Weblogic Server Overview Weblogic Scripting Tool
- 1. WebLogic Server Overview WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) May 2008
- 2. © 2007 Oracle Corporation – Proprietary and Confidential The forward-looking statements in the following are intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle.
- 3. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 4. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
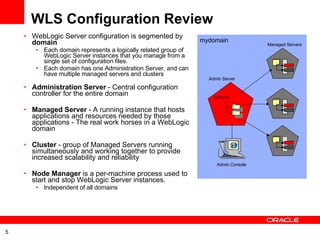
- 5. WLS Configuration Review WebLogic Server configuration is segmented by domain Each domain represents a logically related group of WebLogic Server instances that you manage from a single set of configuration files. Each domain has one Administration Server, and can have multiple managed servers and clusters Administration Server - Central configuration controller for the entire domain Managed Server - A running instance that hosts applications and resources needed by those applications - The real work horses in a WebLogic domain Cluster - group of Managed Servers running simultaneously and working together to provide increased scalability and reliability Node Manager is a per-machine process used to start and stop WebLogic Server instances. Independent of all domains mydomain Admin Server Managed Servers config.xml Admin Console
- 6. Two-Phase Configuration Changes Changes activated in batches: Reliability, consistency: Make (related) changes as a group Validate before making the change Activate or Roll back as a single unit (all changes on all servers) General process: Get an edit lock make changes changes are stored in the pending directory activate your changes (with implicit validation through the Admin Console or WLST) changes are distributed to servers in the domain Two phases: prepare and commit Prepared on all servers; any failures will cause total rollback
- 7. Administration Tools Configuration Wizard GUI/scriptable tool to create and extend WebLogic domains Template based Administration Console Browser-based tool for configuring and monitoring domains, deploying applications, and controlling servers WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Script or command line tool to do the same thing as the Administration Console and Configuration Wizard Note that we will cover details on WLST in a separate document weblogic.Admin Deprecated command line tool for configuring a domain Recommend using WLST instead weblogic.Deployer Command line tool for deploying applications
- 8. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 9. WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Scripting tool for administering a domain (create, configure, manage, monitor, deploy applications) Based on Jython – pure Java implementation of Python Great for automating repetitive tasks Heavily used by customers and within BEA
- 10. Interaction Modes Interactive enter a command and view the response at a command-line prompt In online mode: shell maintains a persistent connection to a WLS instance Script text file with a .py file extension executed using Jython commands for running scripts invoke a sequence of WLST commands without requiring your input Embedded instantiate the WLST interpreter in your Java code execute WLST commands from a Java program
- 11. Connection Modes Offline : analogous to the Configuration Wizard Uses the Offline Configuration Framework Also used by the Configuration Wizard Consistent results when using either tool read and write access to the configuration data that is persisted in the domain’s config directory or in a domain template JAR Intended to create a domain or modify a non-running domain Used during WLS install to create samples domains Online : analogous to the Administration Console JMX client Interacts with a server’s MBeans Intended as a runtime management tool: configuration, management, deployment, monitoring
- 12. WLST Offline Can/Can’t Do Can Do: Create/modify templates Create domains Extend domains Access and modify the configuration for an offline domain Can’t Do: View runtime performance data Modify security data
- 13. WLST Online Can/Can’t Do Can Do: Change configuration View runtime data Deploy applications Start and stop servers Can’t Do: Create a domain (must be offline mode)
- 14. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 15. WLST Offline Uses the Offline Configuration Framework Also used by the Configuration Wizard; Consistent results when using either tool Uses domain templates to create a domain Several shipped with WLS Create your own using Template Builder Modify an existing template using WLST Offline Intended to create a domain or modify a non-running domain Used during WLS install to create samples domains Used by WL Platform products for creating domain configurations (use specific templates for each product) Note: Do not use WLST offline to manage the configuration of an active domain. Offline edits are ignored by running servers and can be overwritten by JMX clients such as WLST online or the WebLogic Server Administration Console.
- 16. WLST Offline – Two Models: Templates and Scripts Templates (put everything in the template) Use Template Builder to capture current domain configuration and artifacts into a rich template Use that template to create new domains, migrate from dev to production Bundles required files Used by WebLogic Platform products Scripts (put little in the template and most in scripts) Use more basic templates for domain creation Use WLST scripts along with some predefined or custom domain templates to create the target domain Modify/customize domain configuration through scripts, and effectively track configuration changes through source control Recommended for: Out of the box config for a layered product Reason: domain is self-contained Recommended for: Customer configuration migration QA automation Reason: easily make and track changes to a domain config
- 17. Starting WLST Setup the environment: setWLSEnv.sh/cmd – sets path and classpath Adds WebLogic Server classes to the CLASSPATH and WL_HOME\server\bin to the PATH Invoke WLST: java weblogic.WLST or java weblogic.WLST c:\myscripts\myscript.py Starts in Offline mode
- 18. Creating a Domain (WLST Offline) Syntax createDomain(domainTemplate, domainDir, user, password) Example wls:/offline> createDomain('c:/bea/wlserver_103/common/templates/domains/wls.jar','c:/mydomain', 'weblogic', 'weblogic')
- 19. Changing a Domain in WLST Offline closeDomain() Close the domain for editing updateDomain() Save Various commands Make changes (optional) addTemplate( templateFileName ) Extend the domain (optional) readDomain( domainDirName ) Open a domain for editing Syntax Step
- 20. Browsing and Editing in WLST Offline Browsing: cd() , ls() Editing: Add an application to a domain: addTemplate(templateFileName) Create and delete management objects: create(name, childMBeanType) delete(name, childMBeanType) Get and set attribute values: get(attrName) set(attrName, value) Set domain creation or update options: setOption(optionName, value) Load SQL files into a database: loadDB(dbVersion, connectionPoolName)
- 21. WLST Offline – accessing a domain Offline – reading a domain: readDomain('c:/bea/user_projects/domains/medrec') Domain configuration data is a collection of XML documents that expresses a hierarchy of management objects WLST represents this hierarchy as a file system The root is the management object that represents the WebLogic Server domain (domain directory) Each managed-object type is a sub directory of the root Each instance of the type is a subdirectory under the type directory Each management attribute and operation is a file within a directory wl_server JDBCSystemResource examples-demoXA Name Target
- 22. Syntax Command names and arguments are case sensitive. Enclose arguments in single or double quotes. For example, 'newServer' or "newServer". If you specify a backslash character (\) in a string, either precede the backslash with another backslash or precede the entire string with a lower-case r character. For example when specifying a file pathname that contains a backslash: readTemplate('c:\\userdomains\\mytemplates\\mytemplate.jar') or readTemplate(r'c:\userdomains\mytemplates\mytemplate.jar') When using WLST offline, the following characters are not valid in names of management objects: period (.), forward slash (/), or backward slash (\). If you need to cd to a management object whose name includes a forward slash (/), surround the object name in parentheses. For example: cd('JMSQueue/(jms/REGISTRATION_MDB_QUEUE)')
- 23. Demo Create a basic WLS domain Read the domain Add a Managed Server
- 24. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, Diagnostics Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 25. WLST Online Analogous to the Administration Console, but without the GUI JMX client; maintains a persistent connection Interacts with a server’s/domain’s MBeans Intended as a runtime management tool: configuration, management, deployment, monitoring
- 26. WLST Online – connecting to a domain Setup the environment: setWLSEnv.sh (in WL_HOME\server\bin) Adds WebLogic Server classes to the CLASSPATH and WL_HOME\server\bin to the PATH Invoke WLST: java weblogic.WLST Starts in Offline mode Connect to a domain: wls:/offline> connect('weblogic','weblogic','localhost:7001')
- 27. Traversing MBean Trees Simpler than JMX – no need to know the JMX object name MBeans are hierarchical, similar to a file system, with the DomainMBean at the top of the tree Multiple MBean trees (described later) Use commands similar to Unix commands to traverse the tree: cd() , ls() Syntax is the same as with WLST Offline Domain MBean (root) |- - - MBean type (ServerMBean) |- - - MBean instance (ManagedServer1) |- - - MBean attributes & operations (AutoRestart) |- - - MBean instance (MedRecServer) |- - - MBean attributes & operations (StartupMode)
- 28. Available MBean Trees domainConfig configuration hierarchy of the entire domain; represents the configuration MBeans in RuntimeMBeanServer read only serverConfig configuration hierarchy (configuration MBeans) of the server your are connected to read only domainRuntime hierarchy of runtime MBeans for the entire domain read only serverRuntime hierarchy of runtime MBeans for the server you are connected to read only edit writable domain configuration with pending changes; represents the configuration MBeans in the EditMBeanServer jndi read-only JNDI tree for the server you are connected to custom list of custom MBeans can be hierarchical/grouped if MBeans use namespaces appropriately
- 29. Switching Between Trees Use the appropriate command to move to a different tree domainConfig() serverConfig() domainRuntime() serverRuntime() edit() jndi() custom() When returning to a tree, you return to the place where you left, except custom and jndi (goes to the root)
- 30. Changing Configuration in WLST Online wls:/wl_server/edit !> activate() Activate/distribute, release lock wls:/wl_server/edit !> save() Save (and implicitly validate) your changes wls:/wl_server/edit !> svr = cmo.createServer("managedServer") wls:/wl_server/edit !> svr.setListenPort(8001) wls:/wl_server/edit !> svr.setListenAddress("my-address") Make changes wls:/wl_server/edit> startEdit() Get an edit lock wls:/wl_server/domainConfig> edit() Change to the edit tree Syntax Step
- 31. Current Management Object CMO variable – current management object Java object that serves as a proxy for direct access to the WLS MBean Makes it easy to directly interact with the MBean – get and set attributes, other commands Always set to the current WLST path Only available for WLS MBeans, not custom MBeans Example: wls:/mydomain/edit> cmo.setAdministrationPort(9092) (This example changes the Administration Port in the Domain MBean)
- 32. Deploying an Application In Online mode, use the deploy command to deploy applications Syntax: deploy(appName, path, [targets], [stageMode], [planPath], [options]) deploy("mainWebApp","C:/samples/server/examples/build/mainWebApp“,”server-1”) Note: You do not need to be in an edit session to deploy applications. Reminder: in Offline mode, add an application using an extension template
- 33. Common Online Deployment Commands deploy Deploy an application to a WebLogic Server instance. distributeApplication Copy the deployment bundle to the specified targets. redeploy Redeploy a previously deployed application startApplication Start an application, making it available to users. stopApplication Stop an application, making it unavailable to users. undeploy Undeploy an application from the specified servers. updateApplication Updates an application configuration using a new deployment plan. Returns a WLSTProgressObject to track the progress of the command You query the progress object to get the status; (pull, not push)
- 34. Interacting with the Node Manager You can use WLST to do the following with Node Manager: Start a Node Manager. Connect to a Node Manager, then use the Node Manager to start and stop servers on the machine on which Node Manager is running. Preferred method: Use the Node Manager to start the Administration Server Connect to the Admin Server Start Managed Servers using the standard WLST lifecycle commands Enables you to start all servers in the domain with one connection, regardless of which machines host the Managed Servers
- 35. Common WLST Node Manager Commands startNodeManager – starts Node Manager on the current machine. nm - Determines whether WLST is connected to Node Manager nmConnect - Connects WLST to Node Manager to establish a session. (Specify domain and credentials) nmDisconnect - Disconnects WLST from a Node Manager session. nmStart - Starts a server in the current domain using Node Manager. nmKill - Kills the specified server instance that was started with Node Manager.
- 36. Managing Server Lifecycle with WLST You can also manage server lifecycle through WLST without directly using Node Manager. The following WLST lifecycle commands are available: startServer - Start the Administration Server. (Online or Offline) start - Start a Managed Server instance or a cluster using Node Manager. suspend - Suspend a running server. resume - Resume a server instance that is suspended or in ADMIN state. shutdown - Gracefully shut down a running server instance or cluster. migrate - Migrate services to a target server within a cluster.
- 37. Demo: WLST Online Start Node Manager Start the Administration Server in the new domain Create a Managed Server
- 38. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 39. Customizing WLST Add custom commands by: Creating the commands in a .py file Add the file to the WLST home directory WLST home directory – WL_HOME/common/wlst (by default) Add custom commands to another namespace: Create the commands in a .py file Add file to the WLST_home/ lib directory Execute commands using <module>.<command> http://e-docs.bea.com/wls/docs100/config_scripting/using_WLST.html#wp1093407
- 40. Support for Custom MBeans You can register custom MBeans and then access them using WLST in the “custom” MBean tree WLST treats all non-WebLogic Server MBeans as custom MBeans: Instead of arranging custom MBeans in a hierarchy, WLST organizes and lists custom MBeans by JMX object name. All MBeans with the same JMX domain name are listed in the same WLST directory. For example, if you register all of your custom MBeans with JMX object names that start with mycompany:, then WLST arranges all of your MBeans in a directory named mycompany. Custom MBeans cannot use the cmo variable because a stub is not available. Custom MBeans are editable, but not subject to the WebLogic Server change management process. You can use MBean get, set, invoke, and create and delete commands on them without first entering the startEdit command.
- 41. Agenda WLS Configuration Review Intro to WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) WLST Offline WLST Online JMX Client Deployment (JSR-88) Client Miscellaneous Clients - Node Manager, JNDI, etc. Customizing WLST Tips and Best Practices
- 42. Reduce WLST Startup Time Cache directory for scanned files: java -Dpython.cachedir="c:\demo\wlst_cache" weblogic.WLST New startup option in WLS 10.3: -skipWLSModuleScanning Default behavior: on startup, WLST scans weblogic.jar and all of the classes referenced in its manifest classpath With this option, files in the modules directory are not scanned If needed, you can manually add files to the classpath
- 43. Some Standard Best Practices Parameterize your script and use the preamble for assigning variables easily assigned and changed Before creating something, check to see that it exists try: cd(‘/servers/’ + serverID) print ‘The server ‘ + serverID + ‘ already exists’ exit() except WLSTException: pass
- 44. Redirecting Error and Debug Output to a File To redirect WLST information, error, and debug messages from standard out to a file, enter: redirect(outputFile,[toStdOut]) This command also redirects the output of the dumpStack() and dumpVariables() commands. For example, to redirect WLST output to the logs/wlst.log file under the directory from which you started WLST, enter the following command: wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> redirect('./logs/wlst.log')
- 45. Run a WLST Script within a Domain Template The configuration framework can execute WLST offline scripts embedded in domain/extension templates (e.g., final.py). Very useful in satisfying some complex auto-configuration requirements (e.g., proper targeting of various resources)
- 46. Running WLST from Ant WebLogic Server provides a custom Ant task, wlst, that invokes a WLST script from an Ant build file. You can create a WLST script (.py) file and then use this task to invoke the script file, or you can create a WLST script in a nested element within this task. http://e-docs.bea.com/wls/docs100/config_scripting/using_WLST.html#wp1093337
- 47. More Resources WLST Guide: http://e-docs.bea.com/wls/docs100/config_scripting/index.html Dev2Dev Articles and Projects: https://wlst.projects.dev2dev.bea.com/ http://dev2dev.bea.com/pub/a/2005/01/wlst_offline.html http://dev2dev.bea.com/pub/a/2005/05/automatic_provisioning.html Template Builder: http://e-docs.bea.com/common/docs100/tempbuild/index.html Samples (installed with WLS 10.3): wlserver_103\common\templates\scripts\wlst wlserver_103\common\wlst\lib samples\server\examples\src\examples\wlst\online samples\server\examples\src\examples\diagnostics\wldfprofiles\src samples\server\examples\src\examples\jdbc\multidatasource
- 48. A Q &






























![Deploying an Application In Online mode, use the deploy command to deploy applications Syntax: deploy(appName, path, [targets], [stageMode], [planPath], [options]) deploy("mainWebApp","C:/samples/server/examples/build/mainWebApp“,”server-1”) Note: You do not need to be in an edit session to deploy applications. Reminder: in Offline mode, add an application using an extension template](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicserveroverviewweblogicscriptingtool012282527528444349-124139770612-phpapp01/85/Weblogic-Server-Overview-Weblogic-Scripting-Tool-32-320.jpg)











![Redirecting Error and Debug Output to a File To redirect WLST information, error, and debug messages from standard out to a file, enter: redirect(outputFile,[toStdOut]) This command also redirects the output of the dumpStack() and dumpVariables() commands. For example, to redirect WLST output to the logs/wlst.log file under the directory from which you started WLST, enter the following command: wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> redirect('./logs/wlst.log')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicserveroverviewweblogicscriptingtool012282527528444349-124139770612-phpapp01/85/Weblogic-Server-Overview-Weblogic-Scripting-Tool-44-320.jpg)



