An Introduction to JVM Internals and Garbage Collection in Java
- 1. An Introduction to JVM internals and Garbage Collection Abhishek Asthana Senior Member of Tech Staff Oracle
- 2. Java Memory Structure Heap Space Method Area / Permanent Gen Native Area
- 3. Method Area Structure Reserved Runtime Constant Pool Field and Method Data Code -XX:PermSize -XX:MaxPermSize
- 4. Method Area • Stores per-class structures such as the run- time constant pool, field and method data, and the code for methods and constructors. • Run-time Constant Pool: contains several kinds of constants, ranging from numeric literals known at compile-time to method and field references that must be resolved at run- time.
- 5. Native Area Structure Thread 1 … N Program Counter (PC) Register Thread Stack Native Stack
- 6. Native Area • PC Register: Contains "address of the instruction currently being executed". If current method is native, its value is undefined. • Thread Stack: stores frames (local variables of primitive types, object references and partial results) and plays a part in method invocation and return. • Native Stack: support native methods.
- 7. Example (what goes where!)
- 8. Heap Method Area Thread Stack Object: FileInputStream Class: FileTest Reference: stream Object: Scanner Class: FileInputStream Reference: scanner Object: String Class: Scanner Reference: line Object: Exception Class: Exception Reference: e Example (what goes where!)
- 9. OutOfMemoryError – but where? • Exception in thread “main”: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space Reason: an object could not be allocated into the heap space. • Exception in thread “main”: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space Reason: classes and methods could not be loaded into the PermGen space. This occurs when an application requires a lot of classes e.g. in various 3rd party libraries.
- 10. • Exception in thread “main”: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit Reason: this occurs when an arrays is created larger than the heap size. • Exception in thread “main”: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: (Native method) Reason: this error indicates that the problem originates from a native call rather than in the JVM. OutOfMemoryError – but where?
- 11. Garbage Collection Concepts A garbage collector is responsible for – allocating memory – ensuring that any referenced objects remain in memory – recovering memory used by objects that are no longer reachable from references in executing code. • Objects that are referenced are said to be live • Objects that are no longer referenced are considered dead and are termed garbage.
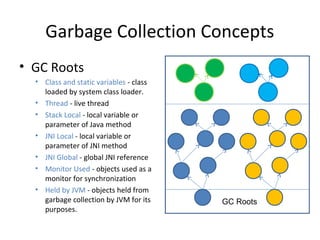
- 12. Garbage Collection Concepts • GC Roots • Class and static variables - class loaded by system class loader. • Thread - live thread • Stack Local - local variable or parameter of Java method • JNI Local - local variable or parameter of JNI method • JNI Global - global JNI reference • Monitor Used - objects used as a monitor for synchronization • Held by JVM - objects held from garbage collection by JVM for its purposes. GC Roots
- 13. Desirable GC Features • Safe: live data must never be erroneously freed. • Comprehensive: garbage should not remain unclaimed for more than a small number of collection cycles. • Efficient: No long pauses during which the application is not running. • Limit fragmentation: Avoid memory fragmentation.
- 14. GC Design Choices • Serial vs Parallel • Concurrent vs Stop-the-World • Compacting : moving all the live objects together and completely reclaiming the remaining memory. vs • Non-Compacting : releases the space utilized by garbage objects in-place vs • Copying : copies live objects to a different memory area.
- 15. Key performance metrics • Throughput: % of total time not spent in garbage collection, considered over long periods of time. • Pauses: times when an application appears unresponsive because GC is occurring. • Frequency of collection: how often collection occurs, relative to application execution. • Promptness: time between when an object is dead and when memory is reclaimed. • Footprint: working set of a process, measured in pages and cache lines.
- 16. • Generations: separate pools holding objects of different ages. • Weak Generational Hypothesis: – Most allocated objects die young. – Few references from older to younger objects exist. Generational Collection
- 17. Young Generation Old/Tenured ReservedOld Generation Eden S 2 S 1 -Xms -Xmx -XX:MaxNewSize -XX:NewSize Java Heap Space StructureReserved PermGen Reserved Permanent Generation
- 18. Young Generation Collection S2Eden Empty Empty O1 O2 O3 O4 O5 Empty Empty O2 O3 O5 O1 O4 S1 After Minor GC 1
- 19. Young Generation Collection Empty Empty O2 O3 O5 O6 O7 O8 O9 O10 O5 O7 O10 Eden S1 S2 Empty Empty O2 O3 O6 O8 O9 Eden S1 S2 After Minor GC2
- 20. Old (and Perm) Generation Collection • mark-sweep-compact collection algorithm. • Mark: the collector identifies which objects are still live. • Sweep: “sweeps” over the generations, identifying garbage. • Compact: The collector then performs sliding compaction, sliding the live objects towards the beginning of the old generation
- 21. Comparing GC Strategies Pause Pause Concurrent Mark Re-Mark Serial Parallel Concurrent Application Thread GC Thread
- 22. Parallel Collector • Minor GC: uses a parallel version of the minor GC algorithm utilized by the Serial Collector. – Reduced pause times. • Full GC: same as Serial Collector – (mark-sweep-compact) • can be explicitly requested by using - XX:+UseParallelGC command line option
- 23. Parallel Compacting Collector • Minor GC: same algorithm as parallel collector. • Full GC: same as Serial Collector – (mark-sweep-compact) • can be explicitly requested by using - XX:+UseParallelGC command line option
- 24. CMS Collector • Concurrent Mark and Sweep 1. Initial marking: GC root objects marked alive. Complete ‘Stop-the-World’. 2. Concurrent marking: marked root objects are traversed and all reachable objects are marked. Another round of marking of objects allocated during this phase! 3. Final marking: Stop-the-World and all remaining newly allocated objects are marked alive. 4. Sweep!
- 25. Collection of Garbage Garbage Collector!
- 26. Garbage First (G1) Collector • The heap is partitioned into a set of equal-sized heap regions, each a contiguous range of virtual memory • Concurrent marking phase to determine liveness of objects across the heap. • After the mark phase completes, G1 focuses on the regions that are likely to be full of garbage. • Copies objects to a single region on the heap, and in the process both compacts and frees up memory
- 27. JConsole
- 28. Thank You!