Utility Procedures in SAS
- 2. Creating SAS Tables, Listings, Basic Statistics Procedures with SAS Graphs ODS HTML Proc Report and Other Utility Procedures TLG’s 11/13/09 SAS Techies 2009
- 3. append catalog cimport compare contents cport datasets export format import options print printto rank report sql sort summary tabulate template transpose SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
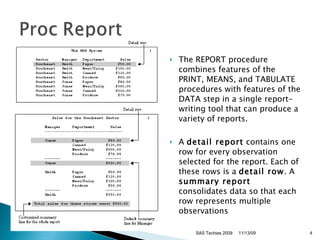
- 4. The REPORT procedure combines features of the PRINT, MEANS, and TABULATE procedures with features of the DATA step in a single report-writing tool that can produce a variety of reports. A detail report contains one row for every observation selected for the report. Each of these rows is a detail row . A summary report consolidates data so that each row represents multiple observations SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 5. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 6. PROC REPORT Statement BREAK Statement BY Statement - By Group processing CALL DEFINE Statement COLUMN Statement - Specify the columns in the report COMPUTE Statement DEFINE Statement ENDCOMP Statement FREQ Statement - Freq statistics LINE Statement RBREAK Statement WEIGHT Statement - calculating weighted statistics SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
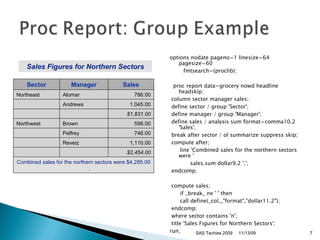
- 7. options nodate pageno=1 linesize=64 pagesize=60 fmtsearch=(proclib); proc report data=grocery nowd headline headskip; column sector manager sales; define sector / group 'Sector'; define manager / group 'Manager'; define sales / analysis sum format=comma10.2 'Sales'; break after sector / ol summarize suppress skip; compute after; line 'Combined sales for the northern sectors were ' sales.sum dollar9.2 '.'; endcomp; compute sales; if _break_ ne ' ' then call define(_col_,"format","dollar11.2"); endcomp; where sector contains 'n'; title 'Sales Figures for Northern Sectors'; run; SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Sales Figures for Northern Sectors Sector Manager Sales Northeast Alomar 786.00 Andrews 1,045.00 $1,831.00 Northwest Brown 598.00 Pelfrey 746.00 Reveiz 1,110.00 $2,454.00 Combined sales for the northern sectors were $4,285.00.
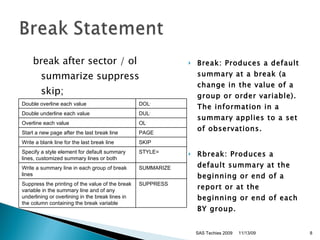
- 8. break after sector / ol summarize suppress skip; Break: Produces a default summary at a break (a change in the value of a group or order variable). The information in a summary applies to a set of observations. Rbreak: Produces a default summary at the beginning or end of a report or at the beginning or end of each BY group. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Double overline each value DOL * Double underline each value DUL * Overline each value OL * Start a new page after the last break line PAGE Write a blank line for the last break line SKIP Specify a style element for default summary lines, customized summary lines or both STYLE= Write a summary line in each group of break lines SUMMARIZE Suppress the printing of the value of the break variable in the summary line and of any underlining or overlining in the break lines in the column containing the break variable SUPPRESS
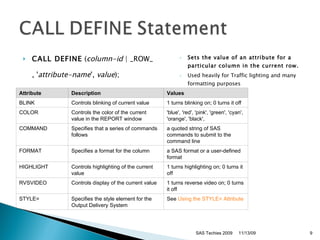
- 9. CALL DEFINE ( column-id | _ROW_ , ' attribute-name ', value ); Sets the value of an attribute for a particular column in the current row. Used heavily for Traffic lighting and many formatting purposes SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Attribute Description Values BLINK Controls blinking of current value 1 turns blinking on; 0 turns it off COLOR Controls the color of the current value in the REPORT window 'blue', 'red', 'pink', 'green', 'cyan', 'orange', 'black', COMMAND Specifies that a series of commands follows a quoted string of SAS commands to submit to the command line FORMAT Specifies a format for the column a SAS format or a user-defined format HIGHLIGHT Controls highlighting of the current value 1 turns highlighting on; 0 turns it off RVSVIDEO Controls display of the current value 1 turns reverse video on; 0 turns it off STYLE= Specifies the style element for the Output Delivery System See Using the STYLE= Attribute
- 10. COMPUTE location < target > </ STYLE=< style-element-name > <[ style-attribute-specification(s) ]>>; LINE specification(s) ; . . . select SAS language elements . . . ENDCOMP ; A compute block can be associated with a report item or with a location (at the top or bottom of a report; at the top or bottom of a page; before or after a set of observations). SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 11. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Assign a SAS or user-defined format to the item FORMAT= Associate a statistic with an analysis variable statistic Specify a style element (for the Output Delivery System) for the report item STYLE= Specify a numeric variable whose values weight the value of the analysis variable WEIGHT= Define the width of the column in which PROC REPORT displays the report item WIDTH= Define the item, which must be a data set variable, as an across variable ACROSS Define the item, which must be a data set variable, as an analysis variable ANALYSIS Define the item as a computed variable COMPUTED Define the item, which must be a data set variable, as a display variable DISPLAY Define the item, which must be a data set variable, as a group variable GROUP Define the item, which must be a data set variable, as an order variable ORDER
- 12. options nodate pageno=1 linesize=64 pagesize=60 fmtsearch=(proclib); proc report data=grocery nowd headline headskip; column sector manager sales; define sector / group 'Sector'; define manager / group 'Manager'; define sales / analysis sum format=comma10.2 'Sales'; break after sector / ol summarize suppress skip; compute after; line 'Combined sales for the northern sectors were ' sales.sum dollar9.2 '.'; endcomp; compute sales; if _break_ ne ' ' then call define(_col_,"format","dollar11.2"); endcomp; where sector contains 'n'; title 'Sales Figures for Northern Sectors'; run; SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Sales Figures for Northern Sectors Sector Manager Sales Northeast Alomar 786.00 Andrews 1,045.00 $1,831.00 Northwest Brown 598.00 Pelfrey 746.00 Reveiz 1,110.00 $2,454.00 Combined sales for the northern sectors were $4,285.00.
- 13. proc report data=grocery nowd colwidth= 10 spacing= 5 headline headskip; column manager department sales; define manager / order order=formatted ; define department / order order=internal; define sales / analysis sum format=dollar7.2; break after manager / ol summarize skip; compute after; line 'Total sales for these stores were: ' sales.sum dollar9.2; endcomp; where sector='se'; title 'Sales for the Southeast Sector'; run ; SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 Sales for the Southeast Sector Manager Department Sales Jones Paper $40.00 Canned $220.00 Meat/Dairy $300.00 Produce $70.00 Jones $630.00 Smith Paper $50.00 Canned $120.00 Meat/Dairy $100.00 Produce $80.00 Smith $350.00 Total sales for these stores were: $980.00
- 14. PROC APPEND BASE=< libref. > SAS-data-set <DATA=< libref. > SAS-data-set > <FORCE> <APPENDVER=V6>; proc append base=exp.results data=exp.sur force; run; Data new; Set a b; a=20 b=20 new=40 Run; proc append base=a data=b force; run; Initially a=20 b=20 after append a=40 Data a; Set a b; initially a=20 b=20 after append Run; a=40 Advantage Proc Append – Does not read contents of dsn a to PDV…performance increases..mostly used for monthly updates and reporting in the industry. The APPEND procedure adds the observations from one SAS data set to the end of another SAS data set. FORCE Option - forces the APPEND statement to concatenate data sets when the DATA= data set contains variables that either are not in the BASE= data set do not have the same type as the variables in the BASE= data set are longer than the variables in the BASE= data set. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 15. PROC CATALOG CATALOG=< libref .> catalog <ENTRYTYPE= etype > <FORCE> <KILL>; CONTENTS <OUT= SAS-data-set > <FILE= fileref >; COPY OUT=< libref .> catalog < options >; SELECT entry(s) </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; EXCLUDE entry(s) </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; CHANGE old-name-1 = new-name-1 <... old-name-n = new-name-n > </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; EXCHANGE name-1 = other-name-1 <... name-n = other-name-n > </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; DELETE entry(s) </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; MODIFY entry (DESCRIPTION=<<'> entry-description <'>>)</ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; SAVE entry(s) </ ENTRYTYPE= etype >; The CATALOG procedure manages entries in SAS catalogs. PROC CATALOG is an interactive, statement-driven procedure that enables you to create a listing of the contents of a catalog copy a catalog or selected entries within a catalog rename, exchange, or delete entries within a catalog change the name of a catalog entry modify, by changing or deleting, the description of a catalog entry. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 16. SAS Techies 2009 options nodate pageno= 1 linesize= 80 pagesize= 60 source; libname perm 'SAS-data-library'; proc catalog cat=perm.sample; delete credit.program credit.log; copy out=tcatall; copy out=testcat; exclude test1 test2 test3 passist (et=slist) / et=log; run ; * RUN GROUP PROCESSING copy in=perm.formats out=perm.finance; select revenue.format dept.formatc; quit ; 11/13/09
- 17. Transport files are created to migrate SAS datasets between platforms (Unix, MVS, Windows) and continue using the same SAS Data Sets as simple transfer of true SAS Data Sets between operating systems will corrupt them. To accomplish the transfer of SAS Data Sets from one operating system to another it is necessary to convert the data set into "transport" format (Proc CPort) move, send or carry the data in "binary" (i.e., non-translated) format to the operating system running the other Version convert the transport data set back into a SAS Data Set (Proc Cimport) Transport files are sequential files that each contain a SAS data library, a SAS catalog, or a SAS data set in transport format. The transport format that PROC CPORT writes is the same for all environments and for many releases of SAS. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 18. PROC CPORT source-type=libref | <libref.>member-name<option(s)>; EXCLUDE SAS file(s) | catalog entry(s)</ MEMTYPE=mtype></ ENTRYTYPE=entry-type>; SELECT SAS file(s) | catalog entry(s) </ MEMTYPE=mtype></ ENTRYTYPE=entry-type>; TRANTAB NAME=translation-table-name <option(s)>; The CPORT procedure writes SAS data sets, SAS catalogs, or SAS data libraries to sequential file formats (transport files). Extension of the Transport files is .xpt SAS Techies 2009 libname source 'SAS-data-library'; filename tranfile 'transport-file' host-option(s)-for-file-characteristics; proc cport library=source file=tranfile memtype=catalog; proc cport catalog=source.finance file=tranfile after = '09sep1996'd ; trantab name=ttable1 type=(format); run ; 11/13/09
- 19. PROC CIMPORT destination=libref | <libref.>member-name <option(s)>; EXCLUDE SAS file(s) | catalog entry(s)</ MEMTYPE=mtype></ ENTRYTYPE=entry-type>; SELECT SAS file(s) | catalog entry(s)</ MEMTYPE=mtype></ ENTRYTYPE=entry-type>; The CIMPORT procedure imports a transport file that was created ( exported ) by the CPORT procedure. PROC CIMPORT ( only created by Proc CPort ) restores the transport file to its original form as a SAS catalog, SAS data set, or SAS data library. SAS Techies 2009 libname newlib 'SAS-data-library'; filename trans2 'transport-file' host-option(s)-for-file-characteristics; proc cimport catalog=newlib.finance infile=trans2; select loan.pmenu loan.scl; run ; 11/13/09
- 20. PROC COMPARE <option(s)>; BY <DESCENDING> variable-1 <...<DESCENDING> variable-n> <NOTSORTED>; ID <DESCENDING> variable-1 <...<DESCENDING> variable-n> <NOTSORTED>; VAR variable(s); WITH variable(s); The COMPARE procedure compares the contents of two SAS data sets, selected variables in different data sets, or variables within the same data set. PROC COMPARE generates the following information about the two data sets that are being compared: whether matching variables have different values whether one data set has more observations than the other what variables the two data sets have in common how many variables are in one data set but not in the other whether matching variables have different formats, labels, or types. a comparison of the values of matching observations. SAS Techies 2009 proc compare base=proclib.one compare=proclib.two nosummary; var gr1; with gr2; title 'Comparison of Variables in Different Data Sets'; run ; 11/13/09
- 21. PROC IMPORT DATAFILE="filename" | TABLE="tablename" OUT=<libref.>SAS-data-set <(SAS-data-set-options)> <DBMS=identifier> <REPLACE> ; <data-source-statement(s);> proc import datafile='c:\Myfiles\Class.xls' out=work.femaleclass (where=(sex='F')); run ; The IMPORT procedure reads data from an external data source and writes it to a SAS data set. External data sources can include Microsoft Access Database, Excel files, Lotus spreadsheets, and delimited external files (in which columns of data values are separated by a delimiter such as a blank, comma, or tab). Unix SAS does not read Excel, MS Access files…. Only .csv or tab delimited. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 22. PROC EXPORT DATA=<libref.>SAS-data-set <(SAS-data-set-options)> OUTFILE="filename" OUTTABLE="tablename" <DBMS=identifier> <REPLACE>; <data-source-statement(s);> proc export data=myfiles.grades1 dbms=excel2000 outfile='c:\Myfiles\Grades.xls'; sheet=Grades1; run ; The EXPORT procedure reads data from a SAS data set and writes it to an external data source. External data sources can include Microsoft Access Database, Excel files, Lotus spreadsheets, and delimited external files (in which columns of data values are separated by a delimiter such as a blank, comma, or tab). Unix SAS does not write to Excel, MS Access files…. Only .csv or tab delimited. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 23. PROC PRINTTO The PRINTTO procedure defines destinations for SAS procedure output and for the SAS log. By default, SAS procedure output and the SAS log are routed to the default procedure output file and the default SAS log file for your method of operation. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09 To do this Use this option provide a description for a SAS log or procedure output stored in a SAS catalog entry LABEL= route the SAS log to a permanent external file or SAS catalog entry LOG= combine the SAS log and procedure output into a single file LOG= and PRINT= with same destination replace the file instead of appending to it NEW route procedure output to a permanent external file or SAS catalog entry or printer. PRINT=
- 24. SAS Techies 2009 options nodate pageno= 1 linesize= 80 pagesize= 60 source; proc printto log=‘c:\temp.txt'; run ; data numbers; input x y z; datalines; 14.2 25.2 96.8 10.8 51.6 96.8 ; proc printto print='output-file' new; run ; proc print data=numbers; title 'Listing of NUMBERS Data Set'; run ; 11/13/09
- 25. PROC RANK < option(s) >; BY <DESCENDING> variable-1 <...<DESCENDING> variable-n > <NOTSORTED>; VAR data-set-variables(s) ; RANKS new-variables(s) ; The RANK procedure computes ranks for one or more numeric variables across the observations of a SAS data set and outputs the ranks to a new SAS data set. PROC RANK by itself produces no printed output. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 26. SAS Techies 2009 options nodate pageno= 1 linesize= 80 pagesize= 60 ; data elect; input Candidate $ 1 - 11 District 13 Vote 15 - 18 Years 20 ; datalines; Cardella 1 1689 8 Latham 1 1005 2 Smith 1 1406 0 Walker 1 846 0 ; proc rank data=elect out=results ties=low descending; by district; var vote years; ranks VoteRank YearsRank; run ; 11/13/09
- 27. PROC SUMMARY <option(s)> <statistic-keyword(s)>; BY <DESCENDING> variable-1<...<DESCENDING> variable-n> <NOTSORTED>; CLASS variable(s) </ option(s)>; FREQ variable; ID variable(s); OUTPUT <OUT=SAS-data-set><output-statistic-specification(s)> TYPES request(s); VAR variable(s)</ WEIGHT=weight-variable>; WAYS list; WEIGHT variable; Proc summary data=some; Output Out=something (drop=_freq_ _type_) sum=total; By year; Var Trx; Run; The SUMMARY procedure provides data summarization tools that compute descriptive statistics for variables across all observations or within groups of observations. The SUMMARY procedure is very similar to the MEANS procedure except for -- By default, PROC SUMMARY produces no display output, but PROC MEANS does produce display output. If you omit the VAR statement, then PROC SUMMARY produces a simple count of observations, whereas PROC MEANS tries to analyze all the numeric variables that are not listed in the other statements SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 28. PROC TRANSPOSE <DATA= input-data-set > <LABEL= label > <LET> <NAME= name > <OUT= output-data-set > <PREFIX= prefix >; BY <DESCENDING> variable-1 <...<DESCENDING> variable-n > <NOTSORTED>; COPY variable(s) ; ID variable ; IDLABEL variable ; VAR variable(s) ; Proc transpose data= some out=something prefix=sm; By CID; Var TRx; Id yrmo; Run; The TRANSPOSE procedure creates an output data set by restructuring the values in a SAS data set, transposing selected variables into observations. If no var statement then transposes All Variables. The TRANSPOSE procedure can often eliminate the need to write a lengthy DATA step to achieve the same result. Further, the output data set can be used in subsequent DATA or PROC steps for analysis, reporting, or further data manipulation. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 29. We will cover this at a later date!! What it does? We can develop a template that we can apply to enhance the appearance of an listing output. Adjusting the header, width, colors… similar to what a proc report call define statement highlighting can do. The TEMPLATE procedure enables you to customize the appearance of your SAS output. For example, you can create, extend, or modify existing definitions for various types of output: styles tables columns headers footers tagsets ODS then uses these definitions to produce formatted output. You can also use the TEMPLATE procedure to navigate and manage the definitions stored in templates stores. Here are some tasks that you can do with PROC TEMPLATE: edit an existing definition create links to an existing definition change the location where you write new definitions search for existing definitions view the source code of a definition SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 30. PROC DATASETS <option(s)>; AGE current-name related-SAS-file(s) APPEND BASE=<libref.>SAS-data-set <DATA=<libref.>SAS-data-set> <FORCE>; AUDIT SAS-file <(SAS-password)>; INITIATE <AUDIT_ALL=NO|YES<GENNUM= integer>)>; SUSPEND|RESUME| TERMINATE; CHANGE old-name-1=new-name-1 CONTENTS <option(s)>; COPY OUT=libref-1 <DATECOPY> <FORCE> <IN=libref-2> EXCLUDE SAS-file(s) SELECT SAS-file(s) DELETE SAS-file(s) EXCHANGE name-1=other-name-1 MODIFY SAS-file <(option(s))> FORMAT variable-list-1 <format-1> IC CREATE <constraint-name=> constraint IC DELETE constraint-name(s)| _ALL_; IC REACTIVATE foreign-key-name INDEX CENTILES index(s) INDEX CREATE index-specification(s) INDEX DELETE index(s) | _ALL_; INFORMAT LABEL variable-1=<'label-1'|' '> RENAME old-name-1=new-name-1 REPAIR SAS-file(s) SAVE SAS-file(s) The DATASETS procedure is a utility procedure that manages your SAS files. With PROC DATASETS, you can copy SAS files from one SAS library to another rename SAS files repair SAS files delete SAS files list the SAS files that are contained in a SAS library list the attributes of a SAS data set, such as the date when the data was last modified, whether the data is compressed, whether the data is indexed, and so on manipulate passwords on SAS files append SAS data sets modify attributes of SAS data sets and variables within the data sets create and delete indexes on SAS data sets create and manage audit files for SAS data sets create and delete integrity constraints on SAS data sets. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 31. SAS Techies 2009 options pagesize= 40 linesize= 80 nodate pageno= 1 source; libname health 'SAS-data-library'; proc datasets library=health nolist; modify group (label='Test Subjects' read=green sortedby=lname); index create vital=(birth salary) / nomiss unique; informat birth date7.; format birth date7.; label salary='current salary excluding bonus'; modify oxygen; rename oxygen=intake; label intake='Intake Measurement'; quit ; 11/13/09
- 32. The only difference between the APPEND and many other procedures and the APPEND (and similar) statements in PROC DATASETS is – the default for libref in the BASE= and DATA= arguments. For PROC APPEND, the default is either WORK or USER. For the APPEND statement, the default is the libref of the procedure input library. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
- 33. CATALOG DATASETS PLOT PMENU TRANTAB GCHART RUN-group processing enables you to submit a PROC step with a RUN statement without ending the procedure. You can continue to use the procedure without issuing another PROC statement. To end the procedure, use a RUN CANCEL or a QUIT statement. SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09
Editor's Notes
- #3: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #4: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #5: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #6: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #7: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #8: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #9: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #10: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #11: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #12: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #13: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #14: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #15: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #16: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #17: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #18: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #19: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #20: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #21: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #22: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #23: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #24: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #25: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #26: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #27: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #28: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #29: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #30: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #31: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #32: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #33: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
- #34: SASTechies.com Sharad C Narnindi Attic Technologies,Inc 2005
![SASTechies [email_address] http://www.sastechies.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasutilityprocedures-091113122750-phpapp02/85/Utility-Procedures-in-SAS-1-320.jpg)




![COMPUTE location < target > </ STYLE=< style-element-name > <[ style-attribute-specification(s) ]>>; LINE specification(s) ; . . . select SAS language elements . . . ENDCOMP ; A compute block can be associated with a report item or with a location (at the top or bottom of a report; at the top or bottom of a page; before or after a set of observations). SAS Techies 2009 11/13/09](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sasutilityprocedures-091113122750-phpapp02/85/Utility-Procedures-in-SAS-10-320.jpg)






















