Data extracted in July 2025.
Planned article update: July 2026.
Highlights
€5 860 billion.
This article analyses recent data on industrial production in the European Union (EU), as well as in some EFTA and candidate countries, based on results of industrial production (PRODCOM) statistics. Cyprus, Malta and Luxembourg are exempt from collecting PRODCOM data and therefore no data is available. Data presented in this article are collected under the industrial production regulation and cover the activities under sections B and C (Mining and quarrying and Manufacturing) of the NACE Rev. 2 classification and since 2019 the activity 38.32 Recovery of sorted materials.
Overview
In 2024, the value of sold production in the European Union amounted to €5 860 billion, a decrease of 1.9% compared with €5 975 billion in 2023 (current prices).
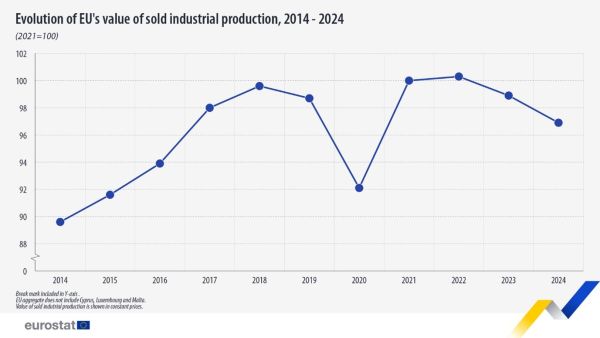
Figure 1 presents the evolution of the EU's value of sold production from 2014 to 2024 in constant prices. After a stable period, EU production shows a constant annual increase from 2015 until 2018 when comparing to each previous year. The results of 2019 show the consolidation of the growth in production with a value of sold production in the European Union that amounted to €4 915 billion.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic and consequent containment measures widely introduced by countries had a significant impact on the EU's industrial production in 2020. The value of sold production in the European Union in 2020 decreased by 6.6% compared with 2019. The EU's industrial production in 2021 recovered and it increased by 8.5% compared with 2020. It continued with an increase in 2022 by 0.3% compared with 2021.
In contrast, in two consecutive years, the EU’s production of manufactured goods decreased by -2.0% in 2024 compared with 2023 and in the previous year, it decreased by -1.4% compared with 2022.
The recent decrease was recorded in 15 industrial activities with the biggest decrease in the manufacturing of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers, followed by manufacturing of machinery and equipment n.e.c, the manufacturing of electrical equipment and the manufacturing of fabricated metal products, except machinery and equipment.
The production under sub-contracted operations within the economic territory of the EU countries, available since 2021, in 2024 amounts to 2.4% of the production value and 10.3% of the production volume.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
Industrial production by country
Figure 2 shows the share of the EU's value of sold production, by individual EU countries in 2024. Six EU countries generated 72% of the EU's value of sold production. Germany recorded the highest value of sold production, equivalent to 26% of the EU total, followed by Italy (14%), France (12%), Spain (9%), Poland (6%) and the Netherlands (4%). The other 21 EU countries contributed with smaller shares (less than 3% and less).

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
Looking in detail at the 3 largest manufacturing sectors within one country, Greece stood out with the manufacturing of food, beverages and tobacco activities, which represented 36% of the country's total value of sold production in 2024. Spain and Netherlands followed, each with 29% and Croatia with 28% of the country's total value of sold production.
The highest share of the total value of sold production in the manufacturing of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers and other transport equipment was reported by Slovakia with 45%, followed by Czechia (34%), Romania (30%) and Hungary (25%).
The manufacturing of basic metals and fabricated metal products generated 23% of the value of sold production in Bulgaria, 20% in Austria and 19% in Greece, Italy and Slovenia each.
Germany was the most substantial producer of all the 3 activities mentioned above (€198 billion, €324 billion, and €203 billion respectively) in the EU.
Industrial production by sector
The analysis that follows refers to the division breakdown (first 2-digit level) of the Statistical classification of economic activities in the European Community (NACE). In some cases, the results are presented as a group of divisions, i.e. Food, beverages and tobacco (Divisions 10, 11 and 12 of NACE Rev. 2).
Figure 3 shows the share of the manufacturing activities in the EU's value of sold production for 2014 and 2024 respectively. The EU's value of sold production is concentrated in 14 groups of activities; 6 of these groups account for almost three-quarters of the total for both reference years. The sectors manufacture of food, beverages & tobacco products, manufacture of motor vehicles and other transport equipment and manufacture of basic metals and fabricated metal products accounted for 47% of the value of the sold production in the EU in 2024.
The value of sold production in all other manufacturing activities than the 6 main groups of activities increased between 0.5% and 74% in 2024 compared with 2014 (in current prices). Looking into the smaller contributing domains, the manufacture of pharmaceutical products and pharmaceutical preparations had the highest increase (74%) in 2024 compared with the 2014 value of sold production.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
The five largest manufacturing activities
The analysis refers to the top 5 manufacturing activities presented at division breakdown (first 2-digit level) of the Statistical classification of economic activities in the European Community (NACE). Among the 5 largest manufacturing activities belong food products; chemicals and chemical products; fabricated metal products; machinery and equipment and motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
Figure 4 shows the evolution of the value of sold production for the 5 largest manufacturing activities in the EU, over the period 2014-2024. Based on constant prices (base year 2021), the manufacturing of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers registered the highest increase (by 11%) in 2024 compared with 2014. It was followed by the manufacturing of food products (by 8%), the manufacturing of machinery and equipment (by 3%) and the manufacturing of fabricated metal products (by 1%) while the manufacturing of chemicals and chemical products decreased by 6%.
In terms of nominal value of the sold production in 2024 compared with 2023, the manufacturing of food products went up by €17 billion and the manufacturing of chemicals and chemical products by €6 billion while the manufacturing of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers went down by €70 billion, the manufacturing of machinery and equipment by €28 billion and the manufacturing of fabricated metal products by €19 billion.
Results for some examples of products or group of products sold
The results are detailed at four-digit level of the Statistical classification of economic activities in the European Community (NACE).
Production of motor vehicles accounted for 58% of the EU's value of sold production of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers
Figure 5 analyses the share of the value of sold production for the manufacturing of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers (Division 29 of NACE Rev. 2) in 2024.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
The total value of sold production created by the production of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers in 2024 was €707 billion; this value represented 12% of the total value of sold EU production. In 2024, the value of sold production for this manufacturing sector decreased by 9% compared with 2023. The production of motor vehicles accounted for approximately €420 billion, which was more than half of the value of sold production of this group. The rest of the sold production in this activity was the production of other parts and accessories, bodies (coachwork), electrical and electronic equipment for motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers (Figure 5).
On average, 1 kg of fresh bread produced in the EU was sold for €1.85
Figure 6 presents the value of production sold for 1 kilogram of fresh bread, in the EU over the period 2014-24 and in each country for 2024.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
Compared with the previous years, the value of fresh bread sold in the period 2014-17 increased constantly, in 2018 it slightly decreased by 1%. In 2019, it increased again by 6%, the value of sold production of fresh bread remained stable in 2020. In 2021, the value of sold production of this product increased significantly by 13%, in 2022 by 1% and in 2023 by 19%. The sold value of 1 kg of fresh bread decreased the most in 2024 by 10%, which was the highest decrease since 2009.
The average value of production sold for 1 kg of fresh bread increased by 21% between 2014 and 2024 and by 5% compared with 2023. The EU average price fluctuated slightly over the past decade from €1.53 to a maximum of €1.85 per kg in 2024.
Finland was the country in the EU where 1 kg of produced fresh bread was sold at the highest price, at more than €3.12. In Austria, Italy and Sweden, the price ranged between €2.99 and €2.24 (per kg). Somewhat low prices, below €1 per kg, were observed in Bulgaria and Serbia. Compared with 2023, bread prices have increased in almost all European countries, with the highest price increases recorded in Italy (€0.55), Spain (€0.39), Finland (€0.30) and Ireland (€0.26). Five EU countries (Germany, Estonia, Lithuania, Czechia and Portugal) recorded a lower price per kg of produced fresh bread in 2024 than in 2023.
EU pharmaceutical production has almost doubled in the last ten years
Figure 7 provides an overview of the value of total sold production of basic pharmaceutical products manufactured in the EU in the period 2014-24. In the period 2014-18, the total sold production value of pharmaceutical products fluctuated between €22.5 billion and €25.5 billion. Over the past 5 years, pharmaceutical production in the EU increased due to the COVID-19 pandemic, reaching a value of €36 billion in 2021. In 2024, pharmaceutical production in the EU reached a peak of €54 billion.
Over the past 10 years, the production of antibiotics continued at a steady pace, with a total sold production value of €2.6 billion in 2024. The pro-vitamins and vitamins reached the highest point recorded in 2018, however, the annual sold value remains the same around €2 billion from 2019 to 2024. Antibiotics and vitamins accounted for 11% of the total basic pharmaceutical production.

Source: Eurostat DS_056120
A look into the EU's production of wind turbines
Figure 8 provides an overview of the number of wind turbines manufactured in the EU from 2014 to 2024. During this period, the average annual production of wind turbines was 11 400 pieces. In 2013, the production of wind generators reached its lowest value ever. The highest production of wind turbines was strengthened again in 2014 (22 200 pieces) and since then the observed production has been completely constant until 2019. In 2020, the sold quantity decreased to just under 6 800 pieces of wind turbines. Between 2021 and 2023, the sold quantity continued to fluctuate stably between 9 000 and 12 000 wind turbines and increased slightly to 14 900 pieces in 2024.
The EU main producers of wind turbines are Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Poland, Portugal and Spain.
Overview of sport goods production in the EU
The production of sporting goods in the EU increased over the past 5 years. The value of the sold production of sport goods was at its peak with more than €4.6 billion in 2023 and slightly decreased to €4.3 billion in 2024. The production of these products increased mainly between 2021 and 2023 as the latest trends show a greater interest in the practice of sports worldwide.
In 2021 and 2022, the sold production of fishing rods increased by 36% and 15%, respectively than the average of the previous 5 years (2015-20). The result may therefore be that this production reached its lowest point in 2024, worth €65 million. Over the past 10 years, the production of winter skis increased by 42%, rising from €532 million in 2019 to €660 million in 2023. However winter skis production dropped by 24% in 2024. The main producers in the EU are Austria, Bulgaria, Czechia, France, Germany, Slovenia and Spain.
The production of tennis and badminton rackets fell by half in 2023 compared with the previous years and significantly dropped down in 2024 due to enterprises ended their production in Spain. Conversely, gym or athletics items and equipment represented €1 billion in 2024, an increase of 28% from 2020.
Figure 9 analyses the 2014-24 production of sport goods (CPA 3230 of NACE Rev. 2) in the EU.
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
The Prodcom list is linked to the activity classification NACE and to the classification of products by activity (CPA): the first four digits of each Prodcom code refer to a NACE class, the fifth and sixth digits relate to a CPA sub-category, and the seventh and eighth digits are specific to the Prodcom list. Most headings correspond to one or more codes from the combined nomenclature (CN), a classification used for statistics on international trade in goods: some headings (mostly industrial services) do not correspond to a CN heading at all. The relationship with CN makes it possible to calculate apparent consumption by linking production statistics to international trade statistics.
The production surveyed covers only the production actually carried out on the territory of the reporting country. This means that the production of subsidiaries, which takes place outside an enterprise's territory, is not included in the survey results for that country. As a general principle, when a production process takes as an input a material that does not match the description of the product, and produces as an output something that does, then production of the product should be recorded. If the processing of a product does not change the heading under which it is listed, it should not be recorded, since this would result in double-counting. This means that the link to turnover data is tenuous, since some activities do not result in new products and should not be recorded in Prodcom statistics.
Prodcom data are available for the EU Member States, Iceland, Norway, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Serbia; Eurostat produces aggregates for the EU. According to the terms of the Prodcom Regulation, Cyprus, Luxembourg and Malta have derogations not to provide Prodcom data to Eurostat because of their size; as such there is no data for these 3 Member States in the database.
Data are available during the year following the reference year, with the first release of information usually taking place in July. As more complete and revised data become available, updates are released on a monthly basis.
Context
The development of Prodcom dates back to 1985 when Eurostat organised a series of meetings on production statistics, whose objective was to harmonise the various ways industrial production statistics were collected in the EU Member States. Although statistics were collected on products in most countries, there was a varied selection of classifications in use reflecting national situations and a range of different survey methods were applied.
The Prodcom Regulation is designed to enable these national statistics to be compared and, where possible, aggregated to give a picture of the developments of an industry or product in the European context. This aim became more urgent with the creation of the single market in 1992 and the statistical system had to adapt.
Before data collection could begin, it was necessary to draw up a common list of products to be covered. Drawing up the Prodcom list was a unique opportunity for Eurostat, the national statistical authorities and the European trade associations to work together to produce a classification that would be understood by businesses and would be appropriate for national and European statistics. Industrial production statistics collected within PRODCOM serves as one of the data sources used in several policy areas of the European Commission and national administrations. Other users such as professional/trade associations and their members use PRODCOM statistics for information on industry. The use of the data in climate change statistics is increasing, as well as in other environmental statistics such as the analysis of material flows or chemicals production and consumption statistics.
<thematicsection>
Thematic section
</thematicsection>
Explore further
Other articles
Database
- Sold production, exports and imports by PRODCOM list (NACE Rev. 2) - annual data (DS_056120)
- Total production by PRODCOM list (NACE Rev. 2) - annual data (DS_056121)
- Traditional international trade database access (ComExt) (comext)
Methodology
Legislation
- Council Regulation (EEC) No 3924/91 of 19 December 1991 on the establishment of a Community survey of industrial production]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 912/2004 of 29 April 2004 implementing Council Regulation (EEC) No 3924/91 on the establishment of a Community survey of industrial production
- Regulation (EU) No 1933/2019 of 6 November 2019 establishing for 2019 the Prodcom list of industrial products provided for by Council Regulation (EEC) No 3924/91


