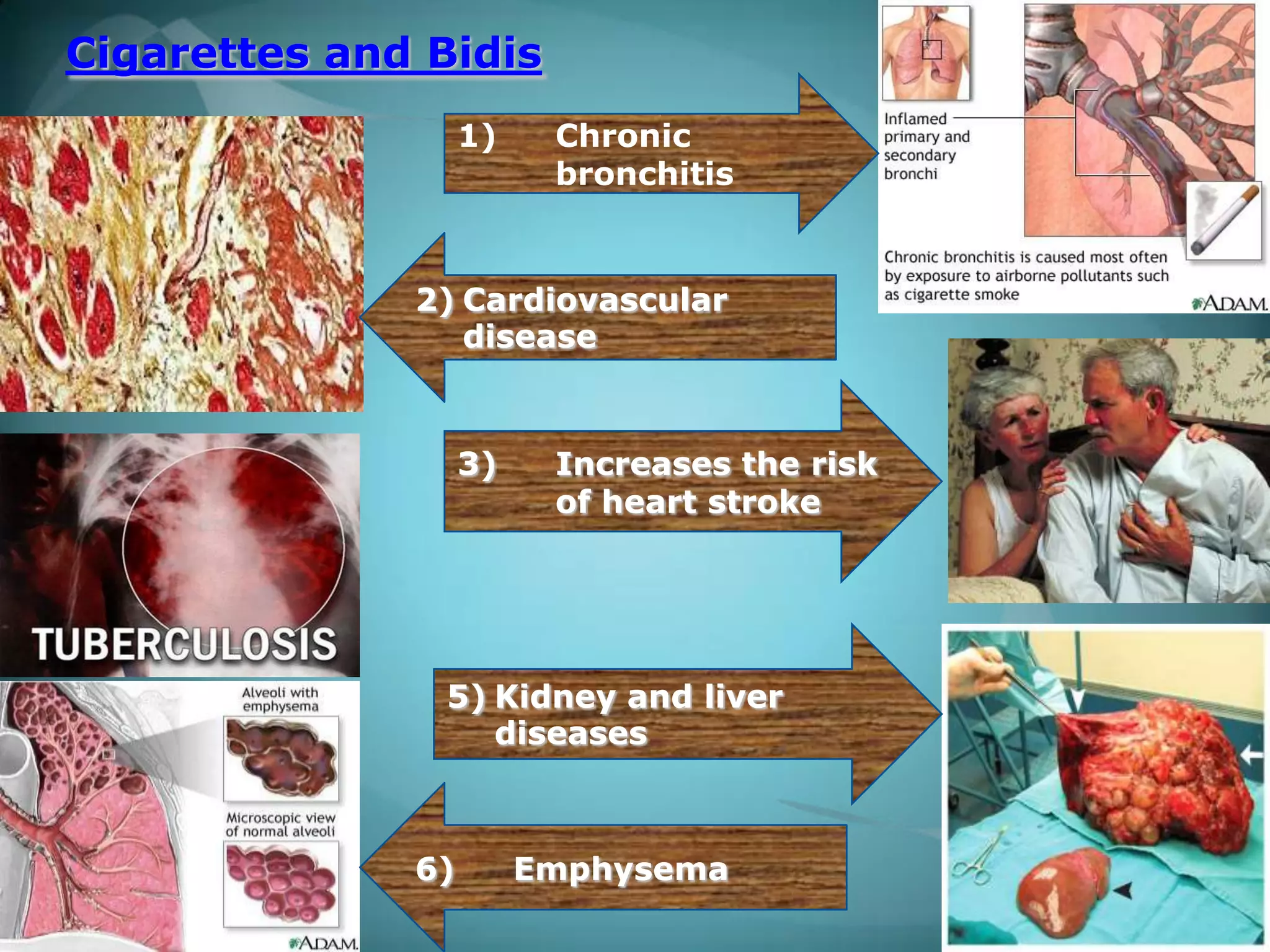
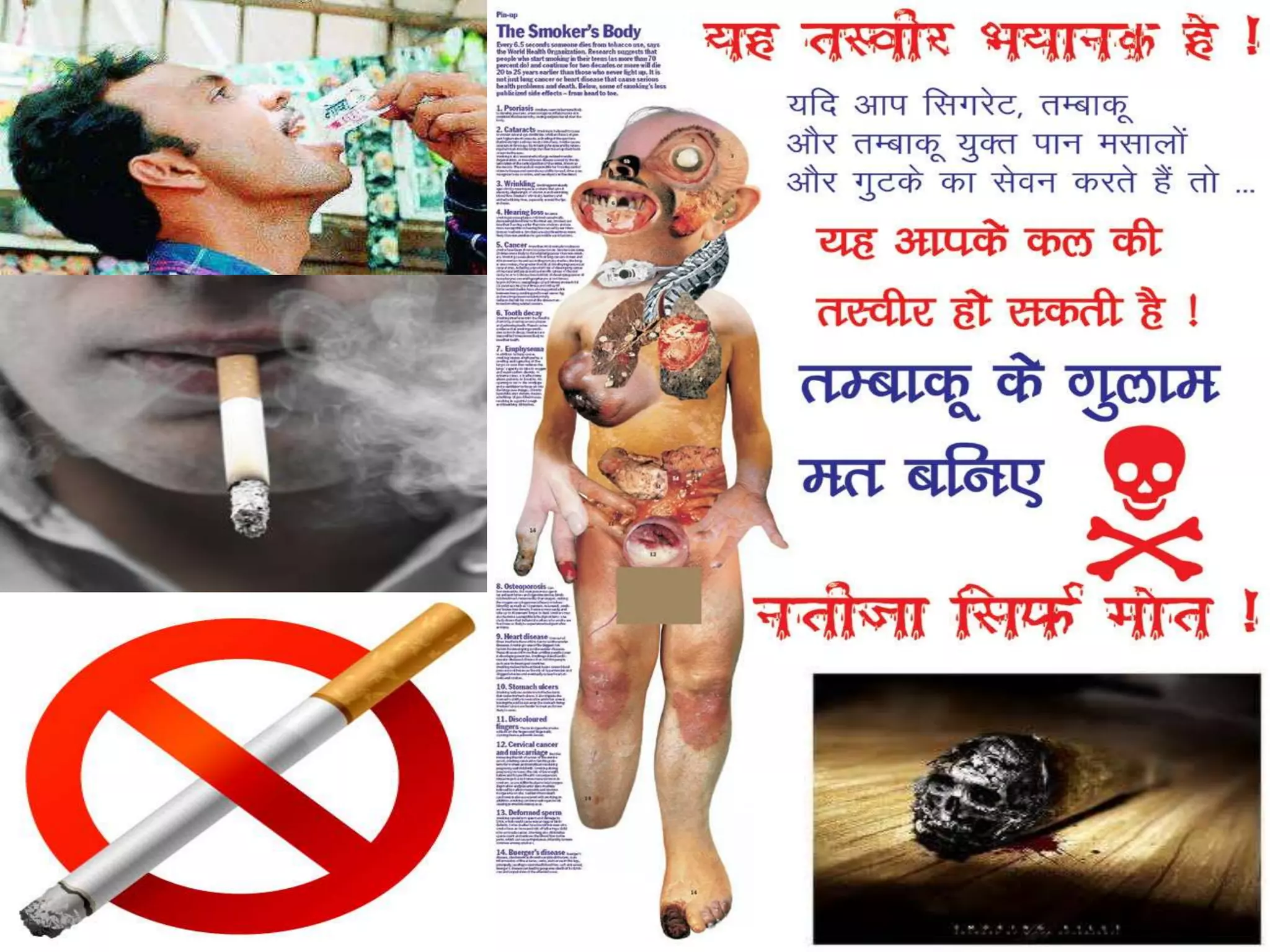
The document discusses World No Tobacco Day, which is observed annually on May 31st to discourage tobacco use and its health hazards. It aims to help users refrain from tobacco for 24 hours. The summary highlights the negative health impacts of tobacco, including that it kills over 800,000 people yearly in India from diseases like cancer. It also notes that tobacco consumption disproportionately affects the poor and that increased taxes could generate billions for public health programs while reducing use.