Raid_intro.ppt
- 1. RAID Overview 91.560 1
- 2. The Motivation for RAID Computing speeds double every 3 years Disk speeds can’t keep up Data needs higher MTBF than any component in system IO Performance and Availability Issues! 2
- 3. RAID to the Rescue! PERFORMANCE Parallelism Load Balancing AVAILABILITY Redundancy: Mirroring, or Striping with Parity FLEXIBILITY Selectable Performance/Availability/Cost 3
- 4. What is RAID Technology? Redundant Array of Independent Disks (a.k.a. “Disk Array”) Multiple drives, single host disk unit Provides opportunity to increase: Performance via Parallelism Data Availability via Redundancy Cheap cost via commodity disks 4
- 5. Performance: Disk Striping Chunk size tuneable for BW vs Thruput tradeoffs Large Chunk High Throughput (IO/sec) Small Chunk High Bandwidth (MB/sec) Drive Drive Drive Drive Drive 1 2 3 4 5 Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 Chunk 4 Chunk 5 Parity Chunk 6 Chunk 7 Chunk 8 Chunk 9 Chunk 10 Chunk 11 Chunk 12 Chunk 13 Chunk 14 Chunk 15 Chunk 16 Chunk 17 Chunk 18 Chunk 19 Chunk 20 Chunk 21 Chunk 22 Chunk 23 Chunk 24 5
- 6. Availability: Redundancy Single Host Unit Mirroring Same data written to both disks. Striping with Parity Data Stream, OR IO Stream, can be multiplexed across multiple disks, depending on BW vs Thruput. Parity data is also stored on disk. > Add XOR’d parity for increased availability. 6
- 7. Parity Redundancy Parity = XOR of data from every disk in the RAID unit DATA 0 - Any single disk’s 1 data can be recovered 1 by XOR’ing the data of the surviving disks. 0 0 parity 7
- 8. RAID Levels Many to choose from Each offers unique tradeoffs Performance Availability Costs We offer levels 0, 1, 3, 5, 10 8
- 9. RAID 0 Disk Striping with No Redundancy • High Performance; Low Availability • Data Striped on Multiple Disks • Multi-threaded Access Data Stream, OR IO Stream, can be Striped across multiple disks (BW vs Thruput). 9
- 10. RAID 0 Striping Chunk size tuneable for BW or Thruput No redundancy Drive Drive Drive Drive Drive 1 2 3 4 5 Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 Chunk 4 Chunk 5 Parity Chunk 6 Chunk 7 Chunk 8 Chunk 9 Chunk 10 Chunk 11 Chunk 12 Chunk 13 Chunk 14 Chunk 15 Chunk 16 Chunk 17 Chunk 18 Chunk 19 Chunk 20 Chunk 21 Chunk 22 Chunk 23 Chunk 24 10
- 11. RAID 1 Disk Mirroring Single-disk Performance; Expensive Availability Data 100% duplicated across both spindles. Single-threaded access Single Host Unit SAME data written to BOTH disks -- no segmenting. 11
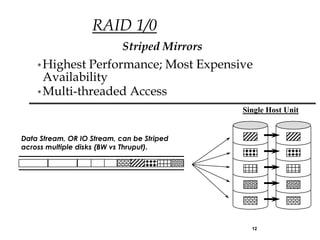
- 12. RAID 1/0 Striped Mirrors • Highest Performance; Most Expensive Availability • Multi-threaded Access Single Host Unit Data Stream, OR IO Stream, can be Striped across multiple disks (BW vs Thruput). 12
- 13. RAID 3 Disk Striping with dedicated parity drive • High BW Performance; Cheap Availability • Sector-granular data striping • Single-threaded Access Data Stream is Striped across N-1 disks for high bandwidth. XOR Parity Data 13
- 14. RAID 3 Striping Chunk size = single sector (pure RAID 3 would be single byte) All parity data on same spindle Drive Drive Drive Drive Drive 1 2 3 4 5 Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 Parity Chunk 4 Parity Chunk 5 Chunk 6 Chunk 7 Parity Chunk 8 Chunk 9 Chunk 10 Chunk 11 Parity Chunk 12 Chunk 13 Chunk 14 Chunk 15 Parity Chunk 16 Chunk 17 Chunk 18 Chunk 19 Parity 14
- 15. RAID 5 Disk Striping with rotating parity drive High Read Performance, expensive Write performance; Cheap Availability Tuneable Stripe granularity Optimized for multi-thread access IO Stream is Striped across N-1 disks for high IOs per second (thruput). XOR Parity Data 15
- 16. RAID 5 Striping Chunk size is tuned such that typical IO aligns on single disk. Parity rotates amongst disks to avoid write bottleneck Drive Drive Drive Drive Drive 1 2 3 4 5 Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 Parity Chunk 4 Parity Chunk 5 Chunk 6 Parity Chunk 7 Chunk 8 Chunk 9 Parity Chunk 10 Chunk 11 Chunk 12 Parity Chunk 13 Chunk 14 Chunk 15 Parity Chunk 16 Chunk 17 Chunk 18 Chunk 19 16
- 17. RAID 5 - Write Operation 1. Read old 2. Write 3. XOR old and 4. Read 5. Xor old parity with data. new data new data to create old parity partial product, writing “Partial Product”. data. out result as new parity. Old New } P. P. Old P. } New P. XOR XOR Drive Drive Drive Drive Drive 1 2 3 4 5 Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 Parity 17
- 18. RAID Level Review RAID 0 - Data striping, Non-redundant. High Performance, Low Availability RAID 1 - Mirroring Moderate Performance, Expensive High Availability RAID 1/0 - Striping and Mirroring High Performance, Expensively High Availability RAID 3 - Striping, single parity disk. High Bandwidth Performance, Cheap Availability RAID 5 - Striping, rotating parity disk. High Thruput Performance, Cheap Availability 18
- 19. Summary Increasing performance gap between CPU and IO Data availability a priority RAID meets the IO challenge: Performance via parallelism Data Availability via redundancy Flexibility via multiple RAID levels, each offer unique performance/availability/cost tradeoffs 19