ─ expensive and slow speed ─ Black & White printer uses black ink to print a document ─ Mostly used in business or office places ─ Less expensive and faster speed
- 44. Personal vs. Network Printers o Personal printer is designed to connect directly to a computer o can not be shared o Network printer is designed to connect directly to a home or office network o can be shared over a network Print Resolution (dpi)– the number of dots (of liquid ink or toner powder flecks) per inch Print Speed (ppm)– measured in pages per minute
- 45. Laser printer– output device that uses laser beam (to charge drum locations) and toner powder to print on paper Ink-jet Printer– output device that sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper Photo Printer– output device designed for printing digital photographs Barcode Printer– output device that print custom barcodes on price tags, shipping labels etc. Portable Printer– small lightweight printer designed to be used while on the go Plotter/Wide-Format Printer– used to print large documents, such as charts, drawings, maps, blueprints, posters, banners etc. 3D Printer– output device designed to print three-dimensional objects, such as product prototypes etc.
- 46. Algorithm-- a step by step procedure for solving a problem Flowchart– diagram that represents steps of an algorithm, workflow or process sequentially Example: adding two numbers; A, B Pseudo Code– informal description of an algorithm in plain English Example: adding two numbers; X, Y Begin input X input Y Sum = X + Y print Sum End
- 47. Computer Languages Machine Language-- binary-based language for representing computer programs that the computer can execute directly Assembly Language– a low- level programming language in which each statement produces exactly one machine instruction Assembler-- a program for converting Assembly language code into Machine code High-level Language– more understandable and portable language in which each statement accomplish substantial tasks Compiler– a program for converting High-level language code into low-level code or binary form
- 48. What is computer network? collection of computers and other hardware devices that are connected together to share hardware, software, and data, as well as to communicate electronically with one another
- 49. Internet Internet benefits Web Browsing E-mail Chatting and Entertainment Communication & business Information sharing the largest computer network in the world
- 50. Types of networks: 1. Local Area Network A network that connects devices located in a small geographical area, such as within a building
- 51. Types of networks: 2. Metropolitan Area Network A network designed to service a metropolitan area
- 52. Types of networks: 3. Wide Area Network (WAN) A network that connects devices located in a large geographical area
- 53. Operating System The main component of system software that enables the computer to manage its activities and the resources under its control, run application programs, and interface with the user
- 54. Function/Benefits of operating system Interfacing with Users Booting the Computer Configuring Devices Managing and Monitoring Resources and Jobs File Management Security
- 55. Differences among Operating Systems Graphical User Interface vs. Command Line Graphical user interface (GUI)– graphics-based interface that allows a user to communicate instructions to the computer easily Command line interface-- user interface that requires the user to communicate instructions to the computer via typed commands
- 56. Differences among Operating Systems Types of Operating Systems Personal operating system-- a type of operating system designed to be installed on a single personal computer Server operating system-- a type of operating system designed to be installed on a network server