Writing DSL's in Scala
- 1. Using Scala for building DSL’s Abhijit Sharma Innovation Lab, BMC Software 1
- 2. What is a DSL? • Domain Specific Language • Appropriate abstraction level for domain - uses precise concepts and semantics of domain • Concise and expressive for a specific domain – not general purpose • Domain experts can communicate, critique better with programmers and amongst themselves • Math – Mathematica, UI – HTML, CSS, Database - SQL 2
- 3. DSL’s at large - Ant • Build tool Ant is an XML based DSL • Task to build a jar with a dependency on task compile 3
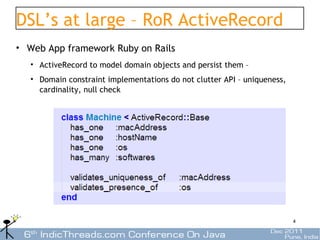
- 4. DSL’s at large – RoR ActiveRecord • Web App framework Ruby on Rails • ActiveRecord to model domain objects and persist them – • Domain constraint implementations do not clutter API – uniqueness, cardinality, null check 4
- 5. Cloud Computing DSL • Audience – Non tech savvy cloud end users • DSL - English language sentence for requesting a machine with technical and price specifications 5
- 6. Cloud Computing DSL - Model • Domain Concept – Machine • Technical specifications - cpu, os • Pricing specifications - spot price, pricing strategy – default or define inline Machine •cpu:Cpu •os:String •spotPrice:Int Cpu •arch: String •cpus: Int 6
- 7. Cloud Computing Java DSL • Builder pattern - Method Chaining Fluent Interface 7
- 8. Cloud Computing Java DSL - Pattern • Builder Pattern - Method Chaining 8
- 9. Cloud Computing Java DSL - Issues • Syntax restrictions, verbosity – parenthesis, dot, semi- colons • Non Domain complexity – Builder • No Inline strategy – no higher order functions 9
- 10. DSL Classification • Internal DSL • Embedded in a host language like Ruby, Scala, Groovy – use their features • Bound by host language syntax and semantics • External DSL – standalone developed ground up • Define syntax and semantics as a grammar • Use tools like lexical analyzers, parsers, interpretation, code generators 10
- 11. Internal DSL Classification • Internal DSL • Generative - Ruby, Groovy Techniques like runtime metaprogramming • Meta Objects – inject new behaviour at runtime • Embedded in host language • Smart API – Method chaining – Java etc. • Syntax tree manipulation – Groovy, Ruby libraries • Type Embedding – Scala – statically typed, type constraints, no invalid operations on types 11
- 12. Scala Language • Scala is a “scalable” language • JVM based – leverage libs, JVM perf, tools, install base etc • Mixed Paradigm – Object Oriented + Functional Programming • Object Oriented Programming - Improves on Java OOP (Traits, no statics, advanced types) 12
- 13. Scala Language • Functional Programming - Functions • No side effects and immutable variables • “First-class” citizens - Can be assigned, passed around, returned • Higher order functions promote composition using other more primitive functions • Lots of powerful features – discussed later • Statically Typed – Type Safe DSL 13
- 14. Scala – Readable style - Syntax • Elegant, succinct syntax unlike verbose Java • Optional dots, Operators are methods • Syntactic sugar method takes one/zero argument, drop period and parentheses 14
- 15. Scala – Readable style - Inference • Type inference minimizes the need for explicit type information – still Type safe 15
- 16. Scala - Implicits • Implicit Conversions – wrap original type e.g. Integer • Generative expression - Implicit conversion converts the 1, an Int, to a RichInt which defines a ‘to’ method • Lexically scoped – Unlike other languages like Groovy where such modifications are global in scope • Implicit argument to function – don’t need to pass – Concise syntax 16
- 17. Scala - Higher order functions • Functions as parameters or return values • Flexible mechanism for composition • Anonymous Functions 17
- 18. Scala - Higher order functions • Currying – set some parameters – concise & powerful 18
- 19. Scala – Functional Combinators • Calculate the total price of all Linux machines – uses several combinators – filter, map, foldLeft – all take other functions as predicates 19
- 20. Scala – Cloud Computing DSL - Relook 20
- 21. Scala – Cloud Computing DSL - Implicits • Consider excerpt - 8 cpus “64bit” – Using Implicit conversion we get the object representing the CPU - Cpu(8, 64bit) 21
- 22. Scala – Cloud Computing DSL – E2E DSL - new Machine having (8 cpus "64bit") with_os “Linux“ • Implicit Conversion • Method Chaining – Builder pattern – without the cruft • Syntactic sugar no parenthesis, dot, brackets 22
- 23. Scala – Cloud Computing DSL – Functions • Using Higher Order Functions – Flexible pricing • Spot Price Threshold - Inline strategy - Anonymous Functions 23
- 24. Scala - Pattern Matching • Pattern Matching – Switch Case on Steroids • Cases can include value, types, wild-cards, sequences, tuples, deep inspection of objects 24
- 25. Scala - Pattern Matching &Case Classes • Case Classes – simplified construction and can be used in pattern matching • Pattern matching on Case Classes • Deep pattern matching on object contents • Make good succinct powerful DSL 25
- 26. Scala - Pattern Matching – Visitor Pattern • Pattern match and case classes – extensible visitor • Different operations on tree • Expression Evaluation • Prefix Notation • Very expressive, flexible and concise code 26
- 27. Scala – For Comprehensions • Loop through Iterable sequences and comprehend/compute something • E.g. Filter 32, 64 bit architectures 27
- 28. Scala – For Comprehensions + Option • Wrap vars & function returns as Option – Null Checks, resilient programming • Option sub classes : None and Some • Options with for comprehensions, automatic removal of None elements from comprehensions 28
- 29. Scala – For Comprehensions + Option • Validate and audit machines • Using Options with for comprehensions eliminate the need for most “null/empty” checks. • Succinct, safe DSL with uncluttered API 29
- 30. External DSL in Scala DSL - having (8 cpus "64bit") with_os "Linux" at_spot_price 30 • Parser Combinator library – available as a library on host language – Scala • External Parser Generators like JavaCC – use tools to generate code for tokenizing, parsing • Parser Combinator Specification is like a BNF grammar 30
- 31. External DSL in Scala • Each function is a parser - works on a portion of the input, parses it and may optionally pass on the remaining part to the next parser in the chain via the combinator • Several combinators provided by the library like ‘~’ the sequencing combinator composes two parsers sequentially. • Optional function application combinator (^^) can work, applying the function on the result of the sequencing combinator. 31
- 32. Thanks [email protected] Twitter : sharmaabhijit Blog : abhijitsharma.blogspot.com 32
- 33. Scala - Traits • Traits are collections of fields and behaviors that you can extend or mixin to your classes. • Modularize these concerns, yet enable the fine-grained “mixing” of their behaviors with other concerns at build or run time – Callbacks & Ordered • Traits can be mixed-in at class level or at instance creation • AOP Pervasive concerns - Logging, Ordering, Callback Handling 33