Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino.pptx
- 2. AGENDA • Micro processors VS Micro-Controllers • Arduino Boards • Digital I/O Pins • IDE & Software Development • Timing
- 3. Micro processor • an IC which has only the CPU inside • Examples : Intel’s Pentium 1,2,3,4, core 2 duo, i3, i5 etc • doesn’t have RAM, ROM, and other peripherals on the chip. • Used in applications where tasks are unspecific like developing software, games, websites, photo editing, creating documents
- 4. Micro controller • Has a CPU, in addition with a fixed amount of RAM, ROM and other peripherals all embedded on a single chip. • Sometimes called computers on chip. • are designed to perform specific tasks. • For example, keyboards, mouse, washing machine, remote, microwave, cars, bikes, telephone, mobiles and watches.
- 6. Arduino and Microcontroller Atmega328p • A microcontroller created by Atmel • in the megaAVR family • Has a modified Harvard architecture 8- bit RISC processor core. • 32 KB ISP flash memory • 32 general purpose working registers • …. and many other things
- 7. Why ?!
- 8. Do you remember this ???
- 9. What if we can replace them all in one chip???
- 10. =
- 11. ARDUINO BOARD • Ready to use Board • Atmega µC • Plug-n-Play • Open Source • Arduino language is based on c and c++ [reference provided] • Large Community
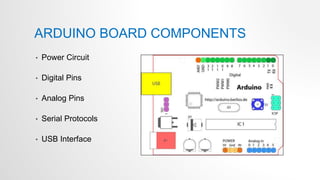
- 12. ARDUINO BOARD COMPONENTS • Power Circuit • Digital Pins • Analog Pins • Serial Protocols • USB Interface
- 14. BUT BEHIND THIS ….
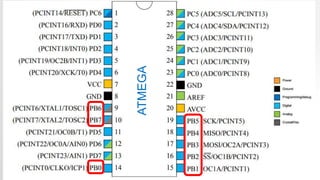
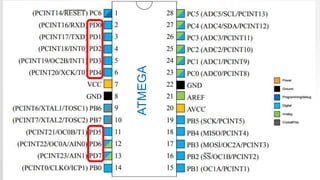
- 16. ATMEGA
- 17. ATMEGA
- 18. ATMEGA
- 19. MAPPING BETWEEN ATMEGA AND ARDUINO UNO I/O PINS
- 20. INSTALL THE ARDUINO IDE • Download from www.arduino.cc • Free • Easy to Use • Code & Upload
- 21. ARDUINO IDE • Sketch • Arduino Project • Setup • Runs at Start-up (1 time) • Initialization • Loop • Runs after “Setup” • Program Logic • Runs forever
- 22. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Embedded C (Similar to C++) • Data types (int, float, char, …) • Functions • Conditional statements (If … else) • Loop statements (for / while) • Use Libraries (math, string, …) • New Functions & Libraries • Deal with I/O Ports • Protocols
- 23. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Data types: • boolean val = false ; • Char chr_a = ‘a’; • Char chr_c = 97 ; • byte m = 25 ; • int counter = 32 ; • Unsigned int counter = 60 ; • word w = 1000 ; • Long velocity = 102346 ; • short val = 13 ; • float num = 1.352; • double num = 45.352 ;
- 24. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Data types ( char arrays) • char like[] = "I like coffee and cake"; // create a string • like[12] = 't’; • char str[40]; • num = strlen(str); // get the length of the string (excludes null terminator) • All the string c library applies here. • We can define arrays with other datatypes.
- 25. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Variable scopes: • Local variables • Global variables: available for use throughout your entire program after its declaration. • example Int T , S ; float c = 0 ; Global variable declaration Void setup () { }
- 26. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Operators: • Arithmetic (+,-,*,/,%,=) • Comparison (==, !=,<,>,<=,>=) • Boolean ( &&,||,! ) • Bitwise (&,|,^,~,<<,>>) • Compound ( +=, -= , …. )
- 27. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Control statements: • If else is example: if (expression_1) { Block of statements; } else if(expression_2) { Block of statements; } . . . else { Block of statements; }
- 28. ARDUINO LANGUAGE • Debugging: • Open the serial monitor Void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // send data only when you receive data: if (Serial.available() > 0) { // read the incoming byte: incomingByte = Serial.read(); char str[] = "This is my string"; // create a string Serial.print("String length is: "); Serial.println(str); }
- 29. DIGITAL I/O PINS • Digital Pin could work as • Input • Output • Special Functionality • Functions we may use • pinMode(pin_num, mode) //mode=INPUT/OUTPUT • digitalWrite(pin_num, value) //value=HIGH/LOW • value = digitalRead(pin_num) • delay(50) ; the time is measured in milliseconds
- 30. • Write Arduino code that sums the elements in array of 10 integers defined as a global variable integer array [87, 68, 94, 100, 83, 78, 85, 91, 76, 87 ] • Make each loop print to the serial one integer only • Make a delay of 0.5 second between each print • Print every integer in a new line Ex1
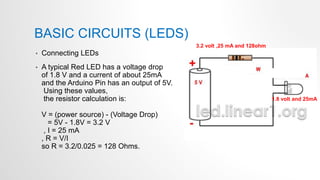
- 31. BASIC CIRCUITS (LEDS) • Connecting LEDs • A typical Red LED has a voltage drop of 1.8 V and a current of about 25mA and the Arduino Pin has an output of 5V. Using these values, the resistor calculation is: V = (power source) - (Voltage Drop) = 5V - 1.8V = 3.2 V , I = 25 mA , R = V/I so R = 3.2/0.025 = 128 Ohms. 3.2 volt ,25 mA and 128ohm 1.8 volt and 25mA
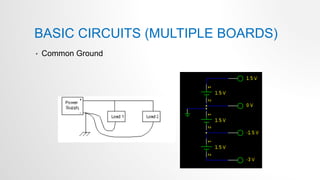
- 32. BASIC CIRCUITS (MULTIPLE BOARDS) • Common Ground
- 34. FUNCTIONS TO USE • pinMode(pin, INPUT/OUTPUT); • digitalWrite(pin, HIGH/LOW); • delay(time_ms);
- 35. TIMING • We need to make delays • Arduino has different Timing Functions • delay(ms_time) • delayMicroseconds(µs_time) • millis() • Returns the num of milliseconds from start of Arduino • micros() • Returns the num of microseconds from start of Arduino • Value depends on Arduino Freq
- 36. EXERCISE TIME • Connect a button to pin 2 • An onboard LED is attached to pin 13 • Ex2) • the blinking LED Example • LED (on) for 1 sec then (off) for 1 sec • Ex3) Write a LED on/off program • Button Pressed -> LED on • Button Released -> LED off • EX2) • Write a LED toggle program • Button Pressed -> Toggle LED state • The led is initially off.
- 37. Thanks !










![ARDUINO BOARD
• Ready to use Board
• Atmega µC
• Plug-n-Play
• Open Source
• Arduino language is based on c and c++ [reference provided]
• Large Community](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/85/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-11-320.jpg)









![ARDUINO LANGUAGE
• Data types ( char arrays)
• char like[] = "I like coffee and cake"; // create a string
• like[12] = 't’;
• char str[40];
• num = strlen(str); // get the length of the string (excludes null terminator)
• All the string c library applies here.
• We can define arrays with other datatypes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/85/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-24-320.jpg)



![ARDUINO LANGUAGE
• Debugging:
• Open the serial monitor
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// send data only when you receive data:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
incomingByte = Serial.read();
char str[] = "This is my string"; // create a string
Serial.print("String length is: ");
Serial.println(str);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/85/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-28-320.jpg)

![• Write Arduino code that sums the elements in array of
10 integers defined as a global variable integer array
[87, 68, 94, 100, 83, 78, 85, 91, 76, 87 ]
• Make each loop print to the serial one integer only
• Make a delay of 0.5 second between each print
• Print every integer in a new line
Ex1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/85/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-30-320.jpg)