Computer Networks Lecture Notes 01
- 1. B.Tech IV Sem CSE ‘C’; Scheme 2017; AY: 2020_21 COMPUTER NETWORKS Dr. C. Sreedhar
- 2. Unit 1 Introduction: Data Communications, Networks, Protocols and Standards OSI Model TCP/IP Protocol Suite Addressing: Physical, Logical, Port Physical Layer and Transmission Media Analog and Digital: Data; Signals Digital Signals: Bit rate, Bit length, Transmission of digital signals Transmission Impairments: Attenuation, Distortion, Noise Performance: Bandwidth, Throughput, Latency, Jitter
- 3. Unit 2 Data Link Layer Error detection: Block coding Error correction: Hamming distance, minimum hamming distance, CRC, Checksum Framing Flow and error control
- 4. Unit 3 Design Issues Store and forward; Services to Transport layer Connectionless and connection oriented services Comparison of virtual circuits; Datagram subnets Routing Algorithms Optimality principle Shortest Path Routing, Flooding Distance Vector Routing, Link State Routing; Hierarchical Routing Broadcast and Multicast Routing
- 5. Unit 4 Congestion Control Principles, congestion prevention policies Congestion control in virtual circuits and datagram subnets Load shedding, Jitter control Internetworking Concatenated virtual circuits, Connectionless internetworking Tunnelling, Internetwork routing; Fragmentation, IP :Protocol, Address; Internet Control Protocols Gateway routing protocols: OSPF, BGP
- 6. Unit 5 UDP; TCP: Service model, protocol, segment header, connection management; Transmission policy Congestion control and timer management Application Layer DNS Namespace; Resource Records Name Servers
- 7. Unit 1 Data Communications Definition Components of DC Data representation Data flow Networks Network criteria Types of connections Categories of topology Network Models Protocols and Standards Definition Standards
- 8. Data Communication: Definition Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
- 9. Data Communication The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on four fundamental characteristics: Delivery: deliver data to the correct destination accuracy: system must deliver the data accurately Timeliness: system must deliver data in a timely manner Jitter: refers to the variation in the packet arrival time
- 10. Data Communication: Components Five components 1. Sender 2. Message 3. Transmission media 4. Protocol 5. Receiver Protocol is a set of rules that govern data communications. It represents an agreement between the communicating devices.
- 11. Data Communication: Components Five components 1. Sender 2. Message 3. Transmission media 4. Protocol 5. Receiver Protocol is a set of rules that govern data communications. It represents an agreement between the communicating devices.
- 12. Data Representation Text: Text is represented as a bit pattern. Unicode uses 32 bits to represent a symbol or character Numbers Numbers are also represented by bit patterns. number is directly converted to a binary number Images Images are also represented by bit patterns. image is composed of a matrix of pixels each pixel is assigned a bit pattern. Audio and Video Sampling rate Analogue signal Time Amplitude
- 13. Data Flow Communication between two devices can be simplex or half-duplex, or full-duplex
- 14. Network A network is a set of devices (nodes) connected by communication links. A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network. A link can be a cable, air, optical fiber, or any medium which can transport a signal carrying information.
- 15. Network Criteria Performance: Measured: transit time and response time Transit time: time required for a message to travel from AB Response time: elapsed time between inquiry and response Evaluated using two metrics: throughput and delay (more throughput and less delay). Reliability: measured by the frequency of failure Security Network security issues include protecting data from unauthorized access
- 16. • Point to Point - single transmitter and receiver Ex: Television remote control • Multipoint - multiple recipients of single transmission • Ex: Telephone Line Types of Connections
- 17. Physical topology topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically
- 18. Mesh topology every device has a dedicated point-to- point link to every other device. Total no. of connections??? n(n-1)/2 Advantages Manages high amounts of traffic Withstands failure of link. Adding nodes easily added Can avoid problems, malicious users Disadvantages amount of cabling number of I/O ports installation and reconnection are difficult practical example: connection of telephone regional offices
- 19. A star topology each device needs only one link and one I/O port to connect it to any number of others Advantages less expensive than a mesh topology. robust: If one link fails, only that link is affected Disadvantages If the hub goes down, the whole system goes down. The star topology is used in local- area networks (LANs)
- 20. bus topology Nodes are connected to the bus cable by drop lines and taps A drop line is a connection running between device and main cable. A tap is a connector One long cable acts as a backbone to link all the devices in a network Advantages bus uses less cabling than mesh or star topologies Disadvantages •difficult reconnection and fault isolation •Signal reflection at the taps can cause degradation •a fault or break in the bus cable stops all transmission
- 21. Ring topology
- 22. Ring Topology Each device has a dedicated point to point connection with only two devices on either side of it. Signal is passed along the ring in one direction till it reaches destination Each device has a repeater When a device receives signal to be passed, its repeater regenerates bits and passes along. Advantages Easy to install and reconfigure Fault isolation is simple Disadvantages Unidirectional traffic Break in the ring disables entire network; solved by dual ring
- 23. A hybrid topology: a star backbone with three bus networks Main Star topology with each branch connecting several stations in a bus topology
- 24. Standards Set of rules for data communication that are needed for exchange of information guaranteeing national and international interoperability of data. Two standards: De facto: By fact or by convention Ex: Google, IBM De Jure: By law or by regulations Ex: ANSI, ISO, IEEE
- 25. Standard Committees International Standards Organization (ISO): Ex: ISO 9000 family: Quality Management; ISO 6: Camera film speed International Telecommunications Union (ITU) Ex: ISDN, WDM, DSL American National Standards Institute (ANSI) ANSI C; ANSI Z1.4: Sampling Plan Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11: WLAN; IEEE 802.8: Fiber optic; IEEE 802.3: Ethernet Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) RFC; IPR
- 26. Protocol Protocol is a set of rules that govern all aspect of data communication between computers on a network. regulate the following characteristics of a network: access method, allowed physical topologies, types of cabling, and speed of data transfer. Ex: HTTP, FTP, IP, UDP, PPP, TCP, ARP, RARP
- 27. Protocol The key elements of a protocol are syntax, semantics and timing. 64 bits 8 bits 8 bits Sender address Receiver address data
- 28. Network Models OSI Model TCP/IP Model OSI Model: The Open Systems Interconnection reference model. Introduced in 1984 by International Standards Organization (ISO). TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol Developed in the year 1970s, adopted as protocol standard for ARPANET (predecessor of internet) in 1983
- 29. OSI model
- 30. An exchange using the OSI model
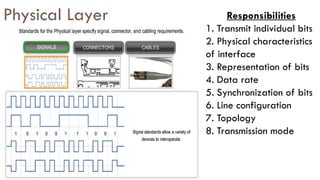
- 31. Physical Layer Responsibilities 1. Transmit individual bits 2. Physical characteristics of interface 3. Representation of bits 4. Data rate 5. Synchronization of bits 6. Line configuration 7. Topology 8. Transmission mode
- 32. Physical layer
- 33. Data link Layer: Functions Moving frames from one hop to the next hop Framing Physical Addressing Flow control Error control Access control Hop to Hop Delivery
- 34. Data Link Layer 10110110101 01100010011 10110000001
- 36. Data Link Layer Example
- 37. Layer 3: Network Layer Responsibilities: Delivery of individual packets from Actual source to final destination. Logical addressing Routing Source-to-destination delivery(End-to-End).
- 38. Layer 4: Transport Layer The transport layer is responsible for: Service point or Port addressing Segmentation and reassembly : a message is divided into transmittable segments each segment containing a sequence no. Connection Control: connection oriented or connectionless. Flow control Error control
- 42. Connection Oriented Service Connectionless Service
- 43. Flow Control at Transport Layer Segments Error Control Error Control at Transport Layer
- 44. Layer 5: Session Layer Dialog control: allows two systems to start communication with each other in half-duplex or full-duplex. Synchronization: allows a process to add checkpoints or synchronization points to a data stream.
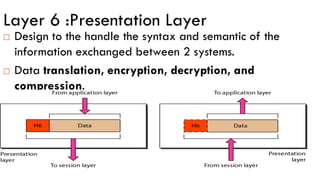
- 45. Layer 6 :Presentation Layer Design to the handle the syntax and semantic of the information exchanged between 2 systems. Data translation, encryption, decryption, and compression.
- 46. Layer 7: Application Layer The application layer is responsible for providing services to the user. Mail services File transfer, access and management Remote log-in or network virtual terminal Accessing the World Wide Web Directory service