Signal Processing Course : Sparse Regularization of Inverse Problems
- 1. Sparse Regularization Of Inverse Problems Gabriel Peyré www.numerical-tours.com
- 2. Overview • Inverse Problems Regularization • Sparse Synthesis Regularization • Examples: Sparse Wavelet Regularizations • Iterative Soft Thresholding • Sparse Seismic Deconvolution
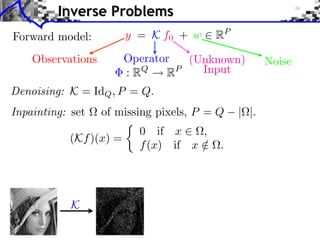
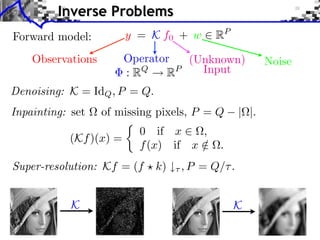
- 3. Inverse Problems Forward model: y = K f0 + w RP Observations Operator (Unknown) Noise : RQ RP Input
- 4. Inverse Problems Forward model: y = K f0 + w RP Observations Operator (Unknown) Noise : RQ RP Input Denoising: K = IdQ , P = Q.
- 5. Inverse Problems Forward model: y = K f0 + w RP Observations Operator (Unknown) Noise : RQ RP Input Denoising: K = IdQ , P = Q. Inpainting: set of missing pixels, P = Q | |. 0 if x , (Kf )(x) = f (x) if x / . K
- 6. Inverse Problems Forward model: y = K f0 + w RP Observations Operator (Unknown) Noise : RQ RP Input Denoising: K = IdQ , P = Q. Inpainting: set of missing pixels, P = Q | |. 0 if x , (Kf )(x) = f (x) if x / . Super-resolution: Kf = (f k) , P = Q/ . K K
- 7. Inverse Problem in Medical Imaging Kf = (p k )1 k K
- 8. Inverse Problem in Medical Imaging Kf = (p k )1 k K Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): ˆ Kf = (f ( )) ˆ f
- 9. Inverse Problem in Medical Imaging Kf = (p k )1 k K Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): ˆ Kf = (f ( )) ˆ f Other examples: MEG, EEG, . . .
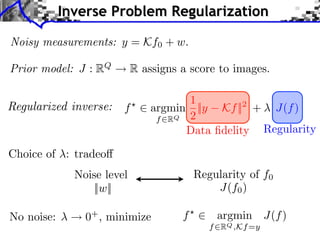
- 10. Inverse Problem Regularization Noisy measurements: y = Kf0 + w. Prior model: J : RQ R assigns a score to images.
- 11. Inverse Problem Regularization Noisy measurements: y = Kf0 + w. Prior model: J : RQ R assigns a score to images. 1 f argmin ||y Kf ||2 + J(f ) f RQ 2 Data fidelity Regularity
- 12. Inverse Problem Regularization Noisy measurements: y = Kf0 + w. Prior model: J : RQ R assigns a score to images. 1 f argmin ||y Kf ||2 + J(f ) f RQ 2 Data fidelity Regularity Choice of : tradeo Noise level Regularity of f0 ||w|| J(f0 )
- 13. Inverse Problem Regularization Noisy measurements: y = Kf0 + w. Prior model: J : RQ R assigns a score to images. 1 f argmin ||y Kf ||2 + J(f ) f RQ 2 Data fidelity Regularity Choice of : tradeo Noise level Regularity of f0 ||w|| J(f0 ) No noise: 0+ , minimize f argmin J(f ) f RQ ,Kf =y
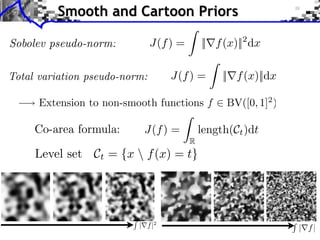
- 14. Smooth and Cartoon Priors J(f ) = || f (x)||2 dx | f |2
- 15. Smooth and Cartoon Priors J(f ) = || f (x)||2 dx J(f ) = || f (x)||dx J(f ) = length(Ct )dt R | f |2 | f|
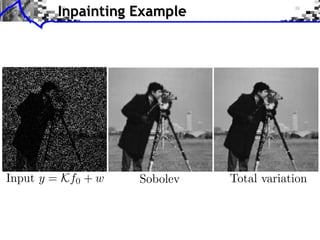
- 16. Inpainting Example Input y = Kf0 + w Sobolev Total variation
- 17. Overview • Inverse Problems Regularization • Sparse Synthesis Regularization • Examples: Sparse Wavelet Regularizations • Iterative Soft Thresholding • Sparse Seismic Deconvolution
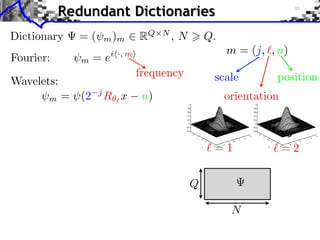
- 18. Redundant Dictionaries Dictionary =( m )m RQ N ,N Q. Q N
- 19. Redundant Dictionaries Dictionary =( m )m RQ N ,N Q. Fourier: m = ei ·, m frequency Q N
- 20. Redundant Dictionaries Dictionary =( m )m RQ N ,N Q. m = (j, , n) Fourier: m =e i ·, m frequency scale position Wavelets: m = (2 j R x n) orientation =1 =2 Q N
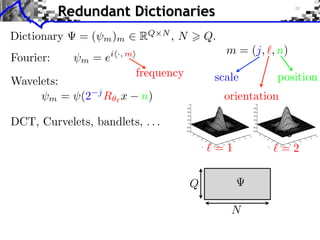
- 21. Redundant Dictionaries Dictionary =( m )m RQ N ,N Q. m = (j, , n) Fourier: m =e i ·, m frequency scale position Wavelets: m = (2 j R x n) orientation DCT, Curvelets, bandlets, . . . =1 =2 Q N
- 22. Redundant Dictionaries Dictionary =( m )m RQ N ,N Q. m = (j, , n) Fourier: m =e i ·, m frequency scale position Wavelets: m = (2 j R x n) orientation DCT, Curvelets, bandlets, . . . Synthesis: f = m xm m = x. =1 =2 Q =f x N Coe cients x Image f = x
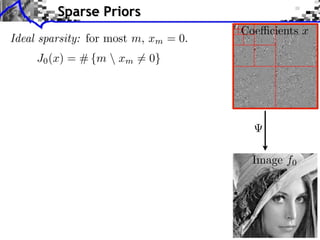
- 23. Sparse Priors Coe cients x Ideal sparsity: for most m, xm = 0. J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} Image f0
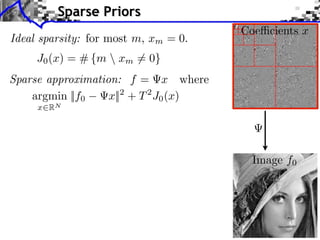
- 24. Sparse Priors Coe cients x Ideal sparsity: for most m, xm = 0. J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} Sparse approximation: f = x where argmin ||f0 x||2 + T 2 J0 (x) x2RN Image f0
- 25. Sparse Priors Coe cients x Ideal sparsity: for most m, xm = 0. J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} Sparse approximation: f = x where argmin ||f0 x||2 + T 2 J0 (x) x2RN Orthogonal : = = IdN f0 , m if | f0 , m | > T, xm = 0 otherwise. ST Image f0 f= ST (f0 )
- 26. Sparse Priors Coe cients x Ideal sparsity: for most m, xm = 0. J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} Sparse approximation: f = x where argmin ||f0 x||2 + T 2 J0 (x) x2RN Orthogonal : = = IdN f0 , m if | f0 , m | > T, xm = 0 otherwise. ST Image f0 f= ST (f0 ) Non-orthogonal : NP-hard.
- 27. Convex Relaxation: L1 Prior J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} J0 (x) = 0 null image. Image with 2 pixels: J0 (x) = 1 sparse image. J0 (x) = 2 non-sparse image. x2 x1 q=0
- 28. Convex Relaxation: L1 Prior J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} J0 (x) = 0 null image. Image with 2 pixels: J0 (x) = 1 sparse image. J0 (x) = 2 non-sparse image. x2 x1 q=0 q = 1/2 q=1 q = 3/2 q=2 q priors: Jq (x) = |xm |q (convex for q 1) m
- 29. Convex Relaxation: L1 Prior J0 (x) = # {m xm = 0} J0 (x) = 0 null image. Image with 2 pixels: J0 (x) = 1 sparse image. J0 (x) = 2 non-sparse image. x2 x1 q=0 q = 1/2 q=1 q = 3/2 q=2 q priors: Jq (x) = |xm |q (convex for q 1) m Sparse 1 prior: J1 (x) = |xm | m
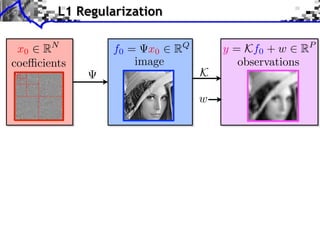
- 30. L1 Regularization x0 RN coe cients
- 31. L1 Regularization x0 RN f0 = x0 RQ coe cients image
- 32. L1 Regularization x0 RN f0 = x0 RQ y = Kf0 + w RP coe cients image observations K w
- 33. L1 Regularization x0 RN f0 = x0 RQ y = Kf0 + w RP coe cients image observations K w = K ⇥ ⇥ RP N
- 34. L1 Regularization x0 RN f0 = x0 RQ y = Kf0 + w RP coe cients image observations K w = K ⇥ ⇥ RP N Sparse recovery: f = x where x solves 1 min ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x RN 2 Fidelity Regularization
- 35. Noiseless Sparse Regularization Noiseless measurements: y = x0 x x= y x argmin |xm | x=y m
- 36. Noiseless Sparse Regularization Noiseless measurements: y = x0 x x x= x= y y x argmin |xm | x argmin |xm |2 x=y m x=y m
- 37. Noiseless Sparse Regularization Noiseless measurements: y = x0 x x x= x= y y x argmin |xm | x argmin |xm |2 x=y m x=y m Convex linear program. Interior points, cf. [Chen, Donoho, Saunders] “basis pursuit”. Douglas-Rachford splitting, see [Combettes, Pesquet].
- 38. Noisy Sparse Regularization Noisy measurements: y = x0 + w 1 x argmin ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x RQ 2 Data fidelity Regularization
- 39. Noisy Sparse Regularization Noisy measurements: y = x0 + w 1 x argmin ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x RQ 2 Equivalence Data fidelity Regularization x argmin ||x||1 || x y|| | x= x y|
- 40. Noisy Sparse Regularization Noisy measurements: y = x0 + w 1 x argmin ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x RQ 2 Equivalence Data fidelity Regularization x argmin ||x||1 || x y|| | x= Algorithms: x y| Iterative soft thresholding Forward-backward splitting see [Daubechies et al], [Pesquet et al], etc Nesterov multi-steps schemes.
- 41. Overview • Inverse Problems Regularization • Sparse Synthesis Regularization • Examples: Sparse Wavelet Regularizations • Iterative Soft Thresholding • Sparse Seismic Deconvolution
- 42. Image De-blurring Original f0 y = h f0 + w
- 43. Image De-blurring Original f0 y = h f0 + w Sobolev SNR=22.7dB Sobolev regularization: f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + ||⇥f ||2 f RN ˆ h(⇥) ˆ f (⇥) = y (⇥) ˆ ˆ |h(⇥)|2 + |⇥|2
- 44. Image De-blurring Original f0 y = h f0 + w Sobolev Sparsity SNR=22.7dB SNR=24.7dB Sobolev regularization: f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + ||⇥f ||2 f RN ˆ h(⇥) ˆ f (⇥) = y (⇥) ˆ ˆ |h(⇥)|2 + |⇥|2 Sparsity regularization: = translation invariant wavelets. 1 f = x where x argmin ||h ( x) y||2 + ||x||1 x 2
- 45. Comparison of Regularizations L2 regularization Sobolev regularization Sparsity regularization SNR SNR SNR opt opt opt L2 Sobolev Sparsity Invariant SNR=21.7dB SNR=22.7dB SNR=23.7dB SNR=24.7dB
- 46. Inpainting Problem K 0 if x , (Kf )(x) = f (x) if x / . Measures: y = Kf0 + w
- 47. Image Separation Model: f = f1 + f2 + w, (f1 , f2 ) components, w noise.
- 48. Image Separation Model: f = f1 + f2 + w, (f1 , f2 ) components, w noise.
- 49. Image Separation Model: f = f1 + f2 + w, (f1 , f2 ) components, w noise. Union dictionary: =[ 1, 2] RQ (N1 +N2 ) Recovered component: fi = i xi . 1 (x1 , x2 ) argmin ||f x||2 + ||x||1 x=(x1 ,x2 ) RN 2
- 52. Overview • Inverse Problems Regularization • Sparse Synthesis Regularization • Examples: Sparse Wavelet Regularizations • Iterative Soft Thresholding • Sparse Seismic Deconvolution
- 53. Sparse Regularization Denoising Denoising: y = x0 + w 2 RN , K = Id. ⇤ ⇤ Orthogonal-basis: = IdN , x = f. Regularization-based denoising: 1 x = argmin ||x y||2 + J(x) ? x2RN 2 P Sparse regularization: J(x) = m |xm |q (where |a|0 = (a))
- 54. Sparse Regularization Denoising Denoising: y = x0 + w 2 RN , K = Id. ⇤ ⇤ Orthogonal-basis: = IdN , x = f. Regularization-based denoising: 1 x = argmin ||x y||2 + J(x) ? x2RN 2 P Sparse regularization: J(x) = m |xm |q (where |a|0 = (a)) q x? m = ST (xm )
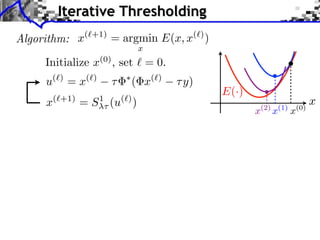
- 55. Surrogate Functionals Sparse regularization: ? 1 x 2 argmin E(x) = ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x2RN 2 ⇤ Surrogate functional: ⌧ < 1/|| || 1 2 1 E(x, x) = E(x) ˜ || (x x)|| + ||x ˜ x||2 ˜ 2 2⌧ E(·, x) ˜ E(·) x S ⌧ (u) x ˜
- 56. Surrogate Functionals Sparse regularization: ? 1 x 2 argmin E(x) = ||y x||2 + ||x||1 x2RN 2 ⇤ Surrogate functional: ⌧ < 1/|| || 1 2 1 E(x, x) = E(x) ˜ || (x x)|| + ||x ˜ x||2 ˜ 2 2⌧ E(·, x) ˜ Theorem: argmin E(x, x) = S ⌧ (u) ˜ E(·) x ⇤ where u = x ⌧ ( x x) ˜ x S ⌧ (u) x ˜ Proof: E(x, x) / 1 ||u ˜ 2 x||2 + ||x||1 + cst.
- 57. Iterative Thresholding Algorithm: x(`+1) = argmin E(x, x(`) ) x Initialize x(0) , set ` = 0. ⇤ u(`) = x(`) ⌧ ( x(`) ⌧ y) E(·) x(`+1) = S 1⌧ (u(`) ) (2) (1) (0) x x x x
- 58. Iterative Thresholding Algorithm: x(`+1) = argmin E(x, x(`) ) x Initialize x(0) , set ` = 0. ⇤ u(`) = x(`) ⌧ ( x(`) ⌧ y) E(·) x(`+1) = S 1⌧ (u(`) ) (2) (1) (0) x x x x Remark: x(`) 7! u(`) is a gradient descent of || x y||2 . 1 S`⌧ is the proximal step of associated to ||x||1 .
- 59. Iterative Thresholding Algorithm: x(`+1) = argmin E(x, x(`) ) x Initialize x(0) , set ` = 0. ⇤ u(`) = x(`) ⌧ ( x(`) ⌧ y) E(·) x(`+1) = S 1⌧ (u(`) ) (2) (1) (0) x x x x Remark: x(`) 7! u(`) is a gradient descent of || x y||2 . 1 S`⌧ is the proximal step of associated to ||x||1 . ⇤ Theorem: if ⌧ < 2/|| ||, then x(`) ! x? .
- 60. Overview • Inverse Problems Regularization • Sparse Synthesis Regularization • Examples: Sparse Wavelet Regularizations • Iterative Soft Thresholding • Sparse Seismic Deconvolution
- 61. Seismic Imaging
- 62. 1D Idealization Initial condition: “wavelet” = band pass filter h 1D propagation convolution f =h f h(x) f ˆ h( ) y = f0 h + w P
- 63. Pseudo Inverse Pseudo-inverse: ˆ+ ( ) = y ( ) f ˆ = f + = h+ ⇥ y = f0 + h+ ⇥ w h( ) ˆ ˆ where h+ ( ) = h( ) 1 ˆ ˆ Stabilization: h+ (⇥) = 0 if |h(⇥)| ˆ h( ) y = h f0 + w ˆ 1/h( ) f+
- 64. Sparse Spikes Deconvolution f with small ||f ||0 y=f h+w Sparsity basis: Diracs ⇥m [x] = [x m] 1 f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + |f [m]|. f RN 2 m
- 65. Sparse Spikes Deconvolution f with small ||f ||0 y=f h+w Sparsity basis: Diracs ⇥m [x] = [x m] 1 f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + |f [m]|. f RN 2 m Algorithm: < 2/|| ˆ || = 2/max |h(⇥)|2 ˜ • Inversion: f (k) = f (k) h ⇥ (h ⇥ f (k) y). ˜ f (k+1) [m] = S 1⇥ (f (k) [m])
- 66. Numerical Example f0 Choosing optimal : oracle, minimize ||f0 f || y=f h+w SNR(f0 , f ) f
- 67. Convergence Study Sparse deconvolution:f = argmin E(f ). f RN 1 Energy: E(f ) = ||h ⇥ f y||2 + |f [m]|. 2 m Not strictly convex = no convergence speed. log10 (E(f (k) )/E(f ) 1) log10 (||f (k) f ||/||f0 ||) k k
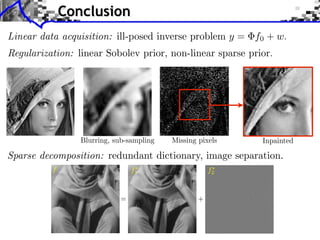
- 68. Conclusion
- 69. Conclusion
- 70. Conclusion



























![Noiseless Sparse Regularization
Noiseless measurements: y = x0
x
x
x= x=
y y
x argmin |xm | x argmin |xm |2
x=y m x=y m
Convex linear program.
Interior points, cf. [Chen, Donoho, Saunders] “basis pursuit”.
Douglas-Rachford splitting, see [Combettes, Pesquet].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-37-320.jpg)


![Noisy Sparse Regularization
Noisy measurements: y = x0 + w
1
x argmin ||y x||2 + ||x||1
x RQ 2 Equivalence
Data fidelity Regularization
x argmin ||x||1
|| x y||
|
x=
Algorithms: x y|
Iterative soft thresholding
Forward-backward splitting
see [Daubechies et al], [Pesquet et al], etc
Nesterov multi-steps schemes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-40-320.jpg)








![Image Separation
Model: f = f1 + f2 + w, (f1 , f2 ) components, w noise.
Union dictionary: =[ 1, 2] RQ (N1 +N2 )
Recovered component: fi = i xi .
1
(x1 , x2 ) argmin ||f x||2 + ||x||1
x=(x1 ,x2 ) RN 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-49-320.jpg)













![Sparse Spikes Deconvolution
f with small ||f ||0 y=f h+w
Sparsity basis: Diracs ⇥m [x] = [x m]
1
f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + |f [m]|.
f RN 2 m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-64-320.jpg)
![Sparse Spikes Deconvolution
f with small ||f ||0 y=f h+w
Sparsity basis: Diracs ⇥m [x] = [x m]
1
f = argmin ||f ⇥ h y||2 + |f [m]|.
f RN 2 m
Algorithm: < 2/|| ˆ
|| = 2/max |h(⇥)|2
˜
• Inversion: f (k) = f (k) h ⇥ (h ⇥ f (k) y).
˜
f (k+1) [m] = S 1⇥ (f (k) [m])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-65-320.jpg)

![Convergence Study
Sparse deconvolution:f = argmin E(f ).
f RN
1
Energy: E(f ) = ||h ⇥ f y||2 + |f [m]|.
2 m
Not strictly convex = no convergence speed.
log10 (E(f (k) )/E(f ) 1) log10 (||f (k) f ||/||f0 ||)
k k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/course-signal-inverse-pbm-sparse-121213053017-phpapp01/85/Signal-Processing-Course-Sparse-Regularization-of-Inverse-Problems-67-320.jpg)