Web Component Development Using Servlet & JSP Technologies (EE6) - Chapter 12 - Implementing Security
- 1. Web Component Development with Servlet & JSP Technologies (EE 6) Module-12: Implementing Security
- 2. Objectives Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: ● Describe a common failure mode in security ● Require that a user log in before accessing specific pages in your web application ● Describe the Java EE security model ● Require SSL encrypted communication for certain URLs or servlets
- 3. Relevance Discussion – The following question is relevant to understanding what technologies are available for developing web applications and the limitations of those technologies: ● If your application uses data that are private to your company or your users, how can you be sure that malicious users cannot inappropriately access or modify those data?
- 4. Security Considerations Every application that is accessible over the web must consider security. Your site must be protected from attack, the private data of your site’s users must be kept confidential, and your site must also protect the browsers and computers used to access your site. This module introduces the following kwy points: ● Confusion of code and data ● Encryption of data in transit over the network ● Authentication and authorization of users
- 5. Confusion of Code and Data: SQL Injection Example Your application might take the text of the item code, provided by the user, and paste it into an SQL statement like this: SELECT count from ITEMTABLE where itemcode=”XXXXXX”; In this case, the XXXXXX would be replaced using the data provided by the user in the field of the form. This looks fine so far, but consider what happens if the user provides the following as the itemCode field in the form: unk”; DROP TABLE ITEMTABLE;
- 6. Confusion of Code and Data: SQL Injection Example Now the result of pasting this “data” into the query is this: SELECT count from ITEMTABLE where itemcode=”unk”; DROP TABLE ITEMTABLE;”;
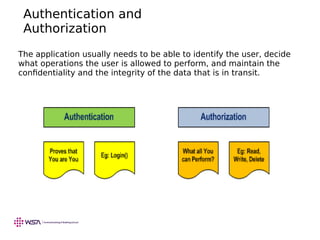
- 7. Authentication and Authorization The application usually needs to be able to identify the user, decide what operations the user is allowed to perform, and maintain the confidentiality and the integrity of the data that is in transit.
- 10. Authenticating the Caller Caller authentication is the process of verifying what the user’s identity is, and consists of the following two steps. ● Determine the identity claimed by the user ● Verify that the user is who they claim to be (Authenticate the user)
- 11. Establishing User Identities The process of caller authentication requires that users of an application be known in advance to the security system. The Java EE specification recognizes the following two types of user identities: ● Principals: A principal is an authenticated user in the application security domain. That is, a principal is identifyable to, and can be authenticated by, a JAAS authentication mechanism deployed in the web container. ● Roles: When writing an application, the users, and the principals to which they will map, are usually not known. Nevertheless, you must design a security model that will specify that certain categories of user will have certain rights and be denied other rights.
- 12. Examining the Java EE Authorization Strategies ● The primary purpose of the Java EE security model is to control access to business services and resources in the application. ● The Java EE security model provides two complementary strategies for access control: ● Programmatic access control and declarative access control. ● Both strategies assume that the user has been authenticated by the application server, and the roles of which the user is a member can therefore be determined by the web container.
- 13. Using Declarative Authorization Declarative authorization for web applications involves the following Tasks: ● Collection of user credentials into a credentials database ● Declaration of roles ● Mapping users to roles ● Specification of role requirements for access to URLs
- 14. Creating a Credential Database Creating the collection of user credential is entirely dependent on the web containerin use. The lab for tis module will show you the most basic way to achieve this in Netbeans/ Glassfish you are using.
- 15. Declaring Security Roles Security roles are declared in the web.xml deployment descriptor, using the <security-role> element. This element lives at the first level of the web.xml file, as a direct child of the <web-app> element. <security-role> <description>...</description> <role-name>...</role-name> </security-role>
- 17. Using Programmatic Authorization Programmatic authorization is the responsibility of the bean developer. The following methods in the HttpServletRequest support programmatic authorization: ● boolean isUserInRole(String role) ● Principal getUserPrincipal() ● Programmatic authorization is more expressive than the declarative approach, but is more cumbersome to maintain, and because of the additional complexity, more error prone.
- 18. Enforcing Encrypted Transport Provided the server has been configured with a public key certificate, you can require that communication between client and server be encrypted. In this case, an additional element, <user-data-constraint> will be added in the web.xml file
- 19. Web Stack Academy (P) Ltd #83, Farah Towers, 1st floor,MG Road, Bangalore – 560001 M: +91-80-4128 9576 T: +91-98862 69112 E: [email protected] www.webstackacademy.com