Python Tutorial | Python Tutorial for Beginners | Python Training | Edureka
- 1. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING What is Hadoop?
- 2. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Agenda ➢ Python Introduction ➢ Who uses Python? ➢ Python Features ➢ Operators in Python ➢ Datatypes in Python ➢ Flow Control ➢ Functions in Python ➢ File Handling in Python
- 3. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Introduction
- 4. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Introduction ➢ Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics ➢ Python was created by Guido Rossum in 1989 and is very easy to learn Procedure Oriented Object Oriented Easy to Learn High Level Language
- 5. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Who uses Python?
- 6. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Who Uses Python? The popular YouTube video sharing service is largely written in Python. C O M P A N I E S U S I N G P Y T H O N Google makes extensive use of Python in its web search systems. The Raspberry Pi single- board computer promotes Python as its educational language. Dropbox storage service codes both its server and desktop client software primarily in Python. BitTorrent peer-to-peer file sharing system began its life as a Python program. NASA, Los Alamos, Fermilab, JPL, and others use Python for scientific programming tasks. The NSA uses Python for cryptography and intelligence analysis. Netflix and Yelp have both documented the role of Python in their software infrastructures.
- 7. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Features
- 8. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Features Simple and Easy to Learn Free and Open Source Python is a simple and easy to learn, read & write Python is an example of a FLOSS (Free/Libre and Open Source Software) which means one can freely distribute copies of this software, read it's source code, modify it, etc.
- 9. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Features High-level Language Portable One does not need to bother about the low-level details like memory allocation, etc. while writing Python script Supported by many platforms like Linux, Windows, FreeBSD, Macintosh, Solaris, OS/2, Amiga, AROS, AS/400, BeOS, OS/390, PlayStation, Windows CE, etc. a=3 b=5 sum=a+b print(sum) 01001010110110 11101100001101 10110101100101 0101011010 compile
- 10. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Features Python code can invoke C and C++ libraries, can be called from and C++ programs, can integrate with Java and .NET components Python supports procedure-oriented programming as well as object-oriented programming. Supports different Programming Paradigm Object Oriented Procedure Oriented C/C++ Extensible
- 11. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Zen of Python C/C++
- 12. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Installation Steps
- 13. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Python Installation Go to www.python.org1 Under Downloads tab, select the latest Python version for Windows 2
- 14. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Open the installer and click on Run3 Python Installation
- 15. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING 4 Select ‘Add Python 3.6 to PATH’ 5 Click on Install Now Python Installation
- 16. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING 6 Start IDLE which is a Python GUI & start scripting Python Installation
- 17. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING C/C++ IDLE stands for integrated Development and Learning Environment Python Installation
- 18. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Operators in Python
- 19. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Arithmetic Operators Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Special Operators Operators in Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
- 20. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Arithmetic Operators Arithmetic Operators Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Special Operators 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 + Add two operands or unary plus - Subtract two operands or unary subtract * Multiply two operands / Divide left operand with the right and result is in float >> 2 + 3 5 >> +2 >> 3 – 1 2 >> -2 >> 2 * 3 6 >> 6 / 3 2.0
- 21. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Arithmetic Operators Arithmetic Operators Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Special Operators 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ** Left operand raised to the power of right % Remainder of the division of left operand by the right // division that results into whole number adjusted to the left in the number line >> 2 + 3 5 >> +2 >> 3 – 1 2 >> -2 >> 2 * 3 6
- 22. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Assignment Operators
- 23. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 3 4 5 6 Special Operators7 /= x = x / <right operand> %= x = x % <right operand> //= x = x // <right operand> **= x = x ** <right operand> >> x/=5 >> print(x) 1.0 >> x%=5 >> print(x) 0 >> x //= 2 >> print(x) 2 >> x**= 5 >> print(x) 32 >> x = 5
- 24. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 3 4 5 6 Special Operators7 &= x = x & <right operand> |= x = x | <right operand> ^= x = x ^ <right operand> >>= x = x >> <right operand> >> x&=2 >> print(x) 0 >> x|=2 >> print(x) >> 7 >> x ^= 2 >> print(x) 7 >> x >>= 2 >> print(x) 1 >> x = 5
- 25. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Comparison Operators
- 26. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Comparison Operators Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 4 5 6 Special Operators7 > True if left operand is greater than the right < True if left operand is less than the right == True if left operand is equal to right != True if left operand is not equal to the right >> 2 > 3 False >> 2 < 3 True >>2 == 2 True >> x >>= 2 >>print(x) 1
- 27. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Logical Operators
- 28. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Logical Operators Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 5 6 Special Operators7 and Returns x if x is False , y otherwise or Returns y if x is False, x otherwise not Returns True if x is True, False otherwise >> 2 and 3 3 >> 2 or 3 2 >> not 1 False
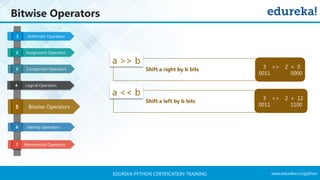
- 29. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Bitwise Operators
- 30. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 Bitwise Operators5 6 Membership Operators7 a | b Perform OR operation on each bit of the no. a & b Perform AND operation on each bit of the number a ^ b Perform XOR operation on each bit of the number 111 7 101 5 111 7 111 7 101 5 111 5 111 7 101 5 111 2
- 31. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Bitwise Operators Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 6 Membership Operators7 a >> b Shift a right by b bits a << b Shift a left by b bits 3 >> 2 = 0 0011 0000 3 << 2 = 12 0011 1100Bitwise Operators5
- 32. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Identity Operators
- 33. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Identity Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 Bitwise Operators5 Identity Operators6 Membership Operators7 is True if the operands are identical (refer to the same object) is not True if the operands are not identical (do not refer to the same object) >> x = 5 >> x is 5 True >> x = 5 >> x is not 5 False
- 34. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Membership Operators
- 35. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Membership Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 Bitwise Operators5 Identity Operators6 Membership Operators7 is True if the operands are identical (refer to the same object) is not True if the operands are not identical (do not refer to the same object) >> 3 in x True >> 3 not in x False X = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- 36. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatypes
- 37. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype C/C++ ➢ No need to declare variables before using them ➢ Python is a loosely typed language. Therefore, no need to define the datatype of variables Datatype Numbers Strings Tuples Lists Dictionaries Sets Immutable Mutable
- 38. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable
- 39. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ Strings are sequences of one-character strings Example: sample = ‘Welcome to Python Tutorial’ or sample = “Welcome to Python Tutorial” ➢ Multi-line strings can be denoted using triple quotes, ''' or ""“ Example: sample = “””Don’t Go Gentle into the good Night Rage! Rage, against the dying light”””
- 40. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing ‘Python’ ‘Tutorial’ ‘Edureka Tutorial’ ‘Edureka’ 2 ‘EdurekaEdureka’ ** string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[2:7] ‘ureka’ string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[-1] + string[1] ‘da’
- 41. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Type Specific Method: ➢ find(): ➢ replace() ➢ split() ➢ count() str = ‘Edureka’ str.find ( ‘ureka’ ) ‘ureka’ str = ‘Edureka’ str.replace ( ‘Ed’,’E’ ) ‘Eureka’ str = ‘E, d, u, r, e, k, a’ s.split ( ‘,’ ) [‘E’, ‘d’, ‘u’, ‘r’, ‘e’, ‘k’, ‘a’] str = ‘Edureka’ str.count(‘e’, beg=2, end=6) 2
- 42. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Type Specific Method: ➢ upper(): ➢ max() ➢ min() ➢ isalpha() str = ‘edureka’ str.upper () ‘EDUREKA’ str = ‘Edureka’ max (str) ‘u’ min ( str ) ‘a’ str = ‘Edureka’ str = ‘Edureka’ str.isalpha() True
- 43. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects like floating number, string literals, etc. ➢ The tuples can’t be changed unlike lists ➢ Tuples are defined using curve braces myTuple = ( ‘Edureka’ , 2.4, 5, ‘Python’ )
- 44. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup +( ‘d’ ) ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘d’ ) tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[1:2] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[0] ‘a’ tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup * 2 (‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ )
- 45. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ A list is a sequence of mutable Python objects like floating number, string literals, etc. ➢ The lists can be modified ➢ Tuples are defined using square braces myList = [ ‘Edureka’ , 2.4, 5, ‘Python’ ]
- 46. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing [ ‘1’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] ‘d’ [ 1 , ‘b’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ] [ ‘a’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] 2 [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ ] ** list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ,’d’] list[1:3] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’, ‘d’ ) list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] list[0] ‘a’
- 47. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Type Specific Method ➢ append(value) ➢ extend(list) ➢ insert(index, value) ➢ pop() list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.append (‘d’ ) [ 1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ] list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] list.extend ( [‘c’, ‘d’] ) [1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘c’, ‘d’] list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.insert(2,’b’) [1, ’a’, ‘b’ , 2.5 ] list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] List.pop() [ ‘a’, ‘b’ ]
- 48. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ Dictionaries are perhaps the most flexible built-in data type in Python ➢ Dictionaries, items are stored and fetched by key, instead of by positional offset Key Value myDict = { 1: ‘Josh’ , 2: ‘Bob’, 3: ‘James’ }
- 49. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ empty dictionary ➢ dictionary with integer keys ➢ dictionary with mixed keys ➢ from sequence having each item as a pair myDict = {} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {'name': 'John', 1: [2, 4, 3]} myDict = dict([(1,'apple'), (2,'ball')]) Dictionary Examples
- 50. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ Accessing Dictionary ➢ len() ➢ key() ➢ values() myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict [1] ‘apple’ len(myDict) 2 myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.key() [1, 2] myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.values() [‘apple’, ‘ball’] Dictionary Methods
- 51. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ items() ➢ get() ➢ update() ➢ pop() myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.items() [(1, ‘apple’), (2, ball)] myDict.get(1) ‘apple’ myDict = {1: ‘a', 2: ‘b'} myDict.update(3: ’c’) {1: ’a’, 2: ‘b’, 3: ‘c’} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict. pop(2) {1: ‘apple’} Dictionary Methods
- 52. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ A set is an unordered collection of items ➢ Every element is unique (no duplicates) and must be immutable (which cannot be changed) mySet = {1, 2, 3}
- 53. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sets Methods ➢ Creating set ➢ Union ➢ intersection ➢ difference myS1 = {1, 2, ‘c’} myS2 = {1, ‘b’, ‘c’} mySet = {1, 2, 3, 3} {1, 2, 3} myS1 | myS2 {1, 2, ‘c’, ‘b’} myS1 = {1, 2, ‘c’} myS2 = {1, ‘b’, c’’} myS1 & myS2 {1, ‘c’} myS1 = {1, 2, ‘c’} myS2 = {1, b’’, ‘c’} myS1 - myS2 { 2 }
- 54. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control
- 55. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control If.. else.. while If… elif… else for if break continue Flow Control
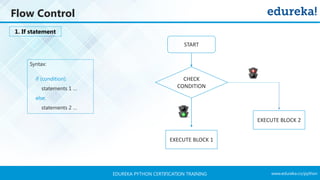
- 56. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control Syntax: if (condition): statements 1 … else: statements 2 … CHECK CONDITION EXECUTE BLOCK 1 EXECUTE BLOCK 2 START 1. If statement
- 57. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING CHECK CONDITION 1 Flow Control 2. if… elif…else statement CHECK CONDITION 1 EXECUTE BLOCK 1 EXECUTE BLOCK 2 START Syntax: if (condition 1): statements 1 … elif (condition 2): statements 2 … else statements 3 … EXECUTE BLOCK 3
- 58. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control LOOPS REPEAT ACTIONS SO YOU DON’T HAVE TO ... For While Repeat things until the loop condition is true Repeat things till the given number of times
- 59. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control 3. while statement CHECK CONDITION 1 EXECUTE BLOCK 1 START Syntax: while (condition is True): statements1… repeat EXIT LOOP
- 60. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control 4. for statement check if Count < 10 Count = 0 START Syntax: for iterator name in iterating sequence: execute statements… Add 1 to Count Execute Statements Exit loop repeat
- 61. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control Syntax: break Check Loop Condition START repeat EXIT LOOP Check Break Condition EXIT LOOP Execute Block 5. for statement
- 62. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Flow Control 6. continue Syntax: continue Check Loop Condition START repeat EXIT LOOP Check Continue Condition Skip Next Statement Execute Block
- 63. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Functions in Python
- 64. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Function A function is a block of organized, reusable sets of instructions that is used to perform some related actions. Why do we use functions? ➢ Re – usability of code minimizes redundancy ➢ Procedural decomposition makes things organized Function Built-in Function User Defined Function
- 65. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Function User Defined Function Syntax: def func_name (arg1, arg2, arg3, ….): statements… return [expression] Example: def add ( a, b ) sum = a + b return sum adding two number defining function Input variable print variable output
- 66. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Function – Pass By Reference Call by Object Reference: Python supports call by value where the value is always an object reference, not the value of the object defining function print the modified list output Modifying list calling the function both list are pointing to different object reference print the initial list
- 67. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Function Call by Object Reference defining function print the list output appending elements to list calling the function both input_list & myList pointing to same list object reference
- 68. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING File Handling in Python
- 69. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING File Handling & I/O Methods A file or a computer file is a chunk of logically related data or information which can be used by computer programs. Search Quality open ( filename, mode ) write( ) close( ) read( ) File Operations in Python Opening a file Reading a file Writing a file Closing a file
- 70. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING File Handling & I/O Methods open file write file read file close file open in Read + write mode output
- 71. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Summary
- 72. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Summary What is Python? Python FeaturesWho uses Python? Python Installation DatatypePython Operators
- 73. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Summary Flow Control File HandlingFunctions
- 74. www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Thank You… Questions/Queries/Feedback


































![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Membership Operators
Arithmetic Operators1
Assignment Operators2
Comparison Operators3
Logical Operators4
Bitwise Operators5
Identity Operators6
Membership Operators7
is
True if the operands are identical (refer to the
same object)
is not True if the operands are not identical (do not
refer to the same object)
>> 3 in x
True
>> 3 not in x
False
X = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-35-320.jpg)




![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
Sequence Operations:
➢ Concatenation:
➢ Repetition
➢ Slicing
➢ Indexing
‘Python’ ‘Tutorial’ ‘Edureka Tutorial’
‘Edureka’ 2 ‘EdurekaEdureka’
**
string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[2:7] ‘ureka’
string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[-1] + string[1] ‘da’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-40-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
Type Specific Method:
➢ find():
➢ replace()
➢ split()
➢ count()
str = ‘Edureka’ str.find ( ‘ureka’ ) ‘ureka’
str = ‘Edureka’ str.replace ( ‘Ed’,’E’ ) ‘Eureka’
str = ‘E, d, u, r, e, k, a’ s.split ( ‘,’ )
[‘E’, ‘d’, ‘u’, ‘r’, ‘e’, ‘k’,
‘a’]
str = ‘Edureka’ str.count(‘e’, beg=2, end=6) 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-41-320.jpg)


![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
Sequence Operations:
➢ Concatenation:
➢ Repetition
➢ Slicing
➢ Indexing
tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup +( ‘d’ ) ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘d’ )
tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[1:2] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’ )
tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[0] ‘a’
tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup * 2 (‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ ,
‘c’ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-44-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable ➢ A list is a sequence of mutable Python objects like floating number, string literals,
etc.
➢ The lists can be modified
➢ Tuples are defined using square braces
myList = [ ‘Edureka’ , 2.4, 5, ‘Python’ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-45-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
Sequence Operations:
➢ Concatenation:
➢ Repetition
➢ Slicing
➢ Indexing
[ ‘1’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] ‘d’ [ 1 , ‘b’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ]
[ ‘a’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] 2 [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ ]
**
list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ,’d’] list[1:3] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’, ‘d’ )
list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] list[0] ‘a’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-46-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
Type Specific Method
➢ append(value)
➢ extend(list)
➢ insert(index, value)
➢ pop()
list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.append (‘d’ ) [ 1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ]
list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] list.extend ( [‘c’, ‘d’] ) [1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘c’, ‘d’]
list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.insert(2,’b’) [1, ’a’, ‘b’ , 2.5 ]
list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] List.pop() [ ‘a’, ‘b’ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-47-320.jpg)

![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
➢ empty dictionary
➢ dictionary with integer keys
➢ dictionary with mixed keys
➢ from sequence having each item as a pair
myDict = {}
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'}
myDict = {'name': 'John', 1: [2, 4, 3]}
myDict = dict([(1,'apple'), (2,'ball')])
Dictionary Examples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-49-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
➢ Accessing Dictionary
➢ len()
➢ key()
➢ values()
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'}
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict [1] ‘apple’
len(myDict) 2
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.key() [1, 2]
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.values() [‘apple’, ‘ball’]
Dictionary Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-50-320.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Datatype
Tuples
Numbers
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
Sets
Mutable
Immutable
➢ items()
➢ get()
➢ update()
➢ pop()
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'}
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.items() [(1, ‘apple’), (2, ball)]
myDict.get(1) ‘apple’
myDict = {1: ‘a', 2: ‘b'} myDict.update(3: ’c’) {1: ’a’, 2: ‘b’, 3: ‘c’}
myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict. pop(2) {1: ‘apple’}
Dictionary Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-51-320.jpg)












![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING
Function
User Defined Function
Syntax:
def func_name (arg1, arg2, arg3, ….):
statements…
return [expression]
Example:
def add ( a, b )
sum = a + b
return sum
adding two number
defining function
Input variable
print variable
output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/85/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-65-320.jpg)








